难度中等,适合 Java 基础扎实,对 Java 核心 API 有所熟悉的同学学习
No1、制作GUI界面
一、实验介绍
1.1 实验内容
本节课程的主要内容是准备开发环境,建立项目并完成 GUI 界面的编程实现。
1.2 实验知识点
Java Swing 编程
1.3 实验环境
本实验环境采用带桌面的 Ubuntu Linux 环境,实验中会用到的环境或软件:
JDK1.7
Eclipse。
1.4 适合人群
本节课程难度较低,属于初级课程,适合要想学习Java Swing 编程的同学学习。
1.5 代码获取
你可以在Xfce终端下通过下面命令将实验的完整工程项目下载到实验楼环境中,作为参照对比进行学习。
$ wget http://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/287/MyEdit.tar.gz
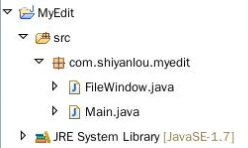
二、项目文件结构
三、实验步骤
这一节我们将开发GUI界面。
3.1 新建项目
首先请双击打开桌面上的 Eclipse ,等待它启动完成后,在菜单 File 中点击 New -> Java Project选项。 此处输入图片的描述
在弹出的窗口里填写项目的名称 MyEdit,然后点击 Finish 按钮。
3.2 创建包和类
项目创建完成后,我们需要按照之前的项目结构来创建各个类。本项目一共有两个类:
FileWindow:主要方法类,用作GUI界面以及逻辑功能的实现
Main:测试类
因此我们首先需要创建一个名为 com.hijackykun.myedit 的包。
请在创建好的项目目录 src 文件夹上右键点击,然后选择 New -> Package。
在弹出的 New Java Package 对话框中填写包名com.shiyanlou.myedit,并点击 Finish 按钮。
最后,在新建好的包下新建FileWindow和Main类。
3.3 GUI 界面的实现
GUI界面的效果图如下:

界面的设计采用卡片布局(CardLayout),白色文本域为程序输入区,粉红色文本域为编译结果显示区,浅蓝色文本域为程序运行结果区。点击上方不同的功能按钮显示对应的文本域。
在FileWindow类中编写实现 GUI 的代码,相关的代码如下,代码的讲解将会以注释的形式进行,请在编写代码的同时留意相关的注释。
注:以下代码均未导入相关的包
public class FileWindow extends JFrame implements ActionListener, Runnable {
/*注意:因为实现了ActionListener 和Runnable接口,所以必须要实现这两个接口的方法。这里我们先把这两个方法简单实现以下。下节课将彻底完成这两个方法。*/
Thread compiler = null;
Thread run_prom = null;
boolean bn = true;
CardLayout mycard; //声明布局,以后会用到
File file_saved = null;
JButton button_input_txt, //按钮的定义
button_compiler_text,
button_compiler,
button_run_prom,
button_see_doswin;
JPanel p = new JPanel();
JTextArea input_text = new JTextArea(); // 程序输入区
JTextArea compiler_text = new JTextArea();// 编译错误显示区
JTextArea dos_out_text = new JTextArea();// 程序的输出信息
JTextField input_file_name_text = new JTextField();
JTextField run_file_name_text = new JTextField();
public FileWindow() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
super("Java语言编译器");
mycard = new CardLayout();
compiler=new Thread(this);
run_prom=new Thread(this);
button_input_txt=new JButton("程序输入区(白色)");
button_compiler_text=new JButton("编译结果区(粉红色)");
button_see_doswin=new JButton("程序运行结果(浅蓝色)");
button_compiler=new JButton("编译程序");
button_run_prom=new JButton("运行程序");
p.setLayout(mycard);//设置卡片布局
p.add("input",input_text);//定义卡片名称
p.add("compiler", compiler_text);
p.add("dos",dos_out_text);
add(p,"Center");
compiler_text.setBackground(Color.pink); //设置颜色
dos_out_text.setBackground(Color.cyan);
JPanel p1=new JPanel();
p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 3)); //设置表格布局
//添加组件
p1.add(button_input_txt);
p1.add(button_compiler_text);
p1.add(button_see_doswin);
p1.add(new JLabel("输入编译文件名(.java):"));
p1.add(input_file_name_text);
p1.add(button_compiler);
p1.add(new JLabel("输入应用程序主类名"));
p1.add(run_file_name_text);
p1.add(button_run_prom);
add(p1,"North");
//定义事件
button_input_txt.addActionListener(this);
button_compiler.addActionListener(this);
button_compiler_text.addActionListener(this);
button_run_prom.addActionListener(this);
button_see_doswin.addActionListener(this);
}
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
//实现方法
}
@Override
public void run() {
//实现方法
}
}
到此,我们的 GUI 界面就算做好了!
3.4 测试类的实现
下面,我们赶紧做个测试类,测试一下我们的界面。
Main.java:
import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter;
import java.awt.event.WindowEvent;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
FileWindow win=new FileWindow();
win.pack();
win.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e)
{
System.exit(0);
}
});
win.setBounds(200, 180,550,360);
win.setVisible(true);
}
}
界面和测试类就完成了。
四、实验总结
在本节实验中,我们完成了项目的创建以及 GUI 界面,下节实验我们将完善本节的遗留问题,实现界面组件事件响应逻辑和Java文件的编辑、编译及运行。主要包括两个方法:
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
public void run()
No2、实现功能
一、实验介绍
1.1 实验内容
在上节实验中我们完成了编辑器的界面,可是按钮的响应功能并未完成,在本节实验中我们将实现界面组件事件响应逻辑和Java文件的编辑、编译及运行。主要包括两个方法:
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
public void run()
1.2 实验知识点
Java Swing 编程
IO 流操作
Runtime 类
Thread 的使用
1.3 实验环境
本实验环境采用带桌面的 Ubuntu Linux 环境,实验中会用到的环境或软件:
JDK1.7
Eclipse。
1.4 适合人群
本节课程难度较难,属于中级课程,适合对 Java 核心 API 有较深入理解的同学学习。
1.5 代码获取
你可以在Xfce终端下通过下面命令将实验的完整工程项目下载到实验楼环境中,作为参照对比进行学习。
$ wget http://labfile.oss.aliyuncs.com/courses/287/MyEdit.tar.gz
二、项目文件结构
三、实验步骤
3.1 actionPerformed 方法的实现
首先咱们实现 public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) 这个方法。代码中的注释进行了详细的讲解。
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
if(e.getSource()==button_input_txt)
{ //显示程序输入区
mycard.show(p,"input");
}
else if(e.getSource()==button_compiler_text)
{ //显示编译结果显示区
mycard.show(p,"compiler");
}
else if(e.getSource()==button_see_doswin)
{ //显示程序运行结果区
mycard.show(p,"dos");
}
else if(e.getSource()==button_compiler)
{ //如果是编译按钮,执行编译文件的方法
if(!(compiler.isAlive()))
{
compiler=new Thread(this);
}
try {
compiler.start();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// TODO: handle exception
e2.printStackTrace();
}
mycard.show(p,"compiler");
}
else if(e.getSource()==button_run_prom)
{ //如果是运行按钮,执行运行文件的方法
if(!(run_prom.isAlive()))
{
run_prom=new Thread(this);
}
try {
run_prom.start();
} catch (Exception e2) {
// TODO: handle exception
e2.printStackTrace();
}
mycard.show(p,"dos");
}
}
以上的代码就是通过比较来判断需要处理哪些事件。
3.2 run 方法的实现
然后就剩一个 run() 方法,也是最重要的一个方法。在这个方法里会判断是编译还是运行:
如果当前Thread是编译,那么会将程序输入区中的代码以.java文件的形式保存到项目的当前目录下,并通过javac命令执行刚才保存的.java文件生成.class文件,编译后的信息会输出到编译结果显示区。
如果当前Thread是运行,那么会通过java命令执行编译生成的.class文件,并将程序结果显示到程序运行结果区中。
public void run() {
//TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(Thread.currentThread()==compiler)
{
compiler_text.setText(null);
String temp=input_text.getText().trim();
byte [] buffer=temp.getBytes();
int b=buffer.length;
String file_name=null;
file_name=input_file_name_text.getText().trim();
try {
file_saved=new File(file_name);
FileOutputStream writefile=null;
writefile=new FileOutputStream(file_saved);
writefile.write(buffer, 0, b);
writefile.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("ERROR");
}
try {
//获得该进程的错误流,才可以知道运行结果到底是失败了还是成功。
Runtime rt=Runtime.getRuntime();
InputStream in=rt.exec("javac "+file_name).getErrorStream(); //通过Runtime调用javac命令。注意:“javac ”这个字符串是有一个空格的!!
