1. RDF 入门
- RDF(Resource Description Framework)是由W3C规定的,描述资源(resource)的数据模型(data model),;
- RDF 使用Web标识符来标识事物,并通过属性和属性值来描述资源;
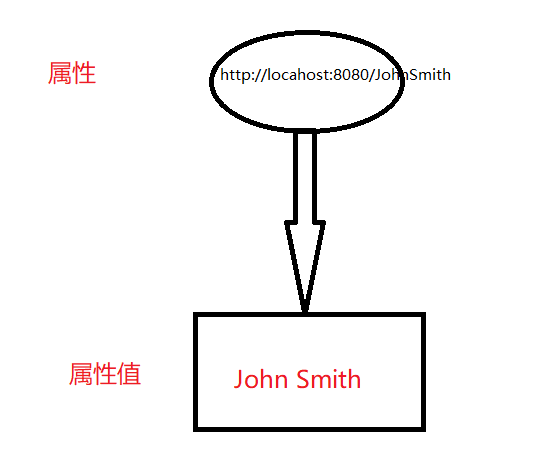
- 资源:可拥有URI的任何事物,如:http://localhost:8080/JohnSmith
- 属性:拥有名称的资源,如:人的全名(FullName),职位等;
- 属性值:某个属性的值,如:JohnSmith;
/**
* 使用Jena表示上图
*/
// 定义
static String personURI = "http://localhost:8080/JohnSmith";
static String fullName = "John Smith";
// 创建空的Model, 即图(Graph)
Model model = ModelFactory.createDefaultModel();
// 创建资源
Resource johnSmith = model.createResource(personURI);
// 添加属性
johnSmith.addProperty(VCARD.FN, fullName);
/**
* 或者
*/
Resource johnSmith = model.createResource(personURI)
.addProperty(VCARD.FN, fullName);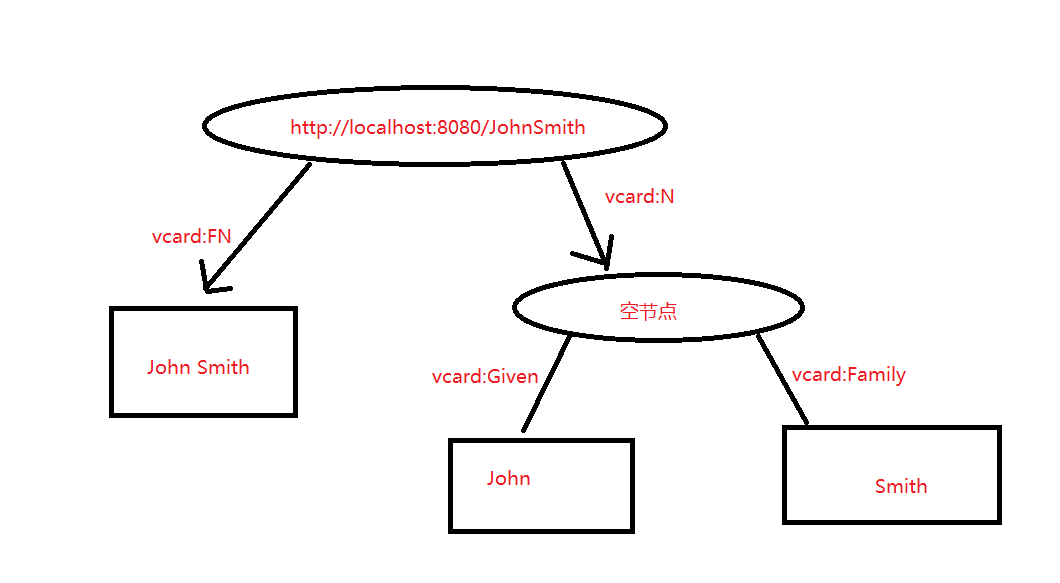
/**
* 更加复杂的图形表示(资源表示中存在空节点)
*/
public class Tutorial2{
public static void main(String[] args){
String personURI = "http://localhost:8080/JohnSmith";
String givenName = "John";
String familyName = "Smith";
String fullName = givenName + " " + familyName;
// 创建Model
Model model = ModelFactory.createDefaultModel();
// 创建Resource,并添加属性
Resource johnSmith = model.createResource(personURI)
.addProperty(VCARD.FN, fullName)
.addProperty(VCARD.N,
model.createResource()
.addProperty(VCARD.Given, givenName)
.addProperty(VCARD.Family, familyName));
}
}2. RDF Statements(RDF 陈述)
- 资源,属性和属性值的组合可形成一个陈述;
- 陈述(Statement)包括:
- subject(主体)
- predicate(谓语)
- object(客体)
/**
* 使用Statement,读取RDF内容(使用上面的代码)
*/
StmtIterator iter = model.listStatements();
while(iter.hasNext()){
// 打印 subject,predicate, object
Statement stmt = iter.nextStatement();
Resource subject = stmt.getSubject();
Property predicate = stmt.getPredicate();
RDFNode object = stmt.getObject();
System.out.print(subject.toString());
System.out.print(" " + predicate.toString() + " ");
if(object instanceof Resource){
// 如果为 资源
System.out.print(object.toString());
} else {
// 如果为文本
System.out.print(" \"" + object.toString() + "\"");
}
System.out.println(" .");
}
// 上述代码,可以简写为: model.write(System.out, "N-TRIPLES");
### 输出结果:
735a32cc-f7a3-4be5-b70f-9689fcd5a4b4 http://www.w3.org/2001/vcard-rdf/3.0#Family "Smith" .
