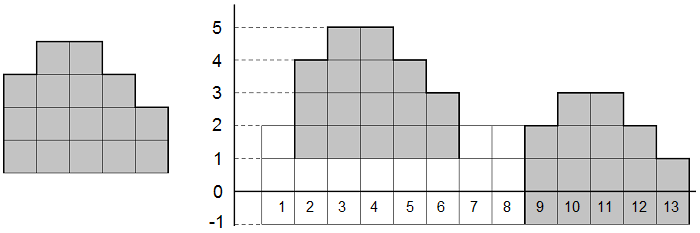
思路:
存的时候直接存相邻元素的差,然后直接KMP就行了。不管起始位置的高度是多少,下一个元素与它的差是固定的。
代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<math.h>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 200005
int n,m,a[MAXN],b[MAXN];
int T[MAXN],P[MAXN],f[MAXN];
void getFail()
{
int len=m;
f[0]=f[1]=0;
for(int i=1;i<len;i++)
{
//如果i点匹配失败,寻找对应的匹配点
int j=f[i];
//如果j点在上一个匹配点依然失败,则继续向上寻找当前点的匹配点,直到匹配或达到起始点。
while(j && P[j]!=P[i]) j=f[j];
//更新下一个失配点,如果本失配点找到了匹配点,则下一个失配值需要更新到匹配点+1;如果没有找到匹配点,则更新到起点。
f[i+1] = P[j]==P[i]? j+1:0;
}
}
int find()
{
int j=0,cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
//如果T[i]匹配失败,则向上寻找前面的匹配点
while(j && P[j]!=T[i]) j=f[j];
//如果找到了一个匹配点,则将j后移一位(即继续匹配下一位)
if(P[j]==T[i]) j++;
if(j==m) cnt++,j=f[j];
}
return cnt;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(int i=0;i<m;i++)
scanf("%d",&b[i]);
if(m==1)
{
printf("%d\n",n);
exit(0);
}
else if(n==1)
{
printf("0\n");
exit(0);
}
else
{
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
T[i]=a[i+1]-a[i];
for(int i=0;i<m-1;i++)
P[i]=b[i+1]-b[i];
n--; m--;
getFail();
printf("%d\n",find());
}
return 0;
}