1 本文记录针对python网络编程学习过程中的socket部分进行记录与总结,内容仅仅涉及最粗浅的部分,日后或许会进行更新与扩展。
2 本文涉及的socket数据传输均使用bytes类型,因此在python3环境下,需要特别注意字符串的编码与解码。
1 socket模块
A pair (host, port) is used for the AF_INET address family, where host is a string representing either a hostname in Internet domain notation like ‘daring.cwi.nl’ or an IPv4 address like ‘100.50.200.5’, and port is an integer.
For IPv4 addresses, two special forms are accepted instead of a host address: the empty string represents INADDR_ANY, and the string ‘’ represents INADDR_BROADCAST. This behavior is not compatible with IPv6, therefore, you may want to avoid these if you intend to support IPv6 with your Python programs.
- 创建socket对象,
socket.socket(family=AF_INET, type=SOCK_STREAM, proto=0, fileno=None) - 根据官方文档说明,socket接受两种特殊形式的IPv4的地址。空白地址代表
INADDR_ANY,允许任意地址接入;而字符串’<broadcast>’则代表INADDR_BROADCAST。
1.1 创建TCP服务器 - socket.socket()
from socket import *
from time import ctime
HOST = '' # 允许任意host接入
PORT = 21567
BUFSIZ = 1024
ADDR = (HOST, PORT)
tcpSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
tcpSerSock.bind(ADDR) # 绑定地址
tcpSerSock.listen(5) # 最多同时监听数量上限为5
while True:
print('waiting for connection...')
