首先举一个最简单的例子:
this.state={ a:1 } this.setState({ a:2 }) console.log(this.state.a)
//1
可以说setState()操作是一个异步,因为要将一段时间内的state改变压入栈,并最终执行一次,同时也是优化性能的一部份
但是:
定时器:
定时器中的setState,每次都会引起新的render,即使是同一个定时器中的多次setState,
因为定时器中的回调不属于react控制
原生事件:
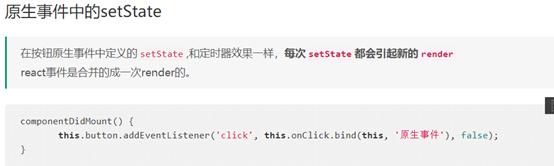

下面简单讲解一下源码的理解
入口:
ReactComponent.prototype.setState = function (partialState, callback) { // 将setState事务放入队列中 this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState); if (callback) { this.updater.enqueueCallback(this, callback, 'setState'); } };
partialState:部分state,传入enqueueSetState(),如果有回调函数,则调用enqueueCallback(),在更改后执行
enquenueSetState:
enqueueSetState: function (publicInstance, partialState) { // 先获取ReactComponent组件对象 var internalInstance = getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate(publicInstance, 'setState'); if (!internalInstance) { return; } // 如果_pendingStateQueue为空,则创建它。可以发现队列是数组形式实现的 var queue = internalInstance._pendingStateQueue || (internalInstance._pendingStateQueue = []); queue.push(partialState); // 将要更新的ReactComponent放入数组中 enqueueUpdate(internalInstance); }
通过getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate()获取到ReactComponent组件对象,
判断这个组件的state等待队列是否为空,为空则创建为空数组,并将state push进这个数组,
将要更新的组件传入enqueueUpdate()并执行
getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate
function getInternalInstanceReadyForUpdate(publicInstance, callerName) { // 从map取出ReactComponent组件,还记得mountComponent时把ReactElement作为key,将ReactComponent存入了map中了吧,ReactComponent是React组件的核心,包含各种状态,数据和操作方法。而ReactElement则仅仅是一个数据类。 var internalInstance = ReactInstanceMap.get(publicInstance); if (!internalInstance) { return null; } return internalInstance; }
publicInstance:enqueueSetState方法传入的this,指当前组件实例
从map取出ReactComponent组件,还记得mountComponent时把ReactElement作为key,
将ReactComponent存入了map中了吧,ReactComponent是React组件的核心,包含各种状态,数据和操作方法。而ReactElement则仅仅是一个数据类
注:(virtual DOM 就是由一个个的React element 组成。React element, 是由React 库提供的createElement 函数创建而来)
enqueueUpdate:
function enqueueUpdate(component) { ensureInjected(); // 如果不是正处于创建或更新组件阶段,则处理update事务 if (!batchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates) { batchingStrategy.batchedUpdates(enqueueUpdate, component); return; } // 如果正在创建或更新组件,则暂且先不处理update,只是将组件放在dirtyComponents数组中 dirtyComponents.push(component); }
基本逻辑:如果现在是正在创建或者更新组件的阶段,则把组件放入dirtyComponents数组中,并不先update,否则就进行batchedUpdates()
enqueueUpdate包含了React避免重复render的逻辑。mountComponent和updateComponent方法在执行的最开始,会调用到batchedUpdates进行批处理更新,此时会将isBatchingUpdates设置为true,也就是将状态标记为现在正处于更新阶段了
。(——可以不看
之后React以事务的方式处理组件update,事务处理完后会调用wrapper.close(), 而TRANSACTION_WRAPPERS中包含了RESET_BATCHED_UPDATES这个wrapper,故最终会调用RESET_BATCHED_UPDATES.close(),
——)
它最终会将isBatchingUpdates设置为false。这个过程比较麻烦,想更清晰的了解的话,建议自行分析源码。
故getInitialState,componentWillMount, render,componentWillUpdate 中setState都不会引起updateComponent。但在componentDidMount和componentDidUpdate中则会。
batchedUpdates:
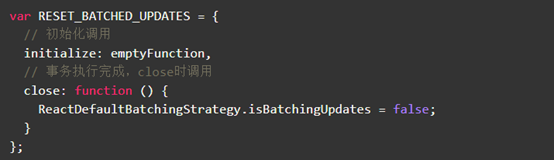
