Building your Deep Neural Network: Step by Step
- 你将使用下面函数来构建一个深层神经网络来实现图像分类。
- 使用像relu这的非线性单元来改进你的模型
- 构建一个多隐藏层的神经网络(有超过一个隐藏层)
符号说明:

1 - Packages(导入的包)
- numpy:进行科学计算的包
- matplotlib :绘图包
- dnn_utils:提供一些必要功能
- testCases 提供一些测试用例来评估函数的正确性
- np.random.seed(1) 设置随机数种子,易于测试。
import numpy as np
import h5py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from testCases_v2 import *
from dnn_utils_v2 import sigmoid, sigmoid_backward, relu, relu_backward
%matplotlib inline
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (5.0, 4.0) # 设置最大图像大小
plt.rcParams['image.interpolation'] = 'nearest'
plt.rcParams['image.cmap'] = 'gray'
%load_ext autoreload
%autoreload 2
np.random.seed(1)
保存在本地
# TODO: 保存在dnn_utils.py
import numpy as np
def sigmoid(Z):
"""
Implements the sigmoid activation in numpy
Arguments:
Z -- numpy array of any shape
Returns:
A -- output of sigmoid(z), same shape as Z
cache -- returns Z as well, useful during backpropagation
"""
A = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
cache = Z
return A, cache
def relu(Z):
"""
Implement the RELU function.
Arguments:
Z -- Output of the linear layer, of any shape
Returns:
A -- Post-activation parameter, of the same shape as Z
cache -- a python dictionary containing "A" ; stored for computing the backward pass efficiently
"""
A = np.maximum(0,Z)
assert(A.shape == Z.shape)
cache = Z
return A, cache
def relu_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single RELU unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
dZ = np.array(dA, copy=True) # just converting dz to a correct object.
# When z <= 0, you should set dz to 0 as well.
dZ[Z <= 0] = 0
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
def sigmoid_backward(dA, cache):
"""
Implement the backward propagation for a single SIGMOID unit.
Arguments:
dA -- post-activation gradient, of any shape
cache -- 'Z' where we store for computing backward propagation efficiently
Returns:
dZ -- Gradient of the cost with respect to Z
"""
Z = cache
s = 1/(1+np.exp(-Z))
dZ = dA * s * (1-s)
assert (dZ.shape == Z.shape)
return dZ
# TODO: testCases.py
import numpy as np
def linear_forward_test_case():
np.random.seed(1)
"""
X = np.array([[-1.02387576, 1.12397796],
[-1.62328545, 0.64667545],
[-1.74314104, -0.59664964]])
W = np.array([[ 0.74505627, 1.97611078, -1.24412333]])
b = np.array([[1]])
"""
A = np.random.randn(3,2)
W = np.random.randn(1,3)
b = np.random.randn(1,1)
return A, W, b
def linear_activation_forward_test_case():
"""
X = np.array([[-1.02387576, 1.12397796],
[-1.62328545, 0.64667545],
[-1.74314104, -0.59664964]])
