MultipartFile是springframe封装好的一个专门用于文件上传的接口,MultipartFile有一下几个抽象方法(直接copy的源码):
public interface MultipartFile {
/**
* Return the name of the parameter in the multipart form.
* @return the name of the parameter (never {@code null} or empty)
*/
String getName();
/**
* Return the original filename in the client's filesystem.
* <p>This may contain path information depending on the browser used,
* but it typically will not with any other than Opera.
* @return the original filename, or the empty String if no file
* has been chosen in the multipart form, or {@code null}
* if not defined or not available
*/
String getOriginalFilename();
/**
* Return the content type of the file.
* @return the content type, or {@code null} if not defined
* (or no file has been chosen in the multipart form)
*/
String getContentType();
/**
* Return whether the uploaded file is empty, that is, either no file has
* been chosen in the multipart form or the chosen file has no content.
*/
boolean isEmpty();
/**
* Return the size of the file in bytes.
* @return the size of the file, or 0 if empty
*/
long getSize();
/**
* Return the contents of the file as an array of bytes.
* @return the contents of the file as bytes, or an empty byte array if empty
* @throws IOException in case of access errors (if the temporary store fails)
*/
byte[] getBytes() throws IOException;
/**
* Return an InputStream to read the contents of the file from.
* The user is responsible for closing the stream.
* @return the contents of the file as stream, or an empty stream if empty
* @throws IOException in case of access errors (if the temporary store fails)
*/
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
/**
* Transfer the received file to the given destination file.
* <p>This may either move the file in the filesystem, copy the file in the
* filesystem, or save memory-held contents to the destination file.
* If the destination file already exists, it will be deleted first.
* <p>If the file has been moved in the filesystem, this operation cannot
* be invoked again. Therefore, call this method just once to be able to
* work with any storage mechanism.
* @param dest the destination file
* @throws IOException in case of reading or writing errors
* @throws IllegalStateException if the file has already been moved
* in the filesystem and is not available anymore for another transfer
*/
void transferTo(File dest) throws IOException, IllegalStateException;
}看下接口的实现类:
有两个实现
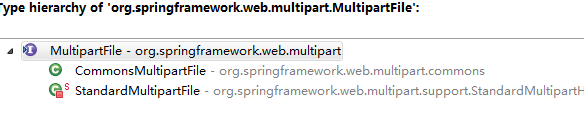
commons:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2012 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.multipart.commons;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileUploadException;
import org.apache.commons.fileupload.disk.DiskFileItem;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
/**
* MultipartFile implementation for Jakarta Commons FileUpload.
*
* @author Trevor D. Cook
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 29.09.2003
* @see CommonsMultipartResolver
*/
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class CommonsMultipartFile implements MultipartFile, Serializable {
protected static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(CommonsMultipartFile.class);
private final FileItem fileItem;
private final long size;
/**
* Create an instance wrapping the given FileItem.
* @param fileItem the FileItem to wrap
*/
public CommonsMultipartFile(FileItem fileItem) {
this.fileItem = fileItem;
this.size = this.fileItem.getSize();
}
/**
* Return the underlying {@code org.apache.commons.fileupload.FileItem}
* instance. There is hardly any need to access this.
*/
public final FileItem getFileItem() {
return this.fileItem;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.fileItem.getFieldName();
}
@Override
public String getOriginalFilename() {
String filename = this.fileItem.getName();
if (filename == null) {
// Should never happen.
