idea自动生成jpa实体类
1.连接数据库
view -> Tool Windows -> Database

2.在右侧弹出的Database选项里
+ -> DataSource -> 数据库类型
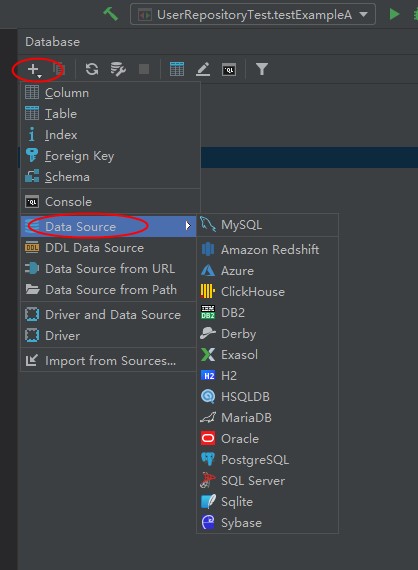
3.在弹出框配置数据库连接,注意左下角可能会有蓝色提示缺少jar,点击就会自动下载,然后测试连接,应用

4.配置生成策略
回到2的Database,可以看到可以显示第三部连接的数据库以及数据库中的表,选中表(可多选),
右键 Scripted Extensions -> Go to Scripts Directory