W = np.array([[ 0.74505627, 1.97611078, -1.24412333]])
b = 5
"""
np.random.seed(2)
A_prev = np.random.randn(3,2)
W = np.random.randn(1,3)
b = np.random.randn(1,1)
return A_prev, W, b
def L_model_forward_test_case():
"""
X = np.array([[-1.02387576, 1.12397796],
[-1.62328545, 0.64667545],
[-1.74314104, -0.59664964]])
parameters = {'W1': np.array([[ 1.62434536, -0.61175641, -0.52817175],
[-1.07296862, 0.86540763, -2.3015387 ]]),
'W2': np.array([[ 1.74481176, -0.7612069 ]]),
'b1': np.array([[ 0.],
[ 0.]]),
'b2': np.array([[ 0.]])}
"""
np.random.seed(1)
X = np.random.randn(4,2)
W1 = np.random.randn(3,4)
b1 = np.random.randn(3,1)
W2 = np.random.randn(1,3)
b2 = np.random.randn(1,1)
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return X, parameters
def compute_cost_test_case():
Y = np.asarray([[1, 1, 1]])
aL = np.array([[.8,.9,0.4]])
return Y, aL
def linear_backward_test_case():
"""
z, linear_cache = (np.array([[-0.8019545 , 3.85763489]]), (np.array([[-1.02387576, 1.12397796],
[-1.62328545, 0.64667545],
[-1.74314104, -0.59664964]]), np.array([[ 0.74505627, 1.97611078, -1.24412333]]), np.array([[1]]))
"""
np.random.seed(1)
dZ = np.random.randn(1,2)
A = np.random.randn(3,2)
W = np.random.randn(1,3)
b = np.random.randn(1,1)
linear_cache = (A, W, b)
return dZ, linear_cache
def linear_activation_backward_test_case():
"""
aL, linear_activation_cache = (np.array([[ 3.1980455 , 7.85763489]]), ((np.array([[-1.02387576, 1.12397796], [-1.62328545, 0.64667545], [-1.74314104, -0.59664964]]), np.array([[ 0.74505627, 1.97611078, -1.24412333]]), 5), np.array([[ 3.1980455 , 7.85763489]])))
"""
np.random.seed(2)
dA = np.random.randn(1,2)
A = np.random.randn(3,2)
W = np.random.randn(1,3)
b = np.random.randn(1,1)
Z = np.random.randn(1,2)
linear_cache = (A, W, b)
activation_cache = Z
linear_activation_cache = (linear_cache, activation_cache)
return dA, linear_activation_cache
def L_model_backward_test_case():
"""
X = np.random.rand(3,2)
Y = np.array([[1, 1]])
parameters = {'W1': np.array([[ 1.78862847, 0.43650985, 0.09649747]]), 'b1': np.array([[ 0.]])}
aL, caches = (np.array([[ 0.60298372, 0.87182628]]), [((np.array([[ 0.20445225, 0.87811744],
[ 0.02738759, 0.67046751],
[ 0.4173048 , 0.55868983]]),
np.array([[ 1.78862847, 0.43650985, 0.09649747]]),
np.array([[ 0.]])),
np.array([[ 0.41791293, 1.91720367]]))])
"""
np.random.seed(3)
AL = np.random.randn(1, 2)
Y = np.array([[1, 0]])
A1 = np.random.randn(4,2)
W1 = np.random.randn(3,4)
b1 = np.random.randn(3,1)
Z1 = np.random.randn(3,2)
linear_cache_activation_1 = ((A1, W1, b1), Z1)
A2 = np.random.randn(3,2)
W2 = np.random.randn(1,3)