BufferedInputStream bufIn=new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] shuzu=new byte[100];
int n=0;
boolean flag=true;
//输入错误信息
while((n=bufIn.read(shuzu, 0,shuzu.length))!=-1)
{
String s=null;
s=new String(shuzu,0,n);
compiler_text.append(s);
if(s!=null)
{
flag=false;
}
}
//判断是否编译成功
if(flag)
{
compiler_text.append("Compile Succeed!");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
else if(Thread.currentThread()==run_prom)
{
//运行文件,并将结果输出到dos_out_text
dos_out_text.setText(null);
try {
Runtime rt=Runtime.getRuntime();
String path=run_file_name_text.getText().trim();
Process stream=rt.exec("java "+path);//调用java命令
InputStream in=stream.getInputStream();
BufferedInputStream bisErr=new BufferedInputStream(stream.getErrorStream());
BufferedInputStream bisIn=new BufferedInputStream(in);
byte[] buf=new byte[150];
byte[] err_buf=new byte[150];
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
int m=0;
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
int i=0;
String s=null;
String err=null;
//打印编译信息及错误信息
while((m=bisIn.read(buf, 0, 150))!=-1)
{
s=new String(buf,0,150);
dos_out_text.append(s);
}
while((i=bisErr.read(err_buf))!=-1)
{
err=new String(err_buf,0,150);
dos_out_text.append(err);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
3.3 进行简单测试
点击编译按钮会出现错误信息,证明距离成功不远了。
运行按钮错误:
点击按钮在程序输入区(白色),写一个简单的测试小程序吧!代码如下:
class a
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello ShiYanLou");
}
}
接着在输入编译文件名(.java)后面的文本框里填入与类名相同的.java文件,如a.java,点击编译程序。
如果程序没有出错,那么编译结果显示如下:
在输入应用程序主类名后面的文本框里填入类名,如a,点击运行程序。
程序的运行结果将会显示在浅蓝色的文本域中。
重新编辑的时候需要点击按钮在程序输入区(白色),在白色文本域进行输入。
三、实验总结
至此,我们终于完成了整个程序,实现了编辑Java代码、编译和运行Java文件的功能。本次课程涉及的知识点比较复杂,特别是 Runtime 类和 Thread 的使用,希望同学们下来能够对这些知识点进行巩固。
五、课后习题
同学们下来考虑如何丰富其功能,例如 “代码高亮”、“代码自动补全” 等等。这些功能有的比较难,不一定要实现,但要勤于思考。
具体代码:
FileWindow.java

package com.hijackykun.myedit; import java.awt.CardLayout; import java.awt.Color; import java.awt.GridLayout; import java.awt.event.ActionEvent; import java.awt.event.ActionListener; import java.io.BufferedInputStream; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.InputStream; import javax.swing.JButton; import javax.swing.JFrame; import javax.swing.JLabel; import javax.swing.JPanel; import javax.swing.JTextArea; import javax.swing.JTextField; @SuppressWarnings("serial") //压制信息,不会的同学可以不理会。 public class FileWindow extends JFrame implements ActionListener,Runnable{ /*注意:因为实现了ActionListener 和Runnable接口,所以必须要实现这两个接口的方法。 * 这里我们先把这两个方法简单实现以下。下节课将彻底完成这两个方法。*/ Thread compiler = null; Thread run_prom = null; boolean bn = true; CardLayout mycard; //声明布局,以后会用到 File file_saved = null; JButton button_input_txt, //按钮的定义 button_compiler_text, button_compiler, button_run_prom, button_see_doswin; JPanel p = new JPanel(); JTextArea input_text = new JTextArea(); // 程序输入区 JTextArea compiler_text = new JTextArea();// 编译错误显示区 JTextArea dos_out_text = new JTextArea();// 程序的输出信息 JTextField input_file_name_text = new JTextField(); JTextField run_file_name_text = new JTextField(); public FileWindow() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub super("Java语言编译器"); mycard = new CardLayout(); compiler=new Thread(this); run_prom=new Thread(this); button_input_txt=new JButton("程序输入区(白色)"); button_compiler_text=new JButton("编译结果区(粉红色)"); button_see_doswin=new JButton("程序运行结果(浅蓝色)"); button_compiler=new JButton("编译程序"); button_run_prom=new JButton("运行程序"); p.setLayout(mycard);//设置卡片布局 p.add("input",input_text);//定义卡片名称 p.add("compiler", compiler_text); p.add("dos",dos_out_text); add(p,"Center"); compiler_text.setBackground(Color.pink); //设置颜色 dos_out_text.setBackground(Color.cyan); JPanel p1=new JPanel(); p1.