batchedUpdates: function (callback, a, b, c, d, e) { var alreadyBatchingUpdates = ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates; // 批处理最开始时,将isBatchingUpdates设为true,表明正在更新 ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates = true; // The code is written this way to avoid extra allocations if (alreadyBatchingUpdates) { callback(a, b, c, d, e); } else { // 以事务的方式处理updates,后面详细分析transaction transaction.perform(callback, null, a, b, c, d, e); } } var RESET_BATCHED_UPDATES = { initialize: emptyFunction, close: function () { // 事务批更新处理结束时,将isBatchingUpdates设为了false ReactDefaultBatchingStrategy.isBatchingUpdates = false; } }; var TRANSACTION_WRAPPERS = [FLUSH_BATCHED_UPDATES, RESET_BATCHED_UPDATES];
设置两个wrapper,
RESET_BATCHED_UPDATES设置isBatchingUpdates,
FLUSH_BATCHED_UPDATES会在一个transaction的close阶段运行runBatchedUpdates,从而执行update
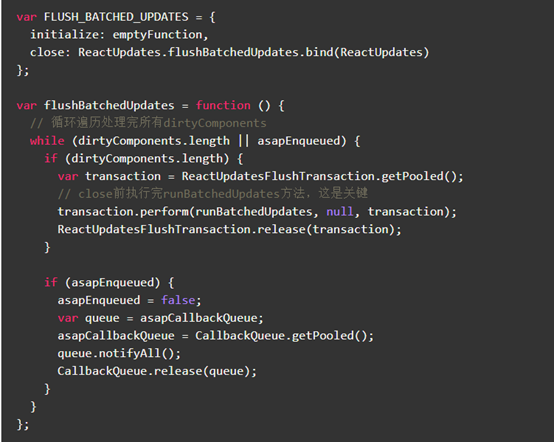
事务transaction
不详述,百度很多文章,大体思路:
- 初始化:事务初始化阶段没有注册方法,故无方法要执行
- 运行:执行setSate时传入的callback方法,一般不会传callback参数
- 结束:更新isBatchingUpdates为false,并执行FLUSH_BATCHED_UPDATES这个wrapper中的close方法
runBatchedUpdates:
function runBatchedUpdates(transaction) { var len = transaction.dirtyComponentsLength; dirtyComponents.sort(mountOrderComparator); for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) { // dirtyComponents中取出一个component var component = dirtyComponents[i]; // 取出dirtyComponent中的未执行的callback,下面就准备执行它了 var callbacks = component._pendingCallbacks; component._pendingCallbacks = null; var markerName; if (ReactFeatureFlags.logTopLevelRenders) { var namedComponent = component; if (component._currentElement.props === component._renderedComponent._currentElement) { namedComponent = component._renderedComponent; } } // 执行updateComponent ReactReconciler.performUpdateIfNecessary(component, transaction.reconcileTransaction); // 执行dirtyComponent中之前未执行的callback if (callbacks) { for (var j = 0; j < callbacks.length; j++) { transaction.callbackQueue.enqueue(callbacks[j], component.getPublicInstance()); } } } }
runBatchedUpdates循环遍历dirtyComponents数组,主要干两件事。
首先执行performUpdateIfNecessary来刷新组件的view,
然后执行之前阻塞的callback。
下面来看performUpdateIfNecessary。
performUpdateIfNecessary: function (transaction) { if (this._pendingElement != null) { // receiveComponent会最终调用到updateComponent,从而刷新View ReactReconciler.receiveComponent(this, this._pendingElement, transaction, this._context); } if (this._pendingStateQueue !== null || this._pendingForceUpdate) { // 执行updateComponent,从而刷新View。这个流程在React生命周期中讲解过 this.updateComponent(transaction, this._currentElement, this._currentElement, this._context, this._context); } },
执行updateComponent进行状态更新,值得注意的是更新操作内会调用_processPendingState进行原有state的合并以及设置this._pendingStateQueue = null,这也就意味着dirtyComponents进入下一次循环时,执行performUpdateIfNecessary不会再去更新组件
总结:
setState流程还是很复杂的,设计也很精巧,避免了重复无谓的刷新组件。它的主要流程如下
- enqueueSetState将state放入队列中,并调用enqueueUpdate处理要更新的Component
- 如果组件当前正处于update事务中,则先将Component存入dirtyComponent中。否则调用batchedUpdates处理。
- batchedUpdates发起一次transaction.perform()事务
- 开始执行事务初始化,运行,结束三个阶段
- 初始化:事务初始化阶段没有注册方法,故无方法要执行
- 运行:执行setSate时传入的callback方法,一般不会传callback参数
- 结束:更新isBatchingUpdates为false,并执行FLUSH_BATCHED_UPDATES这个wrapper中的close方法
- FLUSH_BATCHED_UPDATES在close阶段,会循环遍历所有的dirtyComponents,调用updateComponent刷新组件,并执行它的pendingCallbacks, 也就是setState中设置的callback。
推荐完整地址:https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/72329?t=t1