一、概述(Exception)
二、异常分类
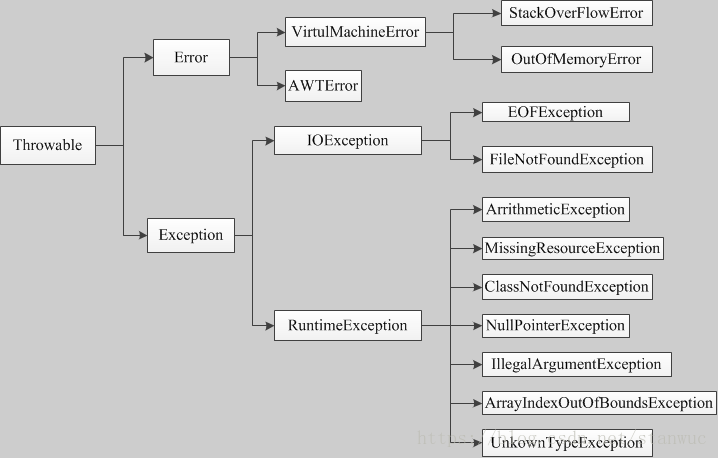
1、继承结构
说明:
- ClassNotFoundException 不属于运行时异常
2、error
(1)Error与Exception的区别
- 我开着车走在路上,一头猪冲在路中间,我刹车,这叫一个异常。
- 我开着车在路上,发动机坏了,我停车,这叫错误,系统处于不可恢复的崩溃状态。
3、exception
(1)RuntimeException
- 合适的异常处理器:异常处理器所能处理的异常类型与方法抛出的异常类型相符;
- 运行时系统从发生异常的方法开始,向上回溯检查直接或间接调用过此方法的方法,寻找合适的异常处理器,最后没找到就抛给 JVM 来处理;
- RuntimeException的异常,如被 0 除、数组下标越界、空指针等,可以直接交给系统处理,可以使用异常处理机制来处理,最好的是提高编程逻辑来避免这些异常;
- 几种常见运行时异常的处理
1、NullPointerException异常:增加非空判断;
2、ClassCastException异常:先用 instanceof 判断;
3、ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException异常:增加边界判断(a < arr.length);
4、NumberFormatException异常:先用正则判断再转
String str = "1234abcf";
Pattern p = Pattern.compile("^\\d+$");
Matcher m = p.matcher(str);
if (m.matches()) { // 如果str匹配代表数字的正则表达式,才会转换
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(str));
}(2)CheckedException
- 所有不是RuntimeException的异常,统称为Checked Exception,如IOException、SQLException、自定义异常等。
- 这类异常在编译时就必须做出处理,否则无法通过编译。
三、异常处理
1、捕获异常
(1)格式
try{
// 程序代码
}catch(异常类型1 异常的变量名1){
// 程序代码
}catch(异常类型2 异常的变量名2){
// 程序代码
}finally{
// 程序代码
}
(2) 说明
- catch 不能独立于 try 存在
- 在 try/catch 后面添加 finally 块并非强制性要求的
- try 代码后不能既没 catch 块也没 finally 块
- try, catch, finally 块之间不能添加任何代码
- 其中多catch子类在前,父类在后
- 即使try和catch块中存在return语句,finally语句也会执行,执行顺序是执行完finally语句后再通过return退出
- finally 中通常是来关闭资源
- 当异常处理的代码执行结束以后,不会回到try语句去执行尚未执行的代码
(3)异常打印
- e.toString ()方法,显示异常的类名和产生异常的原因
- e.getMessage()方法,只显示产生异常的原因,但不显示类名
- e.printStackTrace()方法,用来跟踪异常事件发生时堆栈的内容
(4)练习代码
public class Test8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader reader = null;
try {
reader = new FileReader("d:/a.txt");
char c = (char) reader.read();
char c2 = (char) reader.read();
System.out.println("" + c + c2);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (reader != null) {
reader.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}2、声明异常
(1)方法中
public void deposit(double amount) throws RemoteException
{
throw new RemoteException();
}
(2)方法声明中
public void withdraw(double amount) throws RemoteException,
InsufficientFundsException
{
// Method implementation
}
(3)说明:一般在方法里抛出异常,方法声明上也抛,运行时异常除外,运行时异常不具有代码侵入性;
四、自定义异常
1、写一个 检查性异常类,则需要继承 Exception 类
2、写一个 运行时异常类,那么需要继承 RuntimeException 类
3、说明:
- 异常往往在高层处理;
- 不要进行小粒度的异常处理,应该将整个任务包装在一个try语句块中;