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 3)); //设置表格布局 //添加组件 p1.add(button_input_txt); p1.add(button_compiler_text); p1.add(button_see_doswin); p1.add(new JLabel("输入编译文件名(.java):")); p1.add(input_file_name_text); p1.add(button_compiler); p1.add(new JLabel("输入应用程序主类名")); p1.add(run_file_name_text); p1.add(button_run_prom); add(p1,"North"); //定义事件 button_input_txt.addActionListener(this); button_compiler.addActionListener(this); button_compiler_text.addActionListener(this); button_run_prom.addActionListener(this); button_see_doswin.addActionListener(this); } @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if(e.getSource()==button_input_txt) { //显示程序输入区 mycard.show(p,"input"); } else if(e.getSource()==button_compiler_text) { //显示编译结果显示区 mycard.show(p,"compiler"); } else if(e.getSource()==button_see_doswin) { //显示程序运行结果区 mycard.show(p,"dos"); } else if(e.getSource()==button_compiler) { //如果是编译按钮,执行编译文件的方法 if(!(compiler.isAlive())) { compiler=new Thread(this); } try { compiler.start(); } catch (Exception e2) { // TODO: handle exception e2.printStackTrace(); } mycard.show(p,"compiler"); } else if(e.getSource()==button_run_prom) { //如果是运行按钮,执行运行文件的方法 if(!(run_prom.isAlive())) { run_prom=new Thread(this); } try { run_prom.start(); } catch (Exception e2) { // TODO: handle exception e2.printStackTrace(); } mycard.show(p,"dos"); } } @Override public void run() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub if (Thread.currentThread() == compiler) { compiler_text.setText(null); String temp = input_text.getText().trim(); byte[] buffer = temp.getBytes(); int b = buffer.length; String file_name = null; file_name = input_file_name_text.getText().trim(); try { file_saved = new File(file_name); FileOutputStream writefile = null; writefile = new FileOutputStream(file_saved); writefile.write(buffer, 0, b); writefile.close(); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception System.out.println("ERROR"); } try { // 获得该进程的错误流,才可以知道运行结果到底是失败了还是成功。 Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); InputStream in = rt.exec("javac " + file_name).getErrorStream(); // 通过Runtime调用javac命令。注意:“javac ”这个字符串是有一个空格的!! BufferedInputStream bufIn = new BufferedInputStream(in); byte[] shuzu = new byte[100]; int n = 0; boolean flag = true; // 输入错误信息 while ((n = bufIn.read(shuzu, 0, shuzu.length)) != -1) { String s = null; s = new String(shuzu, 0, n); compiler_text.append(s); if (s != null) { flag = false; } } // 判断是否编译成功 if (flag) { compiler_text.append("Compile Succeed!"); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } else if (Thread.currentThread() == run_prom) { // 运行文件,并将结果输出到dos_out_text dos_out_text.setText(null); try { Runtime rt = Runtime.getRuntime(); String path = run_file_name_text.getText().trim(); Process stream = rt.exec("java " + path);// 调用java命令 InputStream in = stream.getInputStream(); BufferedInputStream bisErr = new BufferedInputStream( stream.getErrorStream()); BufferedInputStream bisIn = new BufferedInputStream(in); byte[] buf = new byte[150]; byte[] err_buf = new byte[150]; @SuppressWarnings("unused") int m = 0; @SuppressWarnings("unused") int i = 0; String s = null; String err = null; // 打印编译信息及错误信息 while ((m = bisIn.read(buf, 0, 150)) != -1) { s = new String(buf, 0, 150); dos_out_text.append(s); } while ((i = bisErr.read(err_buf)) != -1) { err = new String(err_buf, 0, 150); dos_out_text.append(err); } } catch (Exception e) { // TODO: handle exception } } } }
Main.java

package com.hijackykun.myedit; import java.awt.event.WindowAdapter; import java.awt.event.WindowEvent; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { FileWindow win =new FileWindow(); win.pack();//根据窗口里面的布局及组件的preferredSize来确定frame的最佳大小 win.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() { @Override public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) { System.exit(0); } }); //setBounds(x,y,width,height); //x:组件在容器X轴上的起点 y:组件在容器Y轴上的起点 width:组件的长度 height:组件的高度 win.setBounds(200, 180, 550, 360); win.setVisible(true); } }
参考来源:https://www.shiyanlou.com/courses/287
