一:Vuex是什么
1.1 简介
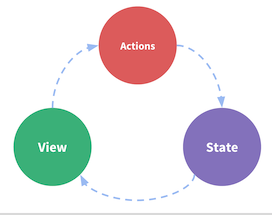
组件中包含视图(模板template)、双向绑定的数据(data)、以及一些方法(methods),这3个都写在同一个组件(component)里面, 一般视图(View)触发方法动作(Actions),动作影响数据状态(State), 数据状态的改变又反应到视图(View)上来,这样在一个组件内就形成了一个闭环。即当前组件的视图使用当前组件的数据,当前组件的动作(方法)只修改当前组件的数据,总体来说只能自己跟自己玩,不能多个组件相互玩。
我们有这样两个需求:
- 多个视图依赖于同一状态。
- 来自不同视图的行为需要变更同一状态。
对于问题一,传参的方法对于多层嵌套的组件将会非常繁琐,并且对于兄弟组件间的状态传递无能为力。
对于问题二,我们经常会采用父子组件直接引用或者通过事件来变更和同步状态的多份拷贝。以上的这些模式非常脆弱,通常会导致无法维护的代码。
为了解决以上问题,我们把组件的共享状态(data)抽取出来,以一个全局单例模式管理, 这样所有组件在任意时候都可以访问全局状态,当在任意组件中修改全局状态,所有引用全局状态的视图也会随之改变(响应式)。这就是Vuex的功能。
简单来说Vuex在一个工程中只能有一个全局实例对象(Store),也就是该实例对象是整个应用级别的, 一个对象就包含了全部的应用层级状态。 store被称为仓库,用于盛放全局状态的容器。任何组件都能访问全局对象的数据(State),任何组件都可以修改全局对象的数据。这就是我们平常说的设计模式中的“单例模式”。
1.2 全局单例 Store 伪代码
class Vuex.Store {
public Object state;
// 同步操作,接收参数 (state)
public Object mutations;
// 异步操作, 接收参数 (context)
public Object actions;
// 每个函数可以接收两个参数 (state, getters)
// 相当于是state的计算函数
Public Object getters;
// 模块(module)
public Object modules;
// 命名空间(类似于包package的概念)
boolean namespaced;
// 插件
public Object[] plugins;
// 严格模式
public boolean strict;
/*
* 提交mutation
* 载荷(Payload):就是参数
*/
public void commit(String mutation, Object payload) {
}
/*
* 分发action
* 载荷(Payload):就是参数
*/
public void dispatch(String mutation, Object payload) {
}
}
二: Vuex HelloWorld
2.1 Vuex安装
cnpm install vuex --save
显式使用Vuex插件,一般写在src/main.js中,或者写在其它js中然后再在main.js中引入
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
2.2 多组件共享全局状态示例
分别在Foo.vue和Bar.vue中改变全局属性count值,然后在App.vue中显示count修改后的值。
- 定义全局单例对象 src/store/store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.step
},
decrement: state => state.count--,
}
})
定义一个全局实例对象(Vuex.Store):
-
该对象的状态(state)就是全局属性, 类似于组件的data,每个组件都可以访问和修改属性。
-
可变的(mutations)类似于组件中的methods, mutations中的每个方法称作为 mutation handler,用来修改state中的值,方法的参数可以有两个(state, payload) state表示全局的单例对象,payload(载荷)也就是参数,调用时可以传递参数,该参数是可选的。
扫描二维码关注公众号,回复: 4727178 查看本文章
使用Mutation时需遵守的一些规则:
-
最好提前在你的 store 中初始化好所有所需属性。
-
当需要在对象上添加新属性时,你应该使用 Vue.set(obj, ‘newProp’, 123), 或者以新对象替换老对象
-
Mutation 必须是同步函数
- 在src/main.js中导入store.js并作为Vue的选项
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
import store from './store/store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
/* eslint-disable no-new */
new Vue({
el: '#app',
store,
router,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
将store作为Vue的选项,这样Vue会将store“注入”到每一个子组件中,也就是说每个组件都可以通过this.$store来访问全局单例对象store。
- Foo.vue
<template>
<div>
Foo.vue <button @click="increment">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Foo',
methods: {
increment () {
this.$store.commit('increment', {
step: 10
})
}
}
}
</script>
调用store中的mutations方法只能通过提交的方式this.$store.commit('方法名', 负载参数)这一种形式来调用,而不能使用this.$store.方法名 这种普通的的 对象.方法() 方式直接调用。如果感觉这种方式麻烦,Vuex提供了一种将Mutations映射(map)为methods的方式, 然后在使用时直接调用method就会自动帮你commit。
mapMutations() 函数,它接收一个参数,参数类型可以是数组也可以是对象:
- 数组类型:当使用方法时方法名称和Mutation的名称一样时使用数组类型。
- 对象类型:当使用方法时方法名称不想和Mutation的名称一样,可以对method起一个新的名称
<template>
<div>
Foo.vue <button @click="add({step: 10})">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Foo',
methods: {
// 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// 将 `this.incrementBy({step: 10})` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', {step: 10})`
...mapMutations(['increment', 'incrementBy']),
// 将Mutation(increment)映射为method(add)
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment'
})
}
}
</script>
