【阶梯报告】洛谷P3391【模板】文艺平衡树 splay
题目链接在这里链接
最近在学习splay,终于做对了这道模版题,虽然不是很难的样子。但是我一开始并不会做,而且看完题解之后还打错一直打不对,调试了很久
下面是题目简述
现在给你一个长度为n的序列,序列元素初始为1,2,3...n,同时有m个操作,每个操作给定一个L和R,表示将[L,R]区间的数进行翻转。
输出:完成所有操作之后的序列(n,m≤100000)
首先,这道题用暴力是肯定超时的。但是既然连题目都提示用splay做这道题了,那么我们自然可以用splay做这道题。
首先我们想一下splay的树的性质。
性质
- 如果我们给每一个点添加一个键值,这个键值表示的是这个点在序列中的位置,那么我们对splay树进行中序遍历之后,得到的序列就是原来对应的序列。
- 对于splay树,无论是进行zip还是zap操作,都不会影响最终中序遍历的结果。因为zip和zap都是在保证二叉查找树的性质的前提下进行的。
- 假如我们splay(L-1,root),然后,splay(R+1,root->right_child),那么我们就会惊奇地发现,区间[L,R]内的所有点都在R+1这个结点的左子树种。
- 假如我们把任意一个结点的子树中的每一个结点的左右子树都换边,(包括自己)那么最终中序遍历的结果就是——除了被翻转的子树以外,其他所有点的中序遍历都没有变化,而子树中的所有节点(包括子树根节点)的中序遍历刚刚好反了过来。(你们可以自己画一个图试一下,或者说,如下图)
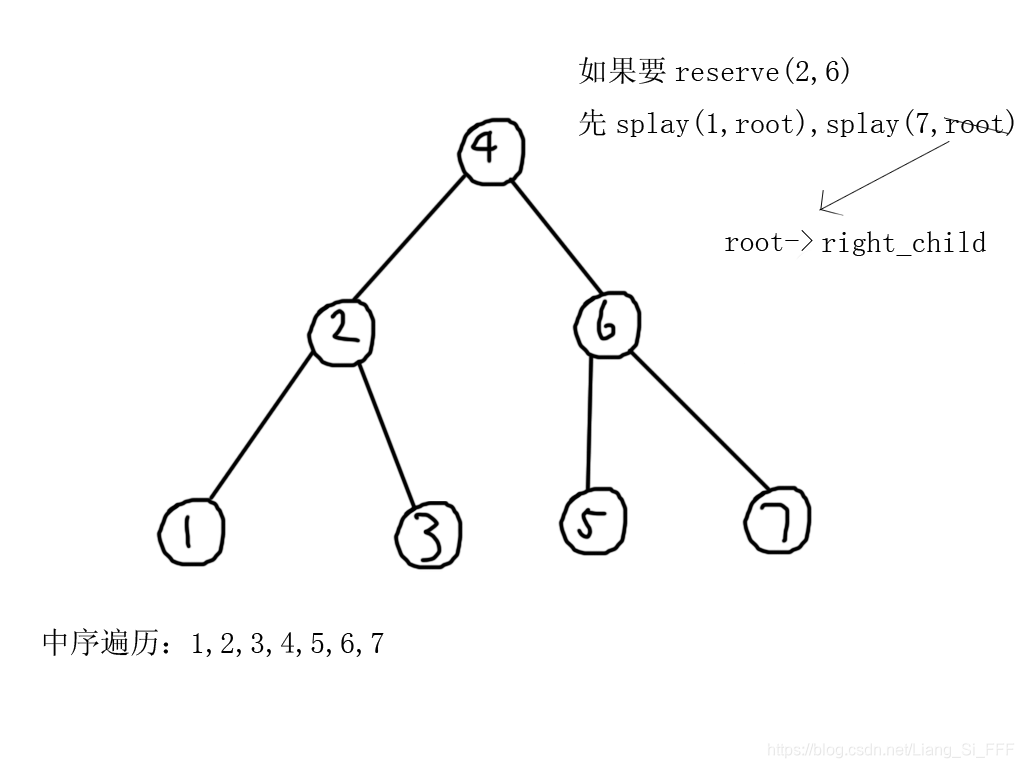