生成策略常用的有两种,第一种是普通的get set的方式,讲下面代码复制到Generate POJOS.groovy里
import com.intellij.database.model.DasTable
import com.intellij.database.util.Case
import com.intellij.database.util.DasUtil
/*
* Available context bindings:
* SELECTION Iterable<DasObject>
* PROJECT project
* FILES files helper
*/
packageName = "com.sample;" //这里要换成自己项目 实体的包路径
typeMapping = [
(~/(?i)int/) : "long", //数据库类型和Jave类型映射关系
(~/(?i)float|double|decimal|real/): "double",
(~/(?i)datetime|timestamp/) : "java.sql.Timestamp",
(~/(?i)date/) : "java.sql.Date",
(~/(?i)time/) : "java.sql.Time",
(~/(?i)/) : "String"
]
FILES.chooseDirectoryAndSave("Choose directory", "Choose where to store generated files") { dir ->
SELECTION.filter { it instanceof DasTable }.each { generate(it, dir) }
}
def generate(table, dir) {
def className = javaName(table.getName(), true)
def fields = calcFields(table)
new File(dir, className + ".java").withPrintWriter { out -> generate(out, className, fields) }
}
def generate(out, className, fields) {
out.println "package $packageName"
out.println ""
out.println ""
out.println "public class $className {"
out.println ""
fields.each() {
if (it.annos != "") out.println " ${it.annos}"
out.println " private ${it.type} ${it.name};"
}
out.println ""
fields.each() {
out.println ""
out.println " public ${it.type} get${it.name.capitalize()}() {"
out.println " return ${it.name};"
out.println " }"
out.println ""
out.println " public void set${it.name.capitalize()}(${it.type} ${it.name}) {"
out.println " this.${it.name} = ${it.name};"
out.println " }"
out.println ""
}
out.println "}"
}
def calcFields(table) {
DasUtil.getColumns(table).reduce([]) { fields, col ->
def spec = Case.LOWER.apply(col.getDataType().getSpecification())
def typeStr = typeMapping.find { p, t -> p.matcher(spec).find() }.value
fields += [[
name : javaName(col.getName(), false),
type : typeStr,
annos: ""]]
}
}
def javaName(str, capitalize) {
def s = com.intellij.psi.codeStyle.NameUtil.splitNameIntoWords(str)
.collect { Case.LOWER.apply(it).capitalize() }
.join("")
.replaceAll(/[^\p{javaJavaIdentifierPart}[_]]/, "_")
capitalize || s.length() == 1? s : Case.LOWER.apply(s[0]) + s[1..-1]
}第二种策略是 lombok提供的注解方式的实体,并且可以映射字段和属性对应关系,这种比较实用一些。
import com.intellij.database.model.DasTable
import com.intellij.database.model.ObjectKind
import com.intellij.database.util.Case
import com.intellij.database.util.DasUtil
/*
* Available context bindings:
* SELECTION Iterable<DasObject>
* PROJECT project
* FILES files helper
*/
packageName = "com.sample;" //这里要换成自己项目 实体的包路径
typeMapping = [
(~/(?i)int/) : "Integer", //数据库类型和Jave类型映射关系
(~/(?i)float|double|decimal|real/): "Double",
(~/(?i)bool|boolean/) : "Boolean",
(~/(?i)datetime|timestamp/) : "java.util.Date",
(~/(?i)date/) : "java.sql.Date",
(~/(?i)time/) : "java.sql.Time",
(~/(?i)/) : "String"
]
FILES.chooseDirectoryAndSave("Choose directory", "Choose where to store generated files") { dir ->
SELECTION.filter { it instanceof DasTable && it.getKind() == ObjectKind.TABLE }.each { generate(it, dir) }
}
def generate(table, dir) {
def className = javaName(table.getName(), true)
def fields = calcFields(table)
new File(dir, className + ".java").withPrintWriter { out -> generate(out, table, className, fields) }
}
def generate(out, table, className, fields) {
def tableName = table.getName()
out.println "package $packageName"
out.println ""
out.println "import lombok.Data;"
out.println ""
out.println "import javax.persistence.*;"
out.println "import java.io.Serializable;"
out.println ""
out.println "@Data"
out.println "@Entity"
out.println "@Table(name = \"$tableName\")"
out.println "public class $className implements Serializable {"
out.println ""
if ((tableName + "_id").equalsIgnoreCase(fields[0].colum) || "id".equalsIgnoreCase(fields[0].colum)) {
out.println "\t@Id"
out.println "\t@GeneratedValue(strategy=GenerationType.IDENTITY)"
}
fields.each() {
if (it.annos != "") out.println " ${it.annos}"
if (it.colum != it.name) {
out.println "\t@Column(name = \"${it.colum}\")"
}
out.println "\tprivate ${it.type} ${it.name};"
out.println ""
}
out.println "}"
}
def calcFields(table) {
DasUtil.getColumns(table).reduce([]) { fields, col ->
def spec = Case.LOWER.apply(col.getDataType().getSpecification())
def typeStr = typeMapping.find { p, t -> p.matcher(spec).find() }.value
fields += [[
name : javaName(col.getName(), false),
colum: col.getName(),
type : typeStr,
annos: ""]]
}
}
def javaName(str, capitalize) {
def s = str.split(/(?<=[^\p{IsLetter}])/).collect { Case.LOWER.apply(it).capitalize() }
.join("").replaceAll(/[^\p{javaJavaIdentifierPart}]/, "_").replaceAll(/_/, "")
capitalize || s.length() == 1 ? s : Case.LOWER.apply(s[0]) + s[1..-1]
}5.生成实体类
在DataBase属性那里Scripted -> Extensions -> Generate POJOS.groovy -> 弹出框选择实体类保存位置。
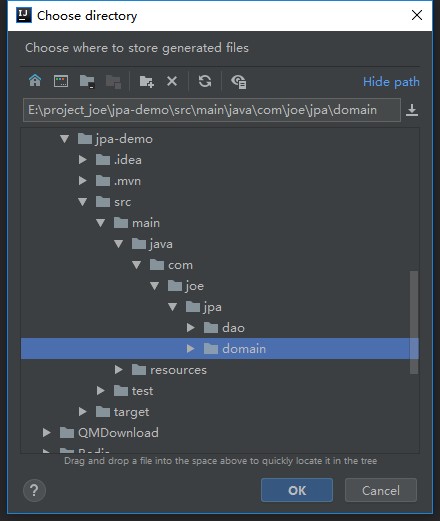
右下角看到提示,成功。

然后在对应目录下就可以看到生成的实体类