b2 = np.random.randn(1,1)
Z2 = np.random.randn(1,2)
linear_cache_activation_2 = ( (A2, W2, b2), Z2)
caches = (linear_cache_activation_1, linear_cache_activation_2)
return AL, Y, caches
def update_parameters_test_case():
"""
parameters = {'W1': np.array([[ 1.78862847, 0.43650985, 0.09649747],
[-1.8634927 , -0.2773882 , -0.35475898],
[-0.08274148, -0.62700068, -0.04381817],
[-0.47721803, -1.31386475, 0.88462238]]),
'W2': np.array([[ 0.88131804, 1.70957306, 0.05003364, -0.40467741],
[-0.54535995, -1.54647732, 0.98236743, -1.10106763],
[-1.18504653, -0.2056499 , 1.48614836, 0.23671627]]),
'W3': np.array([[-1.02378514, -0.7129932 , 0.62524497],
[-0.16051336, -0.76883635, -0.23003072]]),
'b1': np.array([[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.]]),
'b2': np.array([[ 0.],
[ 0.],
[ 0.]]),
'b3': np.array([[ 0.],
[ 0.]])}
grads = {'dW1': np.array([[ 0.63070583, 0.66482653, 0.18308507],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. ]]),
'dW2': np.array([[ 1.62934255, 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[ 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ]]),
'dW3': np.array([[-1.40260776, 0. , 0. ]]),
'da1': np.array([[ 0.70760786, 0.65063504],
[ 0.17268975, 0.15878569],
[ 0.03817582, 0.03510211]]),
'da2': np.array([[ 0.39561478, 0.36376198],
[ 0.7674101 , 0.70562233],
[ 0.0224596 , 0.02065127],
[-0.18165561, -0.16702967]]),
'da3': np.array([[ 0.44888991, 0.41274769],
[ 0.31261975, 0.28744927],
[-0.27414557, -0.25207283]]),
'db1': 0.75937676204411464,
'db2': 0.86163759922811056,
'db3': -0.84161956022334572}
"""
np.random.seed(2)
W1 = np.random.randn(3,4)
b1 = np.random.randn(3,1)
W2 = np.random.randn(1,3)
b2 = np.random.randn(1,1)
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
np.random.seed(3)
dW1 = np.random.randn(3,4)
db1 = np.random.randn(3,1)
dW2 = np.random.randn(1,3)
db2 = np.random.randn(1,1)
grads = {"dW1": dW1,
"db1": db1,
"dW2": dW2,
"db2": db2}
return parameters, grads
2 - 任务概要
- 双隐藏层 和 L层神经网络 的 参数初始化。
- 实现前向传播操作(forward propagation) 。计算 损失函数。
- 完成 层的 前向传播 的 线性部分。(计算出 Z = WX + b) 。
- 使用 relu 和 sigmod 激活函数计算结果值。
- 将前两个步骤组合成一个新的前向函数(线性->激活) [LINEAR->ACTIVATION]
- 对输出层之前的 L-1 层,做 L-1 次 的 前向传播 [LINEAR->RELU] ,L层输出层的 激活函数 为 sigmod
- 实现 后向传播操作 模块(在下图中用红色表示)。最后更新参数。
- 计算神经网络 反向传播的 LINEAR 部分。
- 计算 激活函数 (Relu 或者 sigmod)的 梯度。
- 综合前两个步骤,产生一个新的后向函数【Liner --> Activation】
- 更新参数
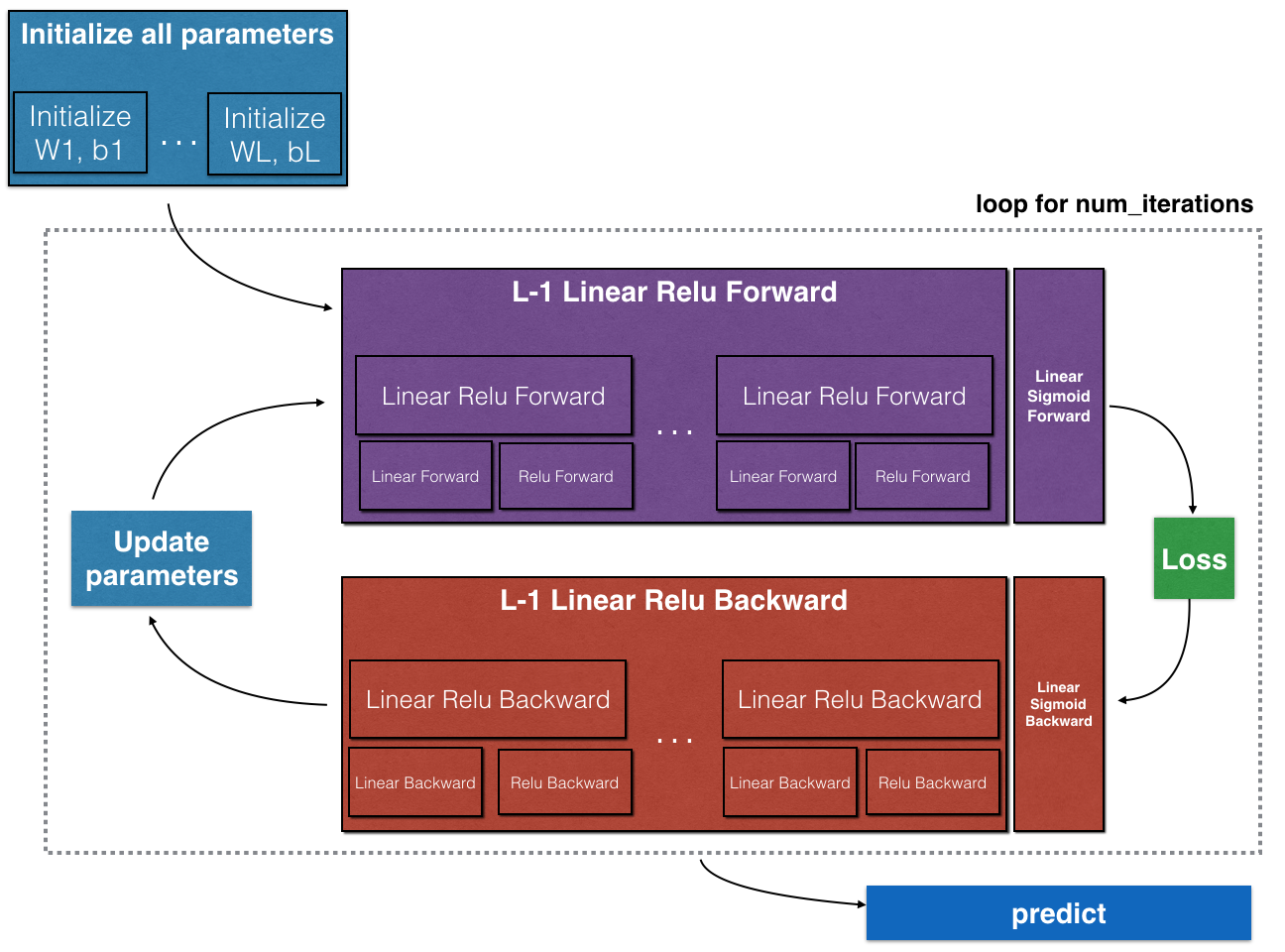
注意,前向函数和反向函数相对应。前向传播的每一步都将反向传播用的到值存储在cache。cache中值对于计算梯度非常有用。
3 - Initialization(初始化)
为你的模型编写函数初始化参数。第一个函数将用于 初始化两层模型 的参数。第二个函数用于 初始化 L层模型 的参数。
3.1 - 2-layer Neural Network (双隐藏层神经网络)
Exercise: 创建和初始化 2层神经网络 的参数.
