1.String为什么是不可变的?




2.Tomcat,Jetty,Apache,Jboss,Nginx的区别:




tomcat与Jetty:

lighttpd,apache,nginx的区别:






3.什么是SQL注入,如何防止SQL注入?

4.java内存模型中,一个对象(两个属性,四个方法)实例化100次,现在内存中的存储状态,几个对象,几个属性,几个方法?

5.反射的性能?如何优化?








6.spring的AOP实现细节?

![]()




![]()




它的一些主要功能:
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()



7.线程同步,并发操作怎么控制?





![]()


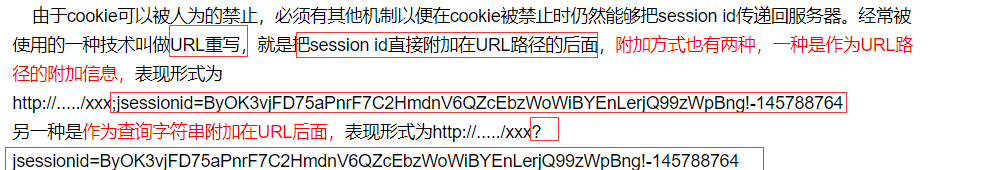
8.tomcat的session机制,如果让你实现一个server,如何实现session机制?

![]()
![]()




![]()





import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
/**
* @author [email protected]
* @time 2019/1/2 16:08
*/
public class ServerTest4server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new Server();
}
static class Server {
static volatile LinkedList socketList = new LinkedList();
public Server() throws IOException {
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
while (true) {
final Socket socket = serverSocket.accept();
if (socket != null) socketList.add(socket);
final Iterator iterator = socketList.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
//引用变量保证线程间的通信
final Socket currSocket = (Socket) iterator.next();
//在主线程中将该对象移除,它是主线程同步的。
socketList.remove(currSocket);
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
InputStream inputStream = currSocket.getInputStream();
byte[] inputByte = new byte[1024];
int length;
if ((length = inputStream.read(inputByte)) != -1) {
if (length != 1024) System.out.println(new String(inputByte, 0, length, Charset.forName("utf-8")));
else System.out.println(new String(inputByte));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
OutputStream outputStream = currSocket.getOutputStream();
String s = "hi,world!";
outputStream.write(s.getBytes("utf-8"));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
}
}
}
}
import java.io.*;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* @author [email protected]
* @time 2019/1/2 16:08
*/
public class ServerTest4client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
new Client();
}
static class Client{
public Client() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",8080);
while (true){
OutputStream outputStream= socket.getOutputStream();
String outputString = "helloworld";
outputStream.write(outputString.getBytes("utf-8"));
InputStream inputStream= socket.getInputStream();
byte[] inputByte = new byte[1024];
int length;
if ((length = inputStream.read(inputByte)) != -1) {
if (length != 1024) System.out.println(new String(inputByte, 0, length));
else System.out.println(new String(inputByte));
}
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
}
}
}
笔记:1.当套接字的socket流显式关闭,该socket也会关闭(无论是输入流,还是输出流);
2. 当输入流采用while循环读取时,可能会发生死锁。 尤其是服务端和客户端同时采用该方式;
3.流的多字节read,即多字节读取操作,是阻塞式。 所谓阻塞是指: 必须读到结果,尽管这个结果有可能是-1,否则它将阻塞。
9.如何分析执行计划?







![]()



![]()




