版权声明:本文为博主自我学习整合内容,欢迎转载,转载请注明出处。 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39388410/article/details/84958683
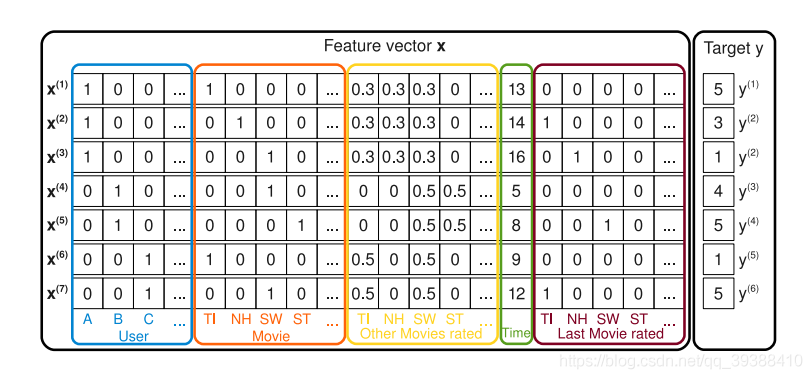
在处理MF矩阵分解时使用过FunkSVD,最后在分解诶P,Q矩阵的时候果然还是用到了一般套路,根据预测y和实际y的差别梯度下降来寻找。所以能否直接从这个思路,把它变成多个特征的回归模型是否可行?
但是普通的线性模型,并没有考虑到特征与特征之间的相互关系。所以加上一项:
但是在数据矩阵很稀疏的情况下,即xi,xj非0的情况非常少,ωij实际上是无法仅仅通过训练得出。于是需要引入一个辅助向量
,其中k为超参,可以将y改写成:
即引入V:
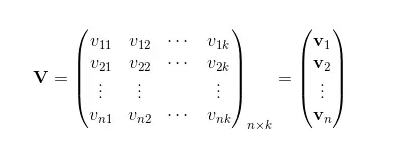
此时的交互矩阵,
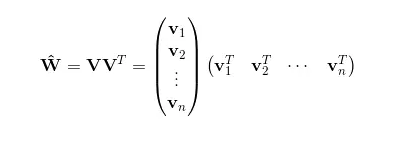
也就是说我们相对对W进行了一种矩阵分解,那么在高稀疏上的表达上得到V相对来说是容易的。同样我们接着要求导,先化简一下后面的式子:
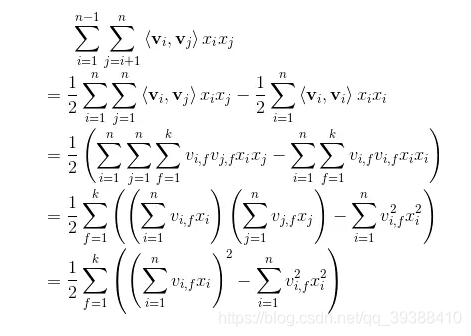
然后再求导和随机梯度下降SGD就行了。下面使用经典的MovieLens100k数据集,也就是由明尼苏达大学和研究人员收集整理的1000209匿名评级约3900部电影的评分。数据包括四列,用户id,电影id,评分和时间戳。
user item rating timestamp 0 1 1 5 874965758 1 1 2 3 876893171 2 1 3 4 878542960 3 1 4 3 876893119 4 1 5 3 889751712 5 1 6 5 887431973 6 1 7 4 875071561 7 1 8 1 875072484 8 1 9 5 878543541 9 1 10 3 875693118
FM的代码为:
from itertools import count
from collections import defaultdict
from scipy.sparse import csr
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
import tensorflow as tf
from tqdm import tqdm
#from tqdm import tqdm_notebook as tqdm
######数据处理
#将原始文件输入转换成我们需要的稀疏矩阵(稀疏矩阵编码格式)
def vectorize_dic(dic,ix=None,p=None,n=0,g=0):
if ix==None:
ix = dict()
nz = n * g
col_ix = np.empty(nz,dtype = int)#每行起始的偏移量
i = 0
for k,lis in dic.items():#遍历文档
for t in range(len(lis)):#遍历每个词
ix[str(lis[t]) + str(k)] = ix.get(str(lis[t]) + str(k),0) + 1
col_ix[i+t*g] = ix[str(lis[t]) + str(k)]
i += 1
row_ix = np.repeat(np.arange(0,n),g)#每个数对应的列号
data = np.ones(nz)
if p == None:
p = len(ix)
ixx = np.where(col_ix < p)#输出满足条件的值
return csr.csr_matrix((data[ixx],(row_ix[ixx],col_ix[ixx])),shape=(n,p)),ix
#batch函数
def batcher(X_, y_=None, batch_size=-1):
n_samples = X_.shape[0]
if batch_size == -1:
batch_size = n_samples
if batch_size < 1:
raise ValueError('Parameter batch_size={} is unsupported'.format(batch_size))
for i in range(0, n_samples, batch_size):
upper_bound = min(i + batch_size, n_samples)
ret_x = X_[i:upper_bound]
ret_y = None
if y_ is not None:
ret_y = y_[i:i + batch_size]
yield (ret_x, ret_y)
#读入数据
cols = ['user','item','rating','timestamp']
train = pd.read_csv('data/ua.base',delimiter='\t',names = cols)
test = pd.read_csv('data/ua.test',delimiter='\t',names = cols)
print(train,test)
x_train,ix = vectorize_dic({'users':train['user'].values,
'items':train['item'].values},n=len(train.index),g=2)
x_test,ix = vectorize_dic({'users':test['user'].values,
'items':test['item'].values},ix,x_train.shape[1],n=len(test.index),g=2)
#变换后的形式
print(x_train)
y_train = train['rating'].values
y_test = test['rating'].values
#得到变换后的矩阵形式
x_train = x_train.todense()
x_test = x_test.todense()
print(x_train)
print(x_train.shape)
print (x_test.shape)
#######Tensorflow搭建
#定义损失函数
n,p = x_train.shape
k = 10#设置超参k
x = tf.placeholder('float',[None,p])
y = tf.placeholder('float',[None,1])
w0 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1]))
w = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([p]))
v = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([k,p],mean=0,stddev=0.01))
#y_hat = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([n,1]))
linear_terms = tf.add(w0,tf.reduce_sum(tf.multiply(w,x),1,keep_dims=True)) #按行求和
#得到化简后的函数
pair_interactions = 0.5 * tf.reduce_sum(tf.subtract( tf.pow( tf.matmul(x,tf.transpose(v)),2), tf.matmul(tf.pow(x,2),tf.transpose(tf.pow(v,2)))),axis = 1 , keep_dims=True)
#完整的预测函数y
y_hat = tf.add(linear_terms,pair_interactions)
#正则化项
lambda_w = tf.constant(0.001,name='lambda_w')
lambda_v = tf.constant(0.001,name='lambda_v')
l2_norm = tf.reduce_sum(
tf.add(tf.multiply(lambda_w,tf.pow(w,2)),tf.multiply(lambda_v,tf.pow(v,2))))
#error和loss
error = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y-y_hat))
loss = tf.add(error,l2_norm)
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate=0.01).minimize(loss)#梯度下降
#模型训练
epochs = 1
batch_size = 5000
# Launch the graph
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in tqdm(range(epochs), unit='epoch'):#输出进行过程
perm = np.random.permutation(x_train.shape[0])#打乱顺序
# iterate over batches
for bX, bY in batcher(x_train[perm], y_train[perm], batch_size):
_,t = sess.run([train_op,loss], feed_dict={x: bX.reshape(-1, p), y: bY.reshape(-1, 1)})
print(t)
errors = []
for bX, bY in batcher(x_test, y_test):
errors.append(sess.run(error, feed_dict={x: bX.reshape(-1, p), y: bY.reshape(-1, 1)}))
print(errors)
RMSE = np.sqrt(np.array(errors).mean())
print (RMSE)