本文将仿写一个 vue 双向数据绑定的实例。
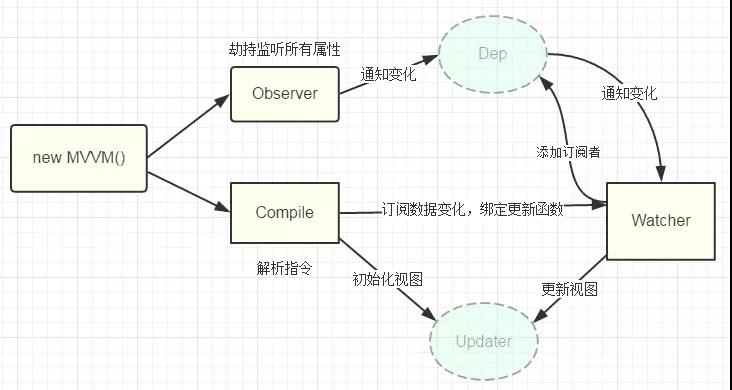
- 原理 vue 的双向数据绑定原理,主要是通过Object对象的 defineProperty属性,重写data 的set和get函数实现。本文将简要实现v-model, v-bind, v-click三个 命令。原理如图:
- 实现页面结构如下:
<div id="app"> <form> <input type="text" v-model="number"> <button type="button" v-click="increment">增加</button> </form> <h3 v-bind="number"></h3> </div>
包含:
一个input,使用v-model指令
一个button,使用v-click指令
一个h3,使用v-bind指令。
我们最后会通过类似于vue的方式来使用我们的双向数据绑定,结合页面及数据结构注释如下:
function Vue(options) {
this._init(options);
}
// 初始化构造函数,给它添加一个_init属性
Vue.prototype._init = function (options) {
this.$options = options; // options为Vue实例使用时传入的参数,包括el,data,methods,props,computed,beforeCreate……等
this.$el = document.querySelector(options.el); // el是#app的元素
this.$data = options.data; // this.$data = {number: 0}
this.$methods = options.methods; // this.$methods = {increment: function(){}}
this._binding = {}; // _binding用以保存model与view的映射关系,即下边定义的Watcher的实例。当model改变时,我们会触发其中的指令类更新,保证view也能实时更新
this._observe(this.$data); //数据监听
this._complie(this.$el); //编译更新视图
}
// _obverse函数,对data进行处理,重写data的set和get函数
Vue.prototype._observe = function (obj) { // obj = {number: 0}
var value;
for (key in obj) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key)) {
this._binding[key] = { // 如前数据则:_binding = {number: {_directives:[]} }
_directives: []
};
value = obj[key];
if (typeof value === "object") { //如果值还是对象,则递归遍历
this._observe(value);
}
var binding = this._binding[key];
Object.defineProperty(this.$data, key, { // 重点
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get: function () {
console.log(`获取${value}`);
return value;
},
set: function (newVal) {
console.log(`更新${newVal}`);
if (value !== newVal) {
value = newVal;
binding._directives.forEach(function (item) { // 当number改变时,触发_binding[number]._directives 中绑定的Watcher类的更新
item.update();
});
}
}
})
}
}
}
// _compile函数,用来解析指令(v-bind, v-model, v-click)等,并在该过程中对view与model进行绑定 Vue.prototype._complie = function (root) { // root即#app,根元素
var _this = this;
var nodes = root.children;
for (var i = 0; i < nodes.length; i++) {
var node = nodes[i];
if (node.children.length) {
this._complie(node);
}
if (node.hasAttribute('v-click')) {
node.onclick = (function () {
var attrVal = nodes[i].getAttribute('v-click');
return _this.$methods[attrVal].bind(_this.$data); //此处 bind使methods的作用域与data作用域一致
})();
}
if (node.hasAttribute('v-model') && (node.tagName == 'INPUT' || node.tagName == 'TEXTAREA')) {
node.addEventListener('input', (function(key) {
var attrVal = node.getAttribute('v-model');
_this._binding[attrVal]._directives.push(new Watcher('input', node, _this, attrVal, 'value'));
return function () {
_this.$data[attrVal] = nodes[key].value; // 使data保持与当前节点的值value一致
}
})(i));
}
if (node.hasAttribute('v-bind')) {
var attrVal = node.getAttribute('v-bind');
_this._binding[attrVal]._directives.push(new Watcher('text', node, _this, attrVal, 'innerHTML'))
}
}
}
// 指令类Watcher,用来绑定更新函数,实现对DOM元素的更新:
function Watcher(name, el, vm, exp, attr) {
this.name = name; //指令名称,例如文本节点,该值设为"text"
this.el = el; //指令对应的DOM元素
this.vm = vm; //指令所属Vue实例
this.exp = exp; //指令对应的值,如"number"
this.attr = attr; //绑定的属性值,如"innerHTML"
this.update();
}
Watcher.prototype.update = function () {
this.el[this.attr] = this.vm.$data[this.exp]; // 当this.exp即number属性改变时,触发update函数,确保其DOM内容更新
}
window.onload = function() {
var app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
number: 0
},
methods: {
increment: function () {
this.number ++;
}
}
});
}
well done, 灌水结束!
有感兴趣的文章可以扫描微信二维码: