一、时间分类
数据库 java类
Date ---- java.sql.Date 表示日期 yyyy-MM--dd (年月日)
Time ----java.sql.Time 表示时间 hh--mm--ss(时分秒)
Timestamp ---- java.sql.Timestamp 表示日期+时间 yyyy--MM--dd hh--mm-ss(年月日时分秒)

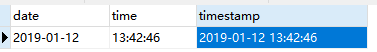
接下来我们重新创建一个test_date表,其中字段名称及类型如上图所示。
建表语句:
CREATE TABLE `test_date` ( `date` date DEFAULT NULL, `time` time DEFAULT NULL, `timestamp` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.sql.Statement; public class TestJDBC{ public static void main(String[] args){ final String connectionUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"; String userName = "root"; String passWord = "123456"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null;
//创建对应时间对象,数据库插入对象时java.sql包下的,
//为了防止和java.util包下的时间类混淆,所以这里写了完整的路径。 java.sql.Date date = new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); java.sql.Time time = new java.sql.Time(System.currentTimeMillis()); java.sql.Timestamp timestamp = new java.sql.Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()); try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl,userName,passWord); conn.setAutoCommit(false); ps = conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO `mybatis`.`test_date`" + "(`date`, `time`, `timestamp`) " + "VALUES (?, ?, ?);"); ps.setObject(1, date);//设置时间(年月日) ps.setObject(2, time);//时分秒 ps.setObject(3, timestamp);//年月日时分秒 ps.execute(); conn.commit(); System.out.println("insert 成功"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
运行结果:
insert 成功
二、查找数据库中指定时间段的数据
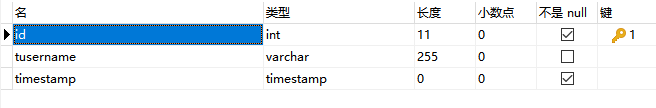
首先我们建立一个新表test_select_timestamp, 表字段名称及类型如下图所示。
建表语句:
CREATE TABLE `test_select_timestamp` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `tusername` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL, `timestamp` timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=18001 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
1.在数据库中插入一些数据(日期采用随机生成)
2.输入查找区间
3.执行对应SQL语句,返回结果集
4.遍历结果集
import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.text.DateFormat; import java.text.ParseException; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import com.mysql.cj.protocol.Resultset; public class TestJDBC{ public static void main(String[] args){ final String connectionUrl = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"; String userName = "root"; String passWord = "123456"; Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement ps = null; try { Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(connectionUrl,userName,passWord); conn.setAutoCommit(false); ps = conn.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO `mybatis`.`test_select_timestamp`" + "(`tusername`, `timestamp`) " + "VALUES ( ?, ?);"); //随机插入数据, 语句对象,插入条数 randomInsertTime(ps,2000);//随机插入2000条不同的时间数据 //根据指定时间区间查找内容 ResultSet rs = findSpecifyTime(conn,"2019-1-11 00-00-00","2019-1-11 20-00-00"); conn.commit(); //输出结果集 while(rs.next()){ System.out.println(rs.getInt(1) +"--" + rs.getString(2) + "--" + rs.getTimestamp(3)); } System.out.println("select 成功"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } catch (SQLException e) { try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e1.printStackTrace(); } // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } //插入dateNum条数据,日期随机 public static void randomInsertTime(PreparedStatement ps,int dateNum) throws SQLException{ for (int i = 0; i <dateNum;i++){ long randTime = (long)(Math.random()*100000000);
//系统获取当前时间减去一个随机数 java.sql.Timestamp timestamp = new java.sql.Timestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()-randTime); ps.setObject(1, "hcf"+i); ps.setObject(2, timestamp); ps.execute(); } } //将yyyy-MM-dd hh-mm-ss格式的字符串转为代表对应时间对象的long型数据 public static long stringToDateLong(String ts){ DateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh-mm-ss"); try { return df.parse(ts).getTime(); } catch (ParseException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); return 0;//异常返回0 } } //寻找时间在start-end之间的数据,返回查找结果集 public static ResultSet findSpecifyTime(Connection conn,String start,String end) throws SQLException{ PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement("select * from test_select_timestamp " + "where timestamp >? and timestamp<?");
//根据字符串转换成的long型数据,构造Timestamp对象,设置查询参数 ps.setObject(1, new java.sql.Timestamp(stringToDateLong(start))); ps.setObject(2, new java.sql.Timestamp(stringToDateLong(end))); ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery(); conn.commit(); return rs; } }
运行结果: 16001--hcf0--2019-01-11 16:26:28.0 16004--hcf3--2019-01-11 11:31:46.0 16006--hcf5--2019-01-11 15:45:16.0 16008--hcf7--2019-01-11 17:12:24.0 . . .//后面还有很多数据就不一一列出了 select 成功
上述代码先插入指定条数据,接着输入查找时间区间的字符串形式,之后将字符串转换为对应时间对象所代表的long型数据。
然后将这个long型数据作为构造Timestamp对象的参数,最后根据Timestamp对象和SQL语句在数据库中查询并得到结果集。