注意:mapMutations只是将Mutations简单的映射为methods, 其中method的方法体只包含this.$store.commit(‘mutation’, payload)这一样代码,如果method还要处理其它业务逻辑的话,那么只能使用提交commit方式,而不能使用映射方式mapMutations。
- Bar.vue
<template>
<div>
Bar.vue <button @click="decrement">-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Bar',
methods: {
decrement () {
this.$store.commit('decrement')
}
}
}
</script>
- App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
App.vue {{count}}
<router-view name="foo"></router-view>
<router-view name="bar"></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
computed: {
count() {
return this.$store.state.count
}
}
}
</script>
可以通过{{ this.$store.state.count }}来获取count的值,也可以将this.$store.state.count这行代码包装到计算属性count中,这样获取值就方便点{{ count }}。
- src/router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Foo from '../components/Foo'
import Bar from '../components/Bar'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
components: {
foo: Foo,
bar: Bar
}
}
]
})
为了在一个组件中使用多个兄弟组件,使用命名视图,将这些兄弟组件作为父组件的孩子组件。
2.3 actions
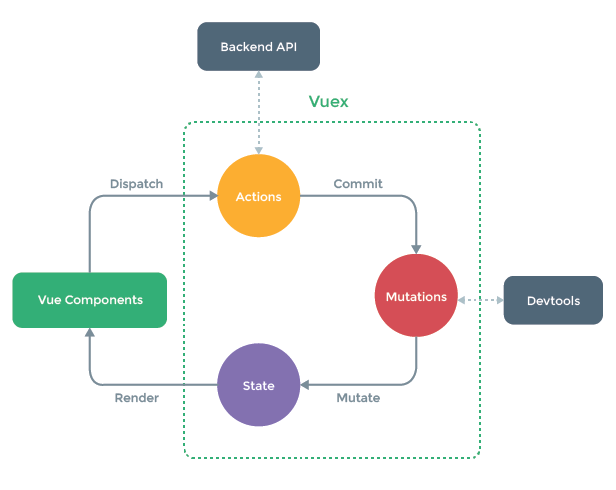
Action 类似于 mutation,Action用于分发(dispatch)mutation,而不直接修改状态。 Action 可以包含任意异步操作(如发送http请求)
action方法接收两个参数(context, payload),context为Context对象,context对象store实例具有相同方法和属性,所以context可以解构成var {state, dispatch, commit, getters} = context
src/store/store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.step
},
decrement: state => state.count--,
},
actions: {
incrementAsync (context, payload) {
console.log(context.state)
console.log(context.getters)
// 延迟1秒执行
setTimeout(() => {
context.commit('increment', payload)
}, 1000)
}
}
})
Foo.vue
<template>
<div>
Foo.vue <button @click="increment">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Foo',
methods: {
increment () {
this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync', { step: 10 })
}
}
}
</script>
如果感觉封装个方法调用store的dispatch()方法麻烦的话可以使用mapActions()辅助函数,它的用法和mapMutations一样。mapActions()的作用就是简单的将this.$store.dispatch('Action名称', payload)这一行代码封装到方法中。同样该函数接收一个参数,该参数的类型可以是数组类型也可以是对象类型。
<template>
<div>
Foo.vue <button @click="add({ step: 10 })">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Foo',
methods: {
// 参数为数组类型:method的名称和action名称一样
...mapActions(['incrementAsync']),
// 参数为对象类型:method的名称和action名称不一致
...mapActions({
add: 'incrementAsync'
})
}
}
</script>
Action中操作一般都是异步的,通常都需要在异步操作完成后做一些其它逻辑,如何知道异步处理完成了呢?可以在action中将异步处理的逻辑封装到Promise对象中,当异步逻辑处理完成就会调用Promise对象的then()方法,这样我们将异步完成后的逻辑写在then()方法中即可。
注意:dispatch('action', payload)函数返回一个Promise对象,如果action中显式返回Promise, 那么dispatch()函数返回的就是action中的promise对象,如果action中没有显式的返回Promise对象,系统会将action中的逻辑封装到一个新的Promise对象中,然后返回一个新的promise对象,所以dispatch()之后可以调用then()
src/store/store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
increment (state, payload) {
state.count += payload.step
},
decrement: state => state.count--,
},
actions: {
incrementAsync (context, payload) {
console.log(context.state)
console.log(context.getters)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 延迟1秒执行
setTimeout(() => {
// 提交mutation
context.commit('increment', payload)
// 成功,继续执行
resolve('异步执行结束')
}, 1000)
})
}
}
})
Foo.vue
<template>
<div>
Foo.vue <button @click="increment">+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Foo',
methods: {
increment () {
// dispatch()函数的返回值为action的返回值, action返回Promise
// 所以dispatch()之后可以调用then()
this.$store.dispatch('incrementAsync', { step: 10 }).then((resp) => {
console.log(resp)
})
}
}
}
</script>
action之间相互调用通过dispatch来调用
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
// ...
