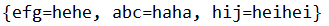为什么需要mpa集合?
学生id 姓名 年龄 成绩
2018050401 张三 18 80.0
2018050402 李四 20 85.0
2018050403 李四 21 89.0
2018050404 王五 21 89.0
如果使用已经学习过的知识点,如何来存储如上数据?
第一列:HashSet<String> idList
第二列:ArrayList<String> nameList
第三列:ArrayList<Integer> ageList
第四列:ArrayList<Double> scoreList
需求:请通过学号查询某个学生的学生信息(姓名 年龄 成绩)?
提供学号2018050401,查询成绩?
1.遍历idList,判断2018050401是否存在
存在:通过学生对象获取学生成绩
不存在: 该学生不存在
不好用
对新技术的要求:
1.能够存在关系的集合
2.左边一列 唯一
3.右边可以根据左边来查找
Map集合:
将键映射到值的对象,map集合不能包含重复的键,
每个键可以映射到最多一个值
1.键必须唯一,无序的,类似set
2.值可以重复,值的顺序取决于键的顺序,类似于Collection
3.键和值存在一一对应的映射关系
4.map集合的数据结构完全取决于键的数据结构,和值无关
常用方法
增加
V put(K key, V value) 当键不存在的时候就是添加,返回前任
void putAll(Map<? extends K,? extends V> m) 添加一个集合
删除
void clea()
V remove(Object key)
修改
V put(K key, V value) 当键存在是时,修改值
遍历
V get(Object key)
Set<K> keySet()
Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet()
判断
boolean contatinsKey(Object key) 是否包含某个键
boolean contatinsvalue(Object value) 是否包含某个值
boolean isEmpty() 是否为null
获取
V get(Object key) 通过某个键,获取某个值
int size()
Set<K> keySet() 获取键的集合
Collection<V> values() 返回值的集合
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
System.out.println("put(K key, V value):" + map.put("老文", "老姚"));
结果:put(K key, V value):null
System.out.println("put(K key, V value):" + map.put("老文", "老马"));
结果:put(K key, V value):老姚
System.out.println("put(K key, V value):" + map.put("老文", "马超"));
结果:put(K key, V value):老马
System.out.println("put(K key, V value):" + map.put("赵四", "小花"));
结果:put(K key, V value):null
System.out.println("put(K key, V value):" + map.put("老王", "翠花"));
结果:put(K key, V value):null
System.out.println("put(K key, V value):" + map.put("老王", "小花"));
结果:put(K key, V value):翠花
System.out.println(map);
结果:{老王=小花, 赵四=小花, 老文=马超}
System.out.println("remove(Object key):" + map.remove("老王"));
结果:remove(Object key):小花
System.out.println(map);
结果:{赵四=小花, 老文=马超}
// map.clear();
// System.out.println(map);
// boolean containsKey(Object key)
System.out.println("containsKey: " + map.containsKey("小花"));
结果:containsKey: false
System.out.println("containsValue: " + map.containsValue("小花"));
结果:containsValue: true
// boolean isEmpty()
// map.clear();
System.out.println("isEmpty(): " + map.isEmpty());
结果:isEmpty(): false
// V get(Object key)
System.out.println("get(Object key): " + map.get("赵四"));
结果:get(Object key): 小花
System.out.println(map.size()); 2
}
遍历
package com.sxt.mapdemo;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import java.util.Set;
/*
* Map中有一个内部接口 Entry
* interfaceEntry<K,V> {
* K getKey();
* V getValue();
* }
* */
public class MapDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("小羽", "小白");
map.put("小王", "小马");
map.put("小贾", "小李");
map.put("小林", "小赵");
map.put("小薛", "小桐");
map.put("老吴", "小陈");
System.out.println(map);
System.out.println("------------------");
//获取键的集合
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
for (String key : keys) {
System.out.println(key);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
// Collection<V> values()
Collection<String> values = map.values();
for (String value : values) {
System.out.println(value);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
/* map的遍历方式一
* 1.获取键的集合
* 2.遍历键的集合获取到每一位
* 3.通过键获取到值
* 4.输出键值对即可
* */
Set<String> mans = map.keySet();
for (String man : mans) {
String woman = map.get(man);
System.out.println(man + "=" + woman);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
Set<String> boys = map.keySet();
Iterator<String> it = boys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String boy = it.next();
String girl = map.get(boy);
System.out.println(boy + "-" + girl);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
/* map的遍历方式二
* Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet
* set集合中每一位元素是map
* 1.获取键值对的集合
* */
Set<Entry<String, String>> KeyValues = map.entrySet();
for (Entry<String, String> KeyValue : KeyValues) {
String man = KeyValue.getKey();
String woman = KeyValue.getValue();
System.out.println(man + "=" + woman);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
/* map的遍历方式三
* System.out.println(map.toString());
* 原理:
* public String toString() {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = map.entrySet().iterator();
if (! i.hasNext())
return "{}";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('{');
for (;;) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
sb.append(key == this ? "(this Map)" : key);
sb.append('=');
sb.append(value == this ? "(this Map)" : value);
if (! i.hasNext())
return sb.append('}').toString();
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
}
* */
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> iterator = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
Entry<String, String> boyGirl = iterator.next();
String boy = boyGirl.getKey();
String girl = boyGirl.getValue();
System.out.println(boy + "~" + girl);
}
System.out.println("------------------");
// 开发中一般用
for(String man : map.keySet()) {
/*String woman = map.get(man);
System.out.println(man + "=" + woman);*/
System.out.println(man + "=" + map.get(man));
}
System.out.println("------------------");
for (Entry<String, String> KeyValue : map.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(KeyValue.getKey() + "=" + KeyValue.getValue());
}
}
}



