生命周期
-
介绍
版本:2.5.17
我们知道每个Vue 实例在被创建之前都要经过一系列的初始化过程。例如需要设置数据监听、编译模板、挂载实例到 DOM、在数据变化时更新 DOM 等。同时在这个过程中也会运行一些函数叫做生命周期钩子的函数:如beforeCreate 、created,beforeMount 、mounted、beforeUpdate 、updated、beforeDestroy、 destroyed、beforeDestroy、 destroyed,给予用户机会在一些特定的场景下添加他们自己的代码。
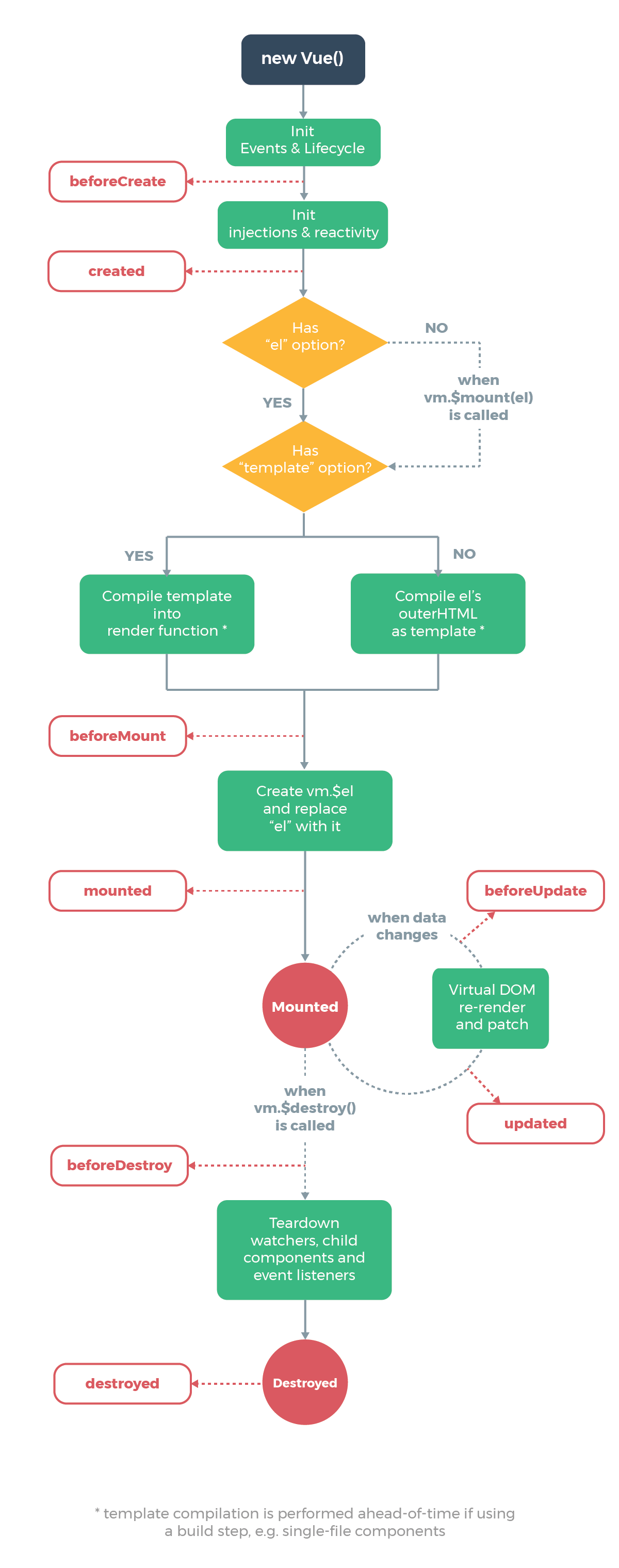
-
callHook函数
源码中最终执行生命周期的函数都是调用 callHook 方法,它的定义在 src/core/instance/lifecycle中,callhook 函数的功能就是调用某个生命周期钩子注册的所有回调函数。
export function callHook (vm: Component, hook: string) {
// #7573 disable dep collection when invoking lifecycle hooks
// pushTarget初始化对Dep.target赋值
pushTarget()
// 根据传入的字符串 hook,去拿到 vm.$options[hook] 对应的回调函数数组,然后遍历执行,执行的时候把 vm 作为函数执行的上下文
const handlers = vm.$options[hook]
if (handlers) {
for (let i = 0, j = handlers.length; i < j; i++) {
try {
handlers[i].call(vm)
} catch (e) {
handleError(e, vm, `${hook} hook`)
}
}
}
if (vm._hasHookEvent) {
vm.$emit('hook:' + hook)
}
popTarget()
}-
beforeCreate & created
beforeCreate 和 created 函数都是在实例化 Vue 的阶段,在 _init 方法中执行的,它的定义在 src/core/instance/init.js 中:
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) {
Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) {
.....
vm._self = vm
initLifecycle(vm)
initEvents(vm)
initRender(vm)
callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate')
initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props
initState(vm)
initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props
callHook(vm, 'created')
.......