# 接受客户端请求之前保持阻塞,连接后获取客户端socket及其地址
tcpCliSock, addr = tcpSerSock.accept()
# 打印请求此次服务的客户端的地址
print('...connection from: {}'.format(addr))
while True:
# 通过客户socket获取客户端信息(bytes类型),并解码为字符串类型
data = tcpCliSock.recv(BUFSIZ).decode('utf8')
if not data:
break
# 处理字符串并重新编码为bytes类型,调用send()方法发送回客户端
tcpCliSock.send('[{}] {}'.format(ctime(), data).encode('utf8'))
# 关闭客户端
tcpCliSock.close()
# 关闭服务器
tcpCliSock.close() 1.2 创建TCP客户端 - socket.socket()
from socket import *
HOST = 'localhost' # 指定客户端访问host
PORT = 21567
BUFSIZ = 1024
ADDR = (HOST, PORT)
tcpCliSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
tcpCliSock.connect(ADDR) # 连接地址
while True:
# 用户输入数据(str类型)
data = input('> ')
if not data:
break
# 将数据进行编码,再通过send()方法发送给之前绑定的地址服务器
tcpCliSock.send(data.encode('utf8'))
# 接收服务器返回的数据(bytes类型),解码为字符串类型
data = tcpCliSock.recv(BUFSIZ).decode('utf8')
if not data:
break
# 打印字符串
print(data)
# 关闭客户端,断开连接
tcpCliSock.close()1.3 终端交互
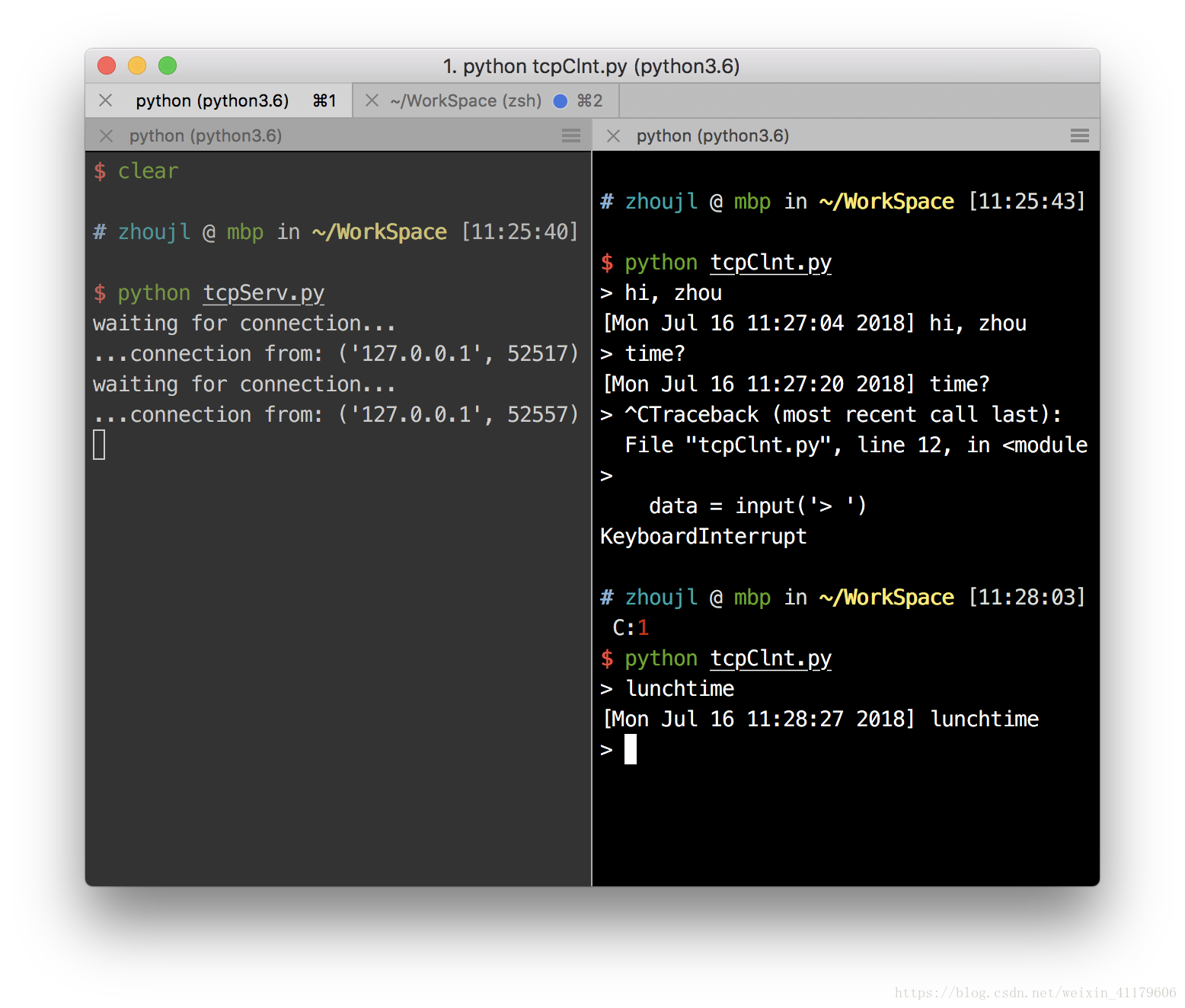
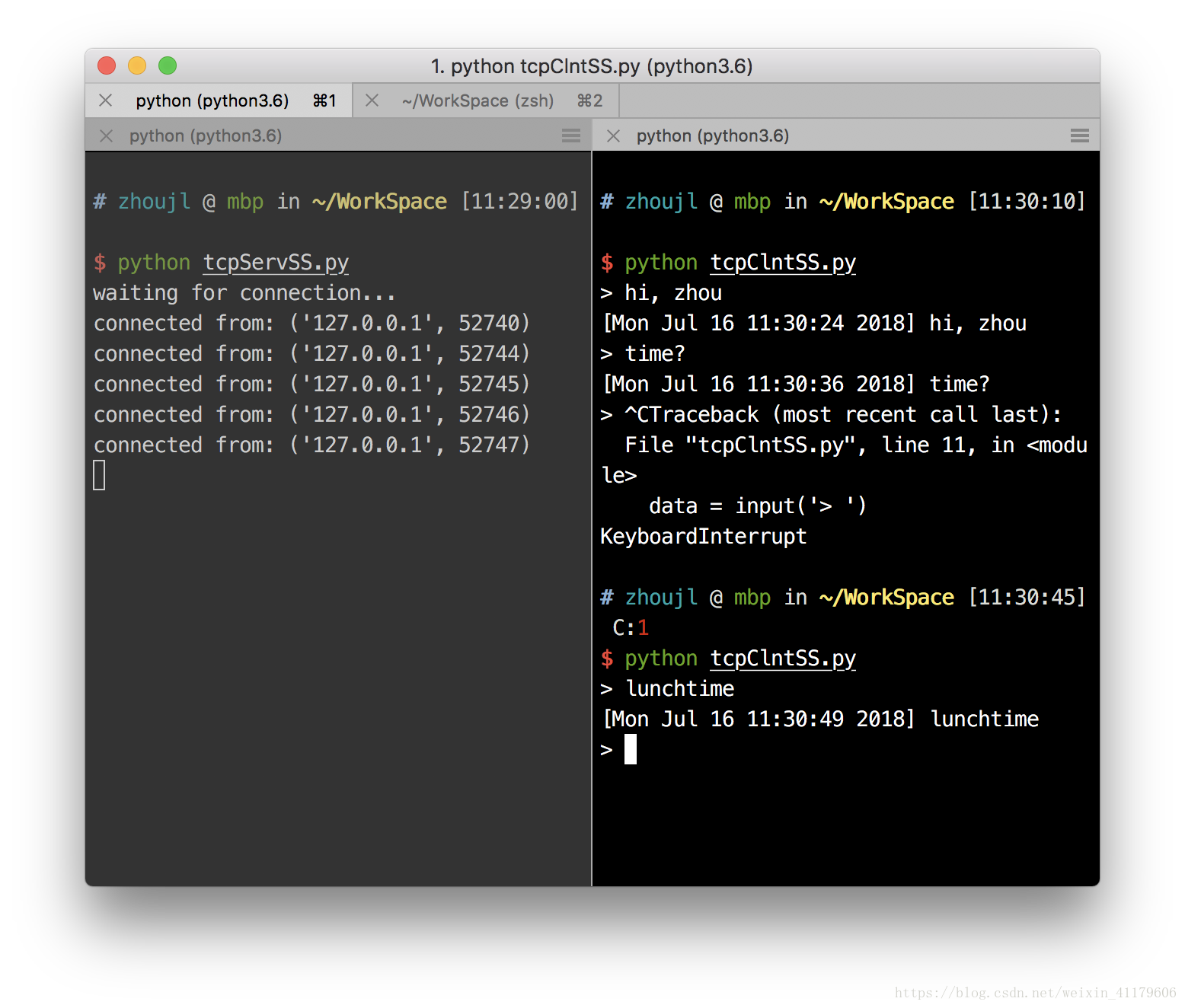
本地连接交互
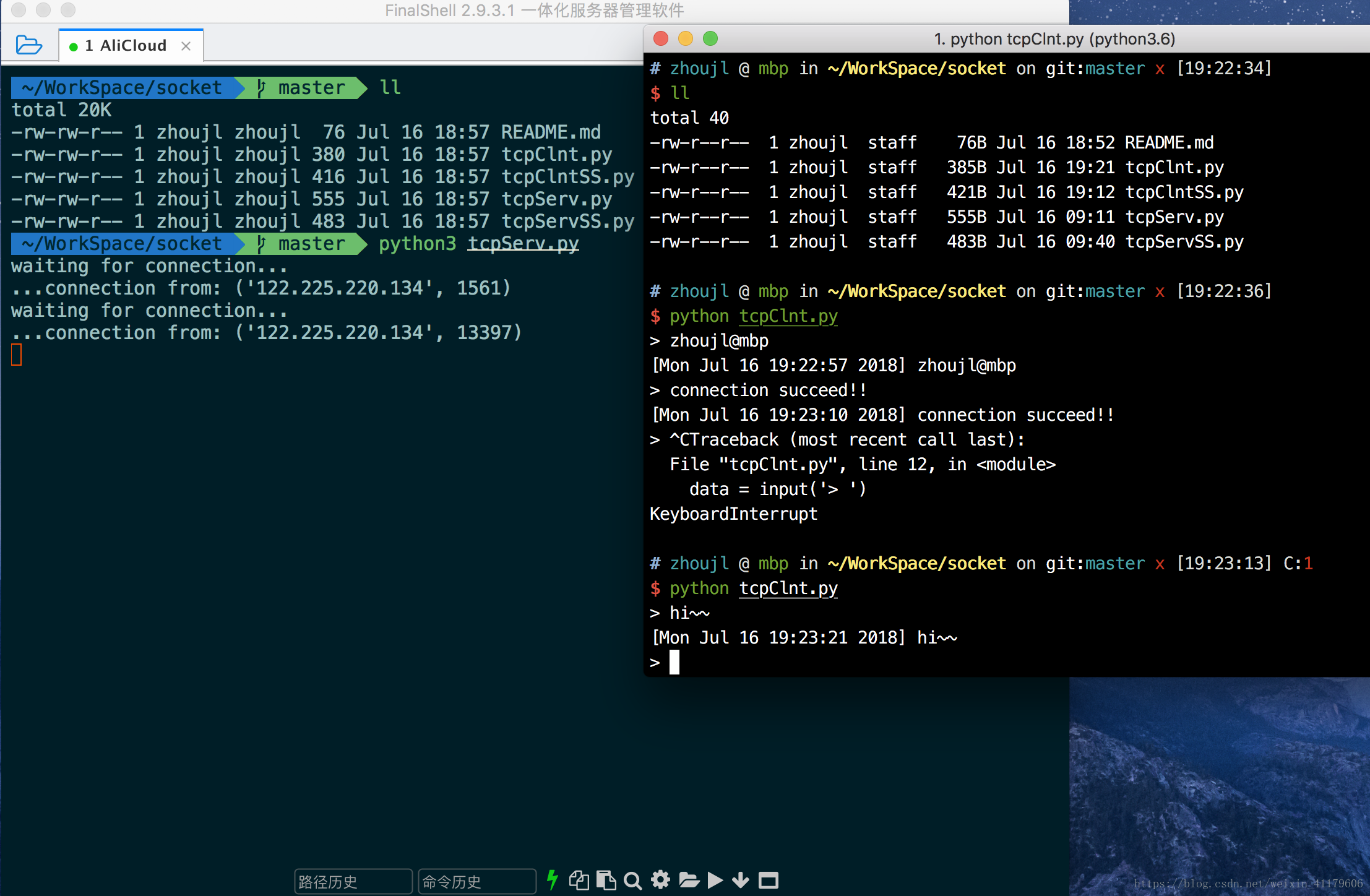
远程连接交互
更改client的host为远程主机地址
2 socketserver模块
创建TCPServer对象,class socketserver.TCPServer(server_address, RequestHandlerClass, bind_and_activate=True)