actions: {
fooAsync () {
console.log('fooAsync')
},
barAsync ({ dispatch }) {
// 使用dispatch调用其它action
dispatch('fooAsync').then(() => {
console.log('barAsync')
});
}
}
})
三 组件之间传递参 示例
3.1 src/store/store.js
预先定义出属性名 pageParams
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
pageParams: {}
}
})
3.2 App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<button @click="goPage">页面传参</button>
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
methods: {
goPage () {
this.$store.state.pageParams = {foo: 'foo', bar: 'bar'}
this.$router.push('/foo')
}
}
}
</script>
修改对象的某个属性除了使用等号=直接赋值外,也可以使用Vue的全局方法set来赋值。Vue.set(对象, '属性名', 属性值)
import Vue from 'vue'
Vue.set(this.$store.state, 'pageParams', {foo: 'foo', bar: 'bar'})
3.3 src/router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Foo from '../components/Foo'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/foo',
component: Foo
}
]
})
3.4 Foo.vue
<template>
<div>
{{ this.$store.state.pageParams }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Foo'
}
</script>
3.5 mapState 辅助函数
当组件中要访问多个store中的状态就需要写多个计算属性,比较麻烦,可以使用mapState辅助函数简化写法, mapState函数的作用就是用于生成计算属性。mapState函数接收一个对象参数
- 数组参数: 如果直接取store下的state值而不需要任何计算,可以直接传数组参数,值为store中的state中的属性名
- 对象参数:如果需要对全局属性进行额外的计算,可以使用一个函数进行计算
mapState({ 计算方法 })
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Foo',
computed: mapState({
pageParams1 (state) {
return state.pageParams
},
// 传字符串参数 'pageParams' 等同于 `state => state.pageParams`
pageParams2: 'pageParams'
})
}
</script>
mapState([‘属性名’])
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Foo',
computed: mapState(['pageParams'])
}
</script>
3.6 对象展开运算符 …mapState
<script>
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Foo',
data () {
return {
msg: 'Hello Vue'
}
},
computed: {
message () {
return this.msg + "!"
},
// 使用对象展开运算符将此对象混入到外部对象中,即computed对象中
// 相当于将mapState(['pageParams'])里的计算函数都拿到computed里,作为computed的函数
// 当计算函数中除了mapState外还有别的计算方法时使用
...mapState(['pageParams'])
}
}
</script>
四:Getter
Getter就是对store对象的状态state进行计算的方法,getter方法接收两个参数(state, getters), 可以通过this.$store.getters.getter方法名来调用getter方法。
src/store/store.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: 'Task A', isDone: true },
{ id: 2, text: 'Task B', isDone: false }
]
},
getters: {
doneTodos (state, getters) {
return state.todos.filter(item => item.isDone)
},
// 调用其他getter方法
doneTodosCount (state, getters) {
return getters.doneTodos.length
},
// getter方法也可以返回一个函数
getTodoById (state) {
var myfun = function (id) {
return state.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id)
}
return myfun;
}
}
})
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
{{ this.$store.getters.doneTodos }} <br>
{{ this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount }} <br>
{{ this.$store.getters.getTodoById(2) }} <br>
{{ doneTodoList }}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'App',
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters({
doneTodoList: 'doneTodos'
})
}
}
</script>
mapGetters 辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性, mapGetters() 函数接收一个参数,参数类型可以是对象类型也可以是数组类型:
- 如果需要将getter方法映射成计算属性起一个别名时使用对象参数
- 如果不需要将getter方法映射成计算属性起一个别名时使用数组参数,数组里的值就是getter的名字,如 [‘doneTodos’, ‘doneTodosCount’]
五:module
-
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象。当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割。
-
由于分割后会导致各个模块中state、mutation、action、getter会命名冲突,为了解决这个问题Vuex使用命名空间的概念来解决,就是类似于java中的package概念。
-
因module属于优化部分,暂时不详细说明。