版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/www851903307/article/details/82314536
一、基本概念
1、关系图:
public class LinkedList<E>
extends AbstractSequentialList<E>
implements List<E>, Deque<E>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable{
...
}实现了List和Deque,内部是一个双向链表
2、图解:
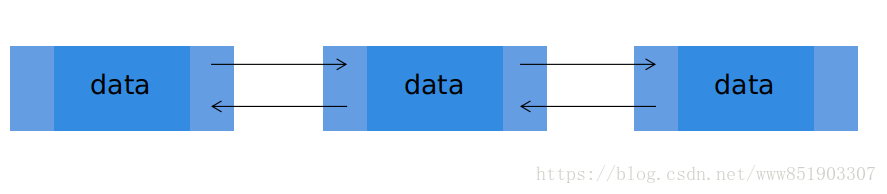
链表数据单元分为数据域和指针域,存储数据和指向下一个元素的位置,双向链表是指某元素的next指向下个元素, preview指向上个元素。
特点:
- 双向链表的实现
- 存放地址的空间不需要连续
- 元素保存了上一个元素和下一个元素的引用
- 首元素的preview和尾元素的next置null
- 元素有序,输出顺序和输入顺序一致
二、构造函数和成员变量:
1、成员变量:
// 记录当前链表的长度
transient int size = 0;
// 第一个节点
transient Node<E> first;
// 最后一个节点
transient Node<E> last;2、Node:
包括了当前数据,上个元素的引用、下个元素的引用
private static class Node<E> {
E item; //当前元素
Node<E> next; //下个元素
Node<E> prev; //上个元素
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
}3、构造函数:
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c);
}添加元素
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return addAll(size, c);
}
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
//转为数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0)
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) {
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
//将每个元素转为Node
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null);
if (pred == null)
//给首个元素赋值
first = newNode;
else
//next指向当前元素
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode;
}
if (succ == null) {
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
//size更新
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}三、添加元素:
1、常用方法
//队首添加元素
public void addFirst(E e) {
linkFirst(e);
}
//队尾添加元素
public void addLast(E e) {
linkLast(e);
}
//添加到队尾
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}
//添加到某个位置
public void add(int index, E element) {
checkPositionIndex(index);
if (index == size)
linkLast(element);
else
linkBefore(element, node(index));
}具体实现都是通过linkFirst、linkLast、linkBefore这三个方法。
2、在队首添加元素
private void linkFirst(E e) {
final Node<E> f = first;
//创建一个新的节点,next指向之前的first节点
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(null, e, f);
//将first节点指向新建的节点
first = newNode;
if (f == null)
last = newNode;
else
//把原链表的preview指向现在的first节点
f.prev = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}3、在某个节点前添加元素:
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) {
// 记录某节点的preview的指向
final Node<E> pred = succ.prev;
// 创建需要被添加的元素
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ);
// 某节点的preview指向新元素
succ.prev = newNode;
if (pred == null)
first = newNode;
else
//之前的next节点指向被添加的元素
pred.next = newNode;
size++;
modCount++;
}四、删除元素
1、常用方法:
//移除某位置元素
public E remove(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index);
return unlink(node(index));
}
//移除队首元素
public E remove() {
return removeFirst();
}
//移除队首元素
public E pop() {
return removeFirst();
}
//移除队首元素
public E removeFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkFirst(f);
}
//移除队尾元素
public E removeLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return unlinkLast(l);
}具体实现通过unlinkFirst、unlink、unlinkLast三个方法。
2、删除首位的元素
private E unlinkFirst(Node<E> f) {
final E element = f.item;
final Node<E> next = f.next;
//首位置空
f.item = null;
f.next = null; // help GC
//下个元素置为首位
first = next;
if (next == null)
last = null;
else
next.prev = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}3、删除某元素
E unlink(Node<E> x) {
final E element = x.item;
//获取当前元素的next和prview元素
final Node<E> next = x.next;
final Node<E> prev = x.prev;
//上个元素的next指向下个元素
if (prev == null) {
first = next;
} else {
prev.next = next;
x.prev = null;
}
//下一个元素的preview指向上个元素
if (next == null) {
last = prev;
} else {
next.prev = prev;
x.next = null;
}
x.item = null;
size--;
modCount++;
return element;
}五、获取元素:
1、常用方法:
//获取队首元素
public E getFirst() {
final Node<E> f = first;
if (f == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return f.item;
}
//获取队尾元素
public E getLast() {
final Node<E> l = last;
if (l == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return l.item;
}2、获取某个位置的元素
public E get(int index) {
//检查索引的合法性
checkElementIndex(index);
return node(index).item;
}
Node<E> node(int index) {
//判断索引所在位置,在中心位置的前面还是后面
//如果在前面,就在首位向后查询
if (index < (size >> 1)) {
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
//在队尾向前查询
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}3、总结:
- 在队尾和队首插入和删除数据非常方便
- 在中间位置根据索引去增删或者查询都是需要进行折半遍历,效率不高。