return "";
}
// check for Unix-style path
int pos = filename.lastIndexOf("/");
if (pos == -1) {
// check for Windows-style path
pos = filename.lastIndexOf("\\");
}
if (pos != -1) {
// any sort of path separator found
return filename.substring(pos + 1);
}
else {
// plain name
return filename;
}
}
@Override
public String getContentType() {
return this.fileItem.getContentType();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (this.size == 0);
}
@Override
public long getSize() {
return this.size;
}
@Override
public byte[] getBytes() {
if (!isAvailable()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("File has been moved - cannot be read again");
}
byte[] bytes = this.fileItem.get();
return (bytes != null ? bytes : new byte[0]);
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
if (!isAvailable()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("File has been moved - cannot be read again");
}
InputStream inputStream = this.fileItem.getInputStream();
return (inputStream != null ? inputStream : new ByteArrayInputStream(new byte[0]));
}
@Override
public void transferTo(File dest) throws IOException, IllegalStateException {
if (!isAvailable()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("File has already been moved - cannot be transferred again");
}
if (dest.exists() && !dest.delete()) {
throw new IOException(
"Destination file [" + dest.getAbsolutePath() + "] already exists and could not be deleted");
}
try {
this.fileItem.write(dest);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String action = "transferred";
if (!this.fileItem.isInMemory()) {
action = isAvailable() ? "copied" : "moved";
}
logger.debug("Multipart file '" + getName() + "' with original filename [" +
getOriginalFilename() + "], stored " + getStorageDescription() + ": " +
action + " to [" + dest.getAbsolutePath() + "]");
}
}
catch (FileUploadException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex.getMessage());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error("Could not transfer to file", ex);
throw new IOException("Could not transfer to file: " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
/**
* Determine whether the multipart content is still available.
* If a temporary file has been moved, the content is no longer available.
*/
protected boolean isAvailable() {
// If in memory, it's available.
if (this.fileItem.isInMemory()) {
return true;
}
// Check actual existence of temporary file.
if (this.fileItem instanceof DiskFileItem) {
return ((DiskFileItem) this.fileItem).getStoreLocation().exists();
}
// Check whether current file size is different than original one.
return (this.fileItem.getSize() == this.size);
}
/**
* Return a description for the storage location of the multipart content.
* Tries to be as specific as possible: mentions the file location in case
* of a temporary file.
*/
public String getStorageDescription() {
if (this.fileItem.isInMemory()) {
return "in memory";
}
else if (this.fileItem instanceof DiskFileItem) {
return "at [" + ((DiskFileItem) this.fileItem).getStoreLocation().getAbsolutePath() + "]";
}
else {
return "on disk";
}
}
}
standard:
/*
* Copyright 2002-2014 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.web.multipart.support;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.Part;
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.util.FileCopyUtils;
import org.springframework.util.LinkedMultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.util.MultiValueMap;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartException;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;
/**
* Spring MultipartHttpServletRequest adapter, wrapping a Servlet 3.0 HttpServletRequest
* and its Part objects. Parameters get exposed through the native request's getParameter
* methods - without any custom processing on our side.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.1
*/
public class StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest extends AbstractMultipartHttpServletRequest {
private static final String CONTENT_DISPOSITION = "content-disposition";
private static final String FILENAME_KEY = "filename=";
private Set<String> multipartParameterNames;
/**
* Create a new StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest wrapper for the given request,
* immediately parsing the multipart content.
* @param request the servlet request to wrap
* @throws MultipartException if parsing failed
*/
public StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws MultipartException {
this(request, false);
}
/**
* Create a new StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest wrapper for the given request.
* @param request the servlet request to wrap
* @param lazyParsing whether multipart parsing should be triggered lazily on
* first access of multipart files or parameters
* @throws MultipartException if an immediate parsing attempt failed
*/
public StandardMultipartHttpServletRequest(HttpServletRequest request, boolean lazyParsing) throws MultipartException {
super(request);
if (!lazyParsing) {
parseRequest(request);
}
}
private void parseRequest(HttpServletRequest request) {
try {
Collection<Part> parts = request.getParts();
