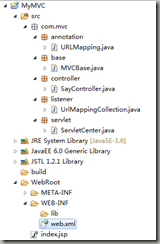
. 介绍
MVC全名是Model View Controller,是模型(model)-视图(view)-控制器(controller)的缩写,一种软件设计典范,用一种业务逻辑、数据、界面显示分离的方法组织代码,将业务逻辑聚集到一个部件里面,在改进和个性化定制界面及用户交互的同时,不需要重新编写业务逻辑。MVC被独特的发展起来用于映射传统的输入、处理和输出功能在一个逻辑的图形化用户界面的结构中。
我们今天就来搭建一个自己的从URL访问到JAVA控制器的简单框架。
2. 准备
首先,我们应该对JAVA的反射机制、Servlet最基本原理、以及JAVA注解有所了解。不了解的读着可先学习:
3. 实现思路
- 首先,我们要将URL访问请求和我们的后台JAVA方法形成一一对应关系。
- 然后,我们需要在tomcat容器启动网站加载的时候获取上一步骤中记录的一一对应关系,并记录下来。
- 最后,完成URL访问到后台JAVA方法的跳转。
4. 实现方式:
(1)通过注解来标记出URL到后台JAVA方法的映射关系。
A. 定义注解:这个注解可以标注在类和方法上。
package com.mvc.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface URLMapping {
public String url() default "";
}
B. JAVA后台中针对URI的相应方法:
package com.mvc.controller;
import com.mvc.annotation.URLMapping;
@URLMapping(url="/Say")
public class SayController{
@URLMapping(url="/Hello")
public String SayHello(){
System.out.println("Hello");
return "Hello";
}
@URLMapping(url="/Hi")
public String SayHi(){
System.out.println("Hi");
return "Hi";
}
}
通过注解,我们可以看出我们拟定将来用SayController这个类来相应/Say/***的URL。其中SayHello方法相应的URL是/Say/Hello,SayHi方法相应的URL是/Say/Hi。
这样,我们就定义好了URL和JAVA后台方法的对应关系。接下来我们要实现如果完成这种对应关系的跳转
。
(2)实现URL到JAVA后台方法的跳转
A. 定义我们用来存储URL到JAVA后台方法对应关系的基础数据类型:
package com.mvc.base;
public class MVCBase {
private String url; //我们将来要访问的URL
private String controller; //这个URL对应的后台JAVA类
private String method; //这个URL对应的后台方法名称
public String getUrl() {
return url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getController() {
return controller;
}
public void setController(String controller) {
this.controller = controller;
}
public String getMethod() {
return method;
}
public void setMethod(String method) {
this.method = method;
}
}
B. 通过监听器在tomcat启动的时候收集URL到JAVA后台方法的对应关系并存储起来:
package com.mvc.listener;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import com.mvc.annotation.URLMapping;
import com.mvc.base.MVCBase;
public class UrlMappingCollection implements ServletContextListener {
//被注解了URLMapper的类方法列表
private static List<MVCBase> mvcBases;
//我们要扫描的Controller列表
private final String[] controllerList = {"com.mvc.controller.SayController"};
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
mvcBases = new ArrayList<MVCBase>();
try {
//循环所有需要扫描的Controller
for (int i = 0; i < controllerList.length; i++) {
String controllerName = controllerList[i];
String classURL = "";
String methodURL = "";
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(controllerName); //获取Controller类
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(URLMapping.class)) { //class被标记了URLMapping注解
classURL = ((URLMapping) clazz.getAnnotation(URLMapping.class)).url();
}
//获取method列表
Method[] methods = clazz.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(URLMapping.class)) {
//method被标记了URLMapping注解
methodURL = ((URLMapping) method.getAnnotation(URLMapping.class)).url();
MVCBase mvcBase = new MVCBase();
mvcBase.setUrl(classURL+methodURL);
mvcBase.setController(controllerName);
mvcBase.setMethod(method.getName());
mvcBases.add(mvcBase);
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
}
}
public static List<MVCBase> getMvcBases() {
return mvcBases;
}
}
-
- mvcBases就是将来我们要将URL到JAVA后台方法对应关系存储到的地方。我们将他定义为静态方法,以便后续我们直接访问获取。
- controllerList是用来告诉监听器,我们要从哪些类中获取URL到JAVA后台方法的对应关系。因为在程序设计期我们就已经知道了,所以定义为final属性。
- 然后在监听器初始化的时候,循环controllerList中的class,根据注解的信息来收集URL到JAVA后台方法的对应关系并存储到mvcBases中。
C. 配置Servlet访问:
首先我们要准备我们的Servlet类,将来所有的URL请求都要跳转到这个Servlet中。
package com.mvc.servlet;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import com.mvc.base.MVCBase;
import com.mvc.listener.UrlMappingCollection;
public class ServletCenter extends HttpServlet {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -1163369749078348562L;
private void doTransfer(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
SecurityException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalArgumentException,
IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException,
InstantiationException {
for (MVCBase mvcBase : UrlMappingCollection.getMvcBases()) {
if (req.getRequestURI().equals(
req.getServletContext().getContextPath()+mvcBase.getUrl())) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(mvcBase.getController());
Method method = clazz.getMethod(mvcBase.getMethod());
method.invoke(clazz.newInstance());
}
}
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
doTransfer(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)
throws ServletException, IOException {
try {
doTransfer(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
}
可以看到,doGet和doPost里面都执行的是doTransfer方法。相应的web.xml配置为:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app version="3.0"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd">
<listener>
<listener-class>com.mvc.listener.UrlMappingCollection</listener-class>
</listener>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>main</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.mvc.servlet.ServletCenter</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>main</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
在web.xml中,我们将所有的请求都跳转到com.mvc.servlet.ServletCenter中。
5. 测试
将MyMVC部署到tomcat容器中,启动tomcat,输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/MyMVC/Say/Hello 以及http://127.0.0.1:8080/MyMVC/Say/Hi 就可以看到后台输出的Hello和Hi了。