package com.sxt.mapdemo;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
public class MapDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String, Integer> hm = new HashMap<String, Integer>();
hm.put("张三", 800);
hm.put("李四", 1500);
hm.put("王五", 3000);
System.out.println("------1-----");
System.out.println(hm);
System.out.println("------2-----");
//张三工资改为2600
hm.put("张三", 2600);
System.out.println(hm);
// System.out.println("------------------------");
// for(Entry<String, Integer> keyValue : hm.entrySet()) {
// System.out.println(keyValue.getKey() + "=" + ((keyValue.getValue())+100));
// }
System.out.println("----------3--------------");
//所有员工工资加100
for (String key : hm.keySet()) {
hm.put(key, hm.get(key)+100);
}
System.out.println(hm);
System.out.println("-----------4-------------");
//遍历所有员工
for (String key : hm.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key);
}
System.out.println("-----------5------------");
//遍历所有员工工资
for (Integer value : hm.values()) {
System.out.println(value);
}
}
}

将键改为Employee
package com.sxt.mapdemo;
import java.util.HashMap;
/*
* HashMap
*
* 特点:底层数据结构的哈希表,无序唯一
* */
public class HashMapDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Employee, String> hm = new HashMap<>();
hm.put(new Employee("张三", 800.0), "老张");
hm.put(new Employee("李四", 1500.0), "老李");
hm.put(new Employee("李四", 1500.0), "老李");
hm.put(new Employee("王五", 3000.0), "老王");
hm.put(new Employee("王五", 3000.0), "老王");
for(Employee emp : hm.keySet()) {
String nickname = hm.get(emp);
System.out.println(emp + "~" + nickname);
}
}
}
class Employee {
private String name;
private Double salary;
public Employee() {
super();
}
public Employee(String name, Double salary) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(Double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee [name=" + name + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int prime = 31;
int result = 1;
result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode());
result = prime * result + ((salary == null) ? 0 : salary.hashCode());
return result;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if (this == obj)
return true;
if (obj == null)
return false;
if (getClass() != obj.getClass())
return false;
Employee other = (Employee) obj;
if (name == null) {
if (other.name != null)
return false;
} else if (!name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (salary == null) {
if (other.salary != null)
return false;
} else if (!salary.equals(other.salary))
return false;
return true;
}
}

TreeMap
基于红黑树(Red-Black tree)的 NavigableMap 实现。
该映射根据其键的自然顺序进行排序,
或者根据创建映射时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,
具体取决于使用的构造方法。
底层数据结构是二叉树,数据结构只对键有效
package com.sxt.treemapdemo;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class TreeMapDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeMap<Integer, String> tm = new TreeMap<>();
tm.put(100, "abdadac");
tm.put(89, "abafc");
tm.put(105, "daabc");
tm.put(32, "abdac");
tm.put(100, "agabc");
tm.put(78, "abfsac");
tm.put(3, "abcga");
tm.put(32, "da");
for(Integer key : tm.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + "=" + tm.get(key));
}
}
}
2、输入"asdkdsljf"获取字符出现的个数
希望打印结果:a(1)d(2)f(1)j(1)k(1)l(1)s(2)
通过分析发现,每个字母对应次数,是一种映射关系。
TreeMap<Character, Integer>
注意:当发现有映射关系的时候,就可以选择map集合。
map集合专门用来存储映射关系
package com.sxt.mapdemo;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.TreeMap;
public class LianXiDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String s = "asdkdsljf";
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入英文字符串:");
String s = input.nextLine();
TreeMap<Character, Integer> tm = new TreeMap<Character, Integer>();
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
System.out.println(ch);
for (char c : ch) {
//获取到每一个字符
Integer count = tm.get(c);
if (count == null) {
tm.put(c, 1);
} else {
++count;
tm.put(c, ++count);
}
}
System.out.println(tm);
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (Character c : tm.keySet()) {
Integer count = tm.get(c);
sb.append(c).append("(").append(count).append(")");
}
System.out.println(sb);
}
}