this.multipartParameterNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>(parts.size());
MultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile> files = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String, MultipartFile>(parts.size());
for (Part part : parts) {
String filename = extractFilename(part.getHeader(CONTENT_DISPOSITION));
if (filename != null) {
files.add(part.getName(), new StandardMultipartFile(part, filename));
}
else {
this.multipartParameterNames.add(part.getName());
}
}
setMultipartFiles(files);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new MultipartException("Could not parse multipart servlet request", ex);
}
}
private String extractFilename(String contentDisposition) {
if (contentDisposition == null) {
return null;
}
// TODO: can only handle the typical case at the moment
int startIndex = contentDisposition.indexOf(FILENAME_KEY);
if (startIndex == -1) {
return null;
}
String filename = contentDisposition.substring(startIndex + FILENAME_KEY.length());
if (filename.startsWith("\"")) {
int endIndex = filename.indexOf("\"", 1);
if (endIndex != -1) {
return filename.substring(1, endIndex);
}
}
else {
int endIndex = filename.indexOf(";");
if (endIndex != -1) {
return filename.substring(0, endIndex);
}
}
return filename;
}
@Override
protected void initializeMultipart() {
parseRequest(getRequest());
}
@Override
public Enumeration<String> getParameterNames() {
if (this.multipartParameterNames == null) {
initializeMultipart();
}
if (this.multipartParameterNames.isEmpty()) {
return super.getParameterNames();
}
// Servlet 3.0 getParameterNames() not guaranteed to include multipart form items
// (e.g. on WebLogic 12) -> need to merge them here to be on the safe side
Set<String> paramNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>();
Enumeration<String> paramEnum = super.getParameterNames();
while (paramEnum.hasMoreElements()) {
paramNames.add(paramEnum.nextElement());
}
paramNames.addAll(this.multipartParameterNames);
return Collections.enumeration(paramNames);
}
@Override
public Map<String, String[]> getParameterMap() {
if (this.multipartParameterNames == null) {
initializeMultipart();
}
if (this.multipartParameterNames.isEmpty()) {
return super.getParameterMap();
}
// Servlet 3.0 getParameterMap() not guaranteed to include multipart form items
// (e.g. on WebLogic 12) -> need to merge them here to be on the safe side
Map<String, String[]> paramMap = new LinkedHashMap<String, String[]>();
paramMap.putAll(super.getParameterMap());
for (String paramName : this.multipartParameterNames) {
if (!paramMap.containsKey(paramName)) {
paramMap.put(paramName, getParameterValues(paramName));
}
}
return paramMap;
}
@Override
public String getMultipartContentType(String paramOrFileName) {
try {
Part part = getPart(paramOrFileName);
return (part != null ? part.getContentType() : null);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new MultipartException("Could not access multipart servlet request", ex);
}
}
@Override
public HttpHeaders getMultipartHeaders(String paramOrFileName) {
try {
Part part = getPart(paramOrFileName);
if (part != null) {
HttpHeaders headers = new HttpHeaders();
for (String headerName : part.getHeaderNames()) {
headers.put(headerName, new ArrayList<String>(part.getHeaders(headerName)));
}
return headers;
}
else {
return null;
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new MultipartException("Could not access multipart servlet request", ex);
}
}
/**
* Spring MultipartFile adapter, wrapping a Servlet 3.0 Part object.
*/
private static class StandardMultipartFile implements MultipartFile {
private final Part part;
private final String filename;
public StandardMultipartFile(Part part, String filename) {
this.part = part;
this.filename = filename;
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return this.part.getName();
}
@Override
public String getOriginalFilename() {
return this.filename;
}
@Override
public String getContentType() {
return this.part.getContentType();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (this.part.getSize() == 0);
}
@Override
public long getSize() {
return this.part.getSize();
}
@Override
public byte[] getBytes() throws IOException {
return FileCopyUtils.copyToByteArray(this.part.getInputStream());
}
@Override
public InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException {
return this.part.getInputStream();
}
@Override
public void transferTo(File dest) throws IOException, IllegalStateException {
this.part.write(dest.getPath());
}
}
}
只看上面的方法,感觉有点抽象,做一个案例试一下:
案例(上传图片):
//这里用到了getOriginalFilename()方法,为了获取文件名
String fileName=uploadFile.getOriginalFilename();
String fileType=fileName.substring(fileName.lastIndexOf("."));
if (! fileType.matches("^.(jpg|png|tif)$")) {
//这里的error=1时,表示操作不正常
result.setError(1);
return result;
}
try {
//这里用到了getInputStream()方法,为了将文件转换成流
//判断是否文件为恶意文件
BufferedImage bufferedImage=ImageIO.read(uploadFile.getInputStream());
int height=bufferedImage.getHeight();
int width=bufferedImage.getWidth();
if (width==0||height==0) {
//这里的error=1时,表示操作不正常
result.setError(1);
return result;
}
//这里用到了transferTo()方法,进行写盘操作
//这里的path需要自己设定,这里我就没有写,只是随便写的path代表路径
uploadFile.transferTo(path);
return result;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}