继承基类RequestHandlerClass,重写自己的MyRequestsHandler

class socketserver.BaseRequestHandler
This is the superclass of all request handler objects. It defines the interface, given below. A concrete request handler subclass must define a new handle() method, and can override any of the other methods. A new instance of the subclass is created for each request.
handle()
This function must do all the work required to service a request. The default implementation does nothing. Several instance attributes are available to it; the request is available as self.request; the client address as self.client_address; and the server instance as self.server, in case it needs access to per-server information.
The type of self.request is different for datagram or stream services. For stream services, self.request is a socket object; for datagram services, self.request is a pair of string and socket.
2.1 创建TCP服务器 - socketserver.TCPServer()
from socketserver import TCPServer as TCP
from socketserver import StreamRequestHandler as SRH
from time import ctime
HOST = ''
PORT = 21567
ADDR = (HOST, PORT)
# 重写自己的RequestHandlerClass类
class MyRequestsHandler(SRH):
# override处理数据的方法,基类默认该方法为空
def handle(self):
# 打印客户端的地址信息,该信息被储存在self.client_address中
print('connected from: {}'.format(self.client_address))
# self.rfile.readline()读取客户端发送的信息(bytes类型),并解码为字符串类型
# 写入字符串类型信息,编码为bytes(此处没有send()方法)
self.wfile.write('[{}] {}'.format(ctime(), self.rfile.readline().decode('utf8')).encode('utf8'))
# 构造socketserver.TCPServer类,传入地址和handler方法参数
tcpServ = TCP(ADDR, MyRequestsHandler)
print('waiting for connection...')
# 开启该服务,直至中断
tcpServ.serve_forever() 2.2 创建TCP客户端 - socket.socket()
from socket import *
HOST = 'localhost'
PORT = 21567
BUFSIZ = 1024
ADDR = (HOST, PORT)
while True:
tcpCliSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)
tcpCliSock.connect(ADDR)
data = input('> ')
if not data:
break
# 以行终止符作为结尾,发送字符串信息并编码
tcpCliSock.send('{}\r\n'.format(data).encode('utf8'))
# 接收服务端传回的数据并解码
data = tcpCliSock.recv(BUFSIZ).decode('utf8')
if not data:
break
print(data.strip())
tcpCliSock.close()2.3 终端交互
本地连接交互
远程连接交互
- 更改client的host为远程主机地址

参考资料
Python核心编程(第3版)
官方文档 – socket模块
官方文档 – socketserver模块
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41179606/article/details/81069729