}
} 可以看到 beforeCreate 和 created 的钩子调用是在 initState 的前后,initState 的作用是初始化 props、data、methods、watch、computed 等属性,那么显然 beforeCreate 的钩子函数中就不能获取到 props、data 中定义的值,也不能调用 methods 中定义的函数。
在这俩个钩子函数执行的时候,并没有渲染 DOM,所以我们也不能够访问 DOM,一般来说,如果组件在加载的时候需要和后端有交互,放在这俩个钩子函数执行都可以,如果是需要访问 props、data 等数据的话,就需要使用 created 钩子函数。
补充:vue 初始化阶段对于 options 的合并会运行initMixin函数,它的定义在src\platforms\web\runtime\index.js中
function Vue (options) {
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' &&
!(this instanceof Vue)
) {
warn('Vue is a constructor and should be called with the `new` keyword')
}
this._init(options)
}
//
// 每个Mixin就是往vue定的原型方法 Vue.prototype.xx = yy 用function方便代码的管理,组装,添加原型方法各个文件各个模板,用class,需要一个主文件,添加主属性等。所以vue使用function
initMixin(Vue)
stateMixin(Vue)
eventsMixin(Vue)
lifecycleMixin(Vue)
renderMixin(Vue)
export default Vue
-
beforeMount & mounted
beforeMount 钩子函数发生在 mount,也就是 DOM 挂载之前,它的调用时机是在 mountComponent 函数中,定义在 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 中:
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
vm.$el = el
if (!vm.$options.render) {
vm.$options.render = createEmptyVNode
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
/* istanbul ignore if */
if ((vm.$options.template && vm.$options.template.charAt(0) !== '#') ||
vm.$options.el || el) {
warn(
'You are using the runtime-only build of Vue where the template ' +
'compiler is not available. Either pre-compile the templates into ' +
'render functions, or use the compiler-included build.',
vm
)
} else {
warn(
'Failed to mount component: template or render function not defined.',
vm
)
}
}
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeMount')
let updateComponent
/* istanbul ignore if */
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) {
updateComponent = () => {
const name = vm._name
const id = vm._uid
const startTag = `vue-perf-start:${id}`
const endTag = `vue-perf-end:${id}`
mark(startTag)
const vnode = vm._render()
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} render`, startTag, endTag)
mark(startTag)
vm._update(vnode, hydrating)
mark(endTag)
measure(`vue ${name} patch`, startTag, endTag)
}
} else {
updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
}
// we set this to vm._watcher inside the watcher's constructor
// since the watcher's initial patch may call $forceUpdate (e.g. inside child
// component's mounted hook), which relies on vm._watcher being already defined
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
return vm
} 在执行 vm._render() 函数渲染 VNode 之前,执行了 beforeMount 钩子函数,在执行完 vm._update() 把 VNode patch 到真实 DOM 后,执行 mouted 钩子。注意,这里对 mouted 钩子函数执行有一个判断逻辑,vm.$vnode 如果为 null,则表明这不是一次组件的初始化过程,而是我们通过外部 new Vue 初始化过程。
组件的 VNode patch 到 DOM 后,会执行 invokeInsertHook 函数,把 insertedVnodeQueue 里保存的钩子函数依次执行一遍,它的定义在 src/core/vdom/patch.js 中:
function invokeInsertHook (vnode, queue, initial) {
// delay insert hooks for component root nodes, invoke them after the
// element is really inserted
if (isTrue(initial) && isDef(vnode.parent)) {
vnode.parent.data.pendingInsert = queue
} else {
for (let i = 0; i < queue.length; ++i) {
queue[i].data.hook.insert(queue[i])
}
}
} 该函数会执行 insert 这个钩子函数,对于组件而言,insert 钩子函数的定义在 src/core/vdom/create-component.js 中的 componentVNodeHooks 中:
const componentVNodeHooks = {
// ...
insert (vnode: MountedComponentVNode) {
const { context, componentInstance } = vnode
if (!componentInstance._isMounted) {
componentInstance._isMounted = true
callHook(componentInstance, 'mounted')
}
// ...
},
} 我们可以看到,每个子组件都是在这个钩子函数中执行 mouted 钩子函数,并且我们之前分析过,insertedVnodeQueue 的添加顺序是先子后父,所以对于同步渲染的子组件而言,mounted 钩子函数的执行顺序也是先子后父。
-
beforeUpdate & updated
顾名思义,beforeUpdate 和 updated 的钩子函数执行时机都应该是在数据更新的时候。beforeUpdate 的执行时机是在渲染 Watcher 的 before 函数中,我们刚才提到过:
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
// ...
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
hydrating = false
// manually mounted instance, call mounted on self
// mounted is called for render-created child components in its inserted hook
if (vm.$vnode == null) {
vm._isMounted = true
callHook(vm, 'mounted')
}
// ...
}注意这里有个判断,也就是在组件已经 mounted 之后,才会去调用这个钩子函数。
update 的执行时机是在flushSchedulerQueue 函数调用的时候, 它的定义在 src/core/observer/scheduler.js 中:
function flushSchedulerQueue () {
// ...