735a32cc-f7a3-4be5-b70f-9689fcd5a4b4 http://www.w3.org/2001/vcard-rdf/3.0#Given "John" .
http://localhost:8080/JohnSmith http://www.w3.org/2001/vcard-rdf/3.0#N 735a32cc-f7a3-4be5-b70f-9689fcd5a4b4 .
http://localhost:8080/JohnSmith http://www.w3.org/2001/vcard-rdf/3.0#FN "John Smith" .3. RDF 的写和读
/**
* RDF XML 格式输出
*/
public class Tutorial2{
public static void main(String[] args){
String personURI = "http://localhost:8080/JohnSmith";
String givenName = "John";
String familyName = "Smith";
String fullName = givenName + " " + familyName;
// 创建Model
Model model = ModelFactory.createDefaultModel();
// 创建Resource,并添加属性
Resource johnSmith = model.createResource(personURI)
.addProperty(VCARD.FN, fullName)
.addProperty(VCARD.N,
model.createResource()
.addProperty(VCARD.Given, givenName)
.addProperty(VCARD.Family, familyName));
// RDF xml 格式输出
model.write(System.out);
}
}
### 输出结果:
<rdf:RDF
xmlns:rdf="http://www.w3.org/1999/02/22-rdf-syntax-ns#"
xmlns:vcard="http://www.w3.org/2001/vcard-rdf/3.0#">
<rdf:Description rdf:about="http://localhost:8080/JohnSmith">
<vcard:N rdf:parseType="Resource">
<vcard:Family>Smith</vcard:Family>
<vcard:Given>John</vcard:Given>
</vcard:N>
<vcard:FN>John Smith</vcard:FN>
</rdf:Description>
</rdf:RDF>
/**
* 读取 RDF/XML 格式的文件
* 下载地址:http://jena.apache.org/tutorials/sparql_data/vc-db-1.rdf
*/
// 创建空Model
Model model = ModelFactory.createDefaultModel();
// 使用FileManager,获取输入流
String inputFileName = "";
InputStream in = FileManager.get().open(inputFileName);
if(in == null){
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"File: " + inputFileName + " not found.");
)
}
// 读取 RDF/XML 文件
model.read(in, null);
// 将读取的内容,输出到控制台
model.write(System.out);4. 操作Model
/**
* 获取Model中存储的信息(接上例)
*/
// 如果存在,直接返回;不存在,则新创建一个,再返回
String johnSmithURI = "http://somewhere/JohnSmith";
Resource vcard = model.getResource(johnSmithURI);
// 获取资源的属性(该属性可能为资源,或者文本)
// 若为资源:
Resource name = vcard.getProperty(VCARD.N)
.getResource();
// 若为文本:
String fullName = vcard.getProperty(VCARD.FN)
.getString();
// 如果存在多个同名属性:
StmtIterator iter = vcard.listProperties("属性名");
while(iter.hasNext()){
System.out.println(iter.nextStatement()
.getObject()
.toString());
}
参考资料: