一 字节流
1.1字节输出流OutputStream
OutputStream是一个抽象类,操作的数据都是字节。
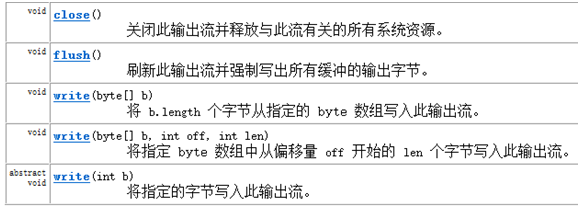
输出流中定义都是写write方法,如下图:
1.1.1 FileOutputStream类
OutputStream有很多子类,其中子类FileOutputStream可用来写入数据到文件。FileOutputStream类,即文件输出流,是用于将数据写入 File的输出流。
构造方法:

将数据写入文件中
public static void method01() throws IOException{ //创建字节输出流对象 //如果该文件有则覆盖,如果没有则覆盖 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt"); fos.write(100);//ASCII码 //释放资源 fos.close(); }
public static void method02() throws IOException{ //创建字节输出流对象 //如果该文件有则覆盖,如果没有则覆盖 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt"); //byte[] bytes={97,98,99,100}; //fos.write(bytes,1,1); //字符串转字节数组 fos.write("你好吗,中国".getBytes()); //释放资源 fos.close(); }
public static void method03() throws IOException{ //创建字节输出流对象 //如果该文件有则覆盖,如果没有则覆盖 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt",true); //换行 \r\n //字符串转字节数组 fos.write("hello,java".getBytes()); //释放资源 fos.close(); }
给文件续写和换行时,在FileOutputStream的构造函数中,可以接受一个boolean类型的值,如果值true,就会在文件末位继续添加。
1.2字节输入流InputStream
InputStream是一个抽象类,定义了读的方法

1.2.1 FileInputStream类
FileInputStream类是InputStream的实现类,用它来读取文件内容
构造方法有
用它来读取数据
1 单个字节读
public static void method01() throws IOException{ //明确数据源 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt"); //从文件中读取一个字节 int len1=fis.read(); //强转字符型 加char System.out.println((char)len1); len1=fis.read(); System.out.println((char)len1); len1=fis.read(); System.out.println((char)len1); len1=fis.read(); System.out.println((char)len1); len1=fis.read(); System.out.println((char)len1); len1=fis.read(); System.out.println(len1); //释放资源 fis.close(); }
2.单个字节循环读
public static void method02() throws IOException{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt"); int len=0; while((len=fis.read())!=-1){ System.out.println((char)len); } //释放资源 fis.close(); }
3.用数组的形式一个个读
public static void method03() throws IOException{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt"); //创建数组 byte[] bytes=new byte[2]; int len=fis.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes)); System.out.println(len); len=fis.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes)); System.out.println(len); len=fis.read(bytes); System.out.println(new String(bytes)); System.out.println(len); //释放资源 fis.close(); }
4.用数组的形式循环读
public static void method04() throws IOException{ FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt"); //创建数组 byte[] bytes=new byte[2]; int len=0; while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){ System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len)); } //释放资源 fis.close(); }
字节流的练习:进行文件的复制
//文件的复制 public static void method05() throws IOException{ //数据源 FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\java\\demo.txt"); //目的地 FileOutputStream fos=new FileOutputStream("F:\\demo.txt"); //开始复制 int len=0; while((len=fis.read())!=-1){ fos.write(len); } //释放资源 fis.close(); fos.close(); }