Instructions:
- 模型结果: LINEAR -> RELU -> LINEAR -> SIGMOID.
- 使用 随机初始化 权重矩阵。用
np.random.randn(shape)*0.01用正确的shape。 - 使用 0 初始化偏差。用
np.zeros(shape)。
# GRADED FUNCTION: initialize_parameters
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
Argument:
n_x -- size of the input layer
n_h -- size of the hidden layer
n_y -- size of the output layer
Returns:
parameters -- python dictionary containing your parameters:
W1 -- weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x)
b1 -- bias vector of shape (n_h, 1)
W2 -- weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h)
b2 -- bias vector of shape (n_y, 1)
"""
np.random.seed(1)
### START CODE HERE ### (≈ 4 lines of code)
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x)*0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h)*0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
### END CODE HERE ###
assert(W1.shape == (n_h, n_x))
assert(b1.shape == (n_h, 1))
assert(W2.shape == (n_y, n_h))
assert(b2.shape == (n_y, 1))
parameters = {"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2}
return parameters
parameters = initialize_parameters(3,2,1)
print("W1 = " + str(parameters["W1"]))
print("b1 = " + str(parameters["b1"]))
print("W2 = " + str(parameters["W2"]))
print("b2 = " + str(parameters["b2"]))
W1 = [[ 0.01624345 -0.00611756 -0.00528172] [-0.01072969 0.00865408 -0.02301539]] b1 = [[ 0.] [ 0.]] W2 = [[ 0.01744812 -0.00761207]] b2 = [[ 0.]]
Expected output:
| W1 | [[ 0.01624345 -0.00611756 -0.00528172] [-0.01072969 0.00865408 -0.02301539]] |
| b1 | [[ 0.] [ 0.]] |
| W2 | [[ 0.01744812 -0.00761207]] |
| b2 | [[ 0.]] |
3.2 - L-layer Neural Network(L-层隐藏层神经网络)
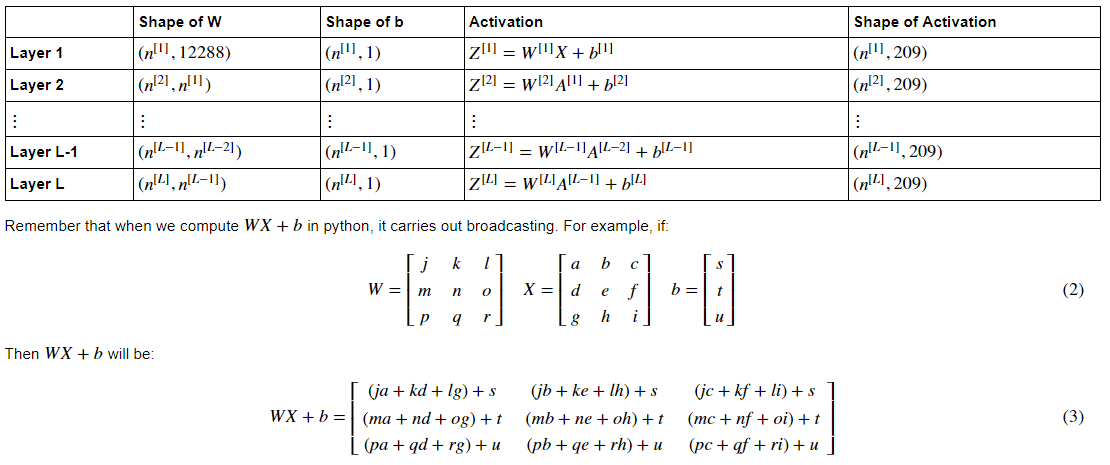
当完成 initialize_parameters_deep 时,你应该确保每个层之间的维度匹配。n^l 是 L层中单位数。如,输入X,size = (12288, 209)(有m=209个样本):
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复:
5089170 查看本文章