________________________________________________
package com.sxt.treemapdemo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeMap;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/*
* 3.统计下面这篇文章and,for,you,us出现个数并按照如下要求输出
单词(出现的次数)例如: and(x), for(y), us(m), you(z)
String article =
"On Friendship \r\n" +
"and a youth said, \"Speak to us of Friendship.\" \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"Your friend is your needs answered. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"He is your field which you sow with love and reap with thanksgiving. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"and he is your board and your fireside. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"for you come to him with your hunger, and you seek him for peace. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"When your friend speaks his mind you fear not the \"nay\" in your own mind, nor do you withhold the \"ay.\" \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"and when he is silent your heart ceases not to listen to his heart; \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"for without words, in friendship, all thoughts, all desires, all expectations are born and shared, with joy that is unacclaimed."
*/
public class TreeMapDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String article =
"On Friendship \r\n" +
"and a youth said, \"Speak to us of Friendship.\" \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"Your friend is your needs answered. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"He is your field which you sow with love and reap with thanksgiving. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"and he is your board and your fireside. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"for you come to him with your hunger, and you seek him for peace. \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"When your friend speaks his mind you fear not the \"nay\" in your own mind, nor do you withhold the \"ay.\" \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"and when he is silent your heart ceases not to listen to his heart; \r\n" +
"\r\n" +
"for without words, in friendship, all thoughts, all desires, all expectations are born and shared, with joy that is unacclaimed.";
System.out.println(getWordsCountInArticle(article, "and", "for", "us", "you", "all"));
}
/*
* 返回值类型: String: and(x), for(y), us(m), you(z)
* 参数列表: String article, String... words
* 方法名: getWordsCountInArticle
*/
public static String getWordsCountInArticle(String article, String... words) {
// 定义容器,保存单词出现的次数
TreeMap<String, Integer> tm = new TreeMap<String, Integer>();
// 定义容器,保存文章中符合正则的单词
List<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
// 定义容器,存储正则表达式字符串
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
// String pattern = "\\b(and|for|us|you)\\b";
// 动态拼接拼接正则表达式
sb.append("\\b(");
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
if (i == words.length - 1) {
sb.append(words[i]);
} else {
sb.append(words[i]).append("|");
}
}
sb.append(")\\b");
Pattern p = Pattern.compile(sb.toString());
Matcher m = p.matcher(article);
while (m.find()) {
list.add(m.group());
}
for (String s : list) {
Integer count = tm.get(s);
if (count == null) {
tm.put(s, 1);
} else {
tm.put(s, ++count);
}
}
// 清空StringBuilder
sb.delete(0, sb.length());
int index = 0;
for (String key : tm.keySet()) {
if (index == tm.size() - 1) {
sb.append(key).append("(").append(tm.get(key)).append(")");
} else {
sb.append(key).append("(").append(tm.get(key)).append(")").append(", ");
}
index ++;
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
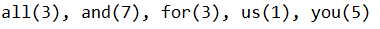
LinkedHashMap
底层数据结构是哈希表和链表
链表保证元素有序
哈希表保证元素唯一
package com.sxt.linkedhashmapdemo;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
public class LinkedHashMapDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedHashMap<String, String> lhm = new LinkedHashMap<>();
lhm.put("abc", "hello");
lhm.put("abc", "hello");
lhm.put("efg", "world");
lhm.put("hij", "java");
for(String key : lhm.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + "=" + lhm.get(key));
}
}
}

WeakHashMap
是以弱键形式存在的
package com.sxt.weakhashmapdemo;
import java.util.WeakHashMap;
public class WeakHashMapDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WeakHashMap<String, String> whm = new WeakHashMap<String, String>();
// whm.put("abc", "haha");
// whm.put("efg", "hehe");
// whm.put("hij", "heihei");
// whm.put("hij", "heihei");
whm.put(new String("abc"), "haha");
whm.put(new String("efg"), "hehe");
whm.put(new String("hij"), "heihei");
/*System.gc();自己回收
System.runFinalization();*/
System.out.println(whm);
}
}
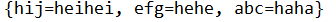
Hashtable
旧版本东西
此类实现一个哈希表,该哈希表将键映射到相应的值。
任何非 null 对象都可以用作键或值
特点:
不允许null键和null值
线程安全,效率低
面试题:HashMap和Hashtable的区别
两个完全兼容
HashMap是不安全的不同步的效率高的 允许null键和null值
Hashtable是安全的同步的效率低的 不允许null键和null值
底层都是哈希表结构
StringBuffer和StringBuilder
ArrayList和Vector
package com.sxt.hashtabledemo;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Hashtabledemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Hashtable<String, String> table = new Hashtable<>();
table.put("abc", "haha");
table.put("efg", "hehe");
table.put("hij", "heihei");
table.put("hij", "heihei");
table.put(null, "abc");
// table.put("null", null);
System.out.println(table);
}
}