// 获取到 updatedQueue
callUpdatedHooks(updatedQueue)
}
function callUpdatedHooks (queue) {
let i = queue.length
while (i--) {
const watcher = queue[i]
const vm = watcher.vm
if (vm._watcher === watcher && vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'updated')
}
}
} updatedQueue 是 更新了的 wathcer 数组,那么在 callUpdatedHooks 函数中,它对这些数组做遍历,只有满足当前 watcher 为 vm._watcher 以及组件已经 mounted 这两个条件,才会执行 updated 钩子函数。
我们知道在组件 mount 的过程中,会实例化一个渲染的 Watcher 去监听 vm 上的数据变化重新渲染,这断逻辑发生在 mountComponent 函数执行的时候:
export function mountComponent (
vm: Component,
el: ?Element,
hydrating?: boolean
): Component {
// ...
// 这里是简写
let updateComponent = () => {
vm._update(vm._render(), hydrating)
}
new Watcher(vm, updateComponent, noop, {
before () {
if (vm._isMounted) {
callHook(vm, 'beforeUpdate')
}
}
}, true /* isRenderWatcher */)
// ...
}那么在实例化 Watcher 的过程中,在它的构造函数里会判断 isRenderWatcher,接着把当前 watcher的实例赋值给 vm._watcher,定义在 src/core/observer/watcher.js 中:
export default class Watcher {
// ...
constructor (
vm: Component,
expOrFn: string | Function,
cb: Function,
options?: ?Object,
isRenderWatcher?: boolean
) {
this.vm = vm
if (isRenderWatcher) {
vm._watcher = this
}
vm._watchers.push(this)
// ...
}
} 同时,还把当前 wathcer 实例 push 到 vm._watchers 中,vm._watcher 是专门用来监听 vm 上数据变化然后重新渲染的,所以它是一个渲染相关的 watcher,因此在 callUpdatedHooks 函数中,只有 vm._watcher 的回调执行完毕后,才会执行 updated 钩子函数。
-
beforeDestroy & destroyed
beforeDestroy 和 destroyed 钩子函数的执行时机在组件销毁的阶段,组件的销毁过程之后,最终会调用 $destroy 方法,它的定义在 src/core/instance/lifecycle.js 中:
Vue.prototype.$destroy = function () {
const vm: Component = this
if (vm._isBeingDestroyed) {
return
}
callHook(vm, 'beforeDestroy')
vm._isBeingDestroyed = true
// remove self from parent
const parent = vm.$parent
if (parent && !parent._isBeingDestroyed && !vm.$options.abstract) {
remove(parent.$children, vm)
}
// teardown watchers
if (vm._watcher) {
vm._watcher.teardown()
}
let i = vm._watchers.length
while (i--) {
vm._watchers[i].teardown()
}
// remove reference from data ob
// frozen object may not have observer.
if (vm._data.__ob__) {
vm._data.__ob__.vmCount--
}
// call the last hook...
vm._isDestroyed = true
// invoke destroy hooks on current rendered tree
vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null)
// fire destroyed hook
callHook(vm, 'destroyed')
// turn off all instance listeners.
vm.$off()
// remove __vue__ reference
if (vm.$el) {
vm.$el.__vue__ = null
}
// release circular reference (#6759)
if (vm.$vnode) {
vm.$vnode.parent = null
}
} beforeDestroy 钩子函数的执行时机是在 $destroy 函数执行最开始的地方,接着执行了一系列的销毁动作,包括从 parent 的 $children 中删掉自身,删除 watcher,当前渲染的 VNode 执行销毁钩子函数等,执行完毕后再调用 destroy 钩子函数。
在 $destroy 的执行过程中,它又会执行 vm.__patch__(vm._vnode, null) 触发它子组件的销毁钩子函数,这样一层层的递归调用,所以 destroy 钩子函数执行顺序是先子后父,和 mounted 过程一样。
-
activated & deactivated
activated 和 deactivated 钩子函数是专门为 keep-alive 组件定制的钩子,activated是keep-alive 组件激活时调用。deactivated是keep-alive 组件停用时调用。它们定义在src/core/instance/lifecycle.js
export function activateChildComponent (vm: Component, direct?: boolean) {
if (direct) {
vm._directInactive = false
if (isInInactiveTree(vm)) {
return
}
} else if (vm._directInactive) {
return
}
if (vm._inactive || vm._inactive === null) {
vm._inactive = false
for (let i = 0; i < vm.$children.length; i++) {
activateChildComponent(vm.$children[i])
}
callHook(vm, 'activated')
}
}
export function deactivateChildComponent (vm: Component, direct?: boolean) {
if (direct) {
vm._directInactive = true
if (isInInactiveTree(vm)) {
return
}
}
if (!vm._inactive) {
vm._inactive = true
for (let i = 0; i < vm.$children.length; i++) {
deactivateChildComponent(vm.$children[i])
}
callHook(vm, 'deactivated')
}
}学习文档:https://ustbhuangyi.github.io/vue-analysis/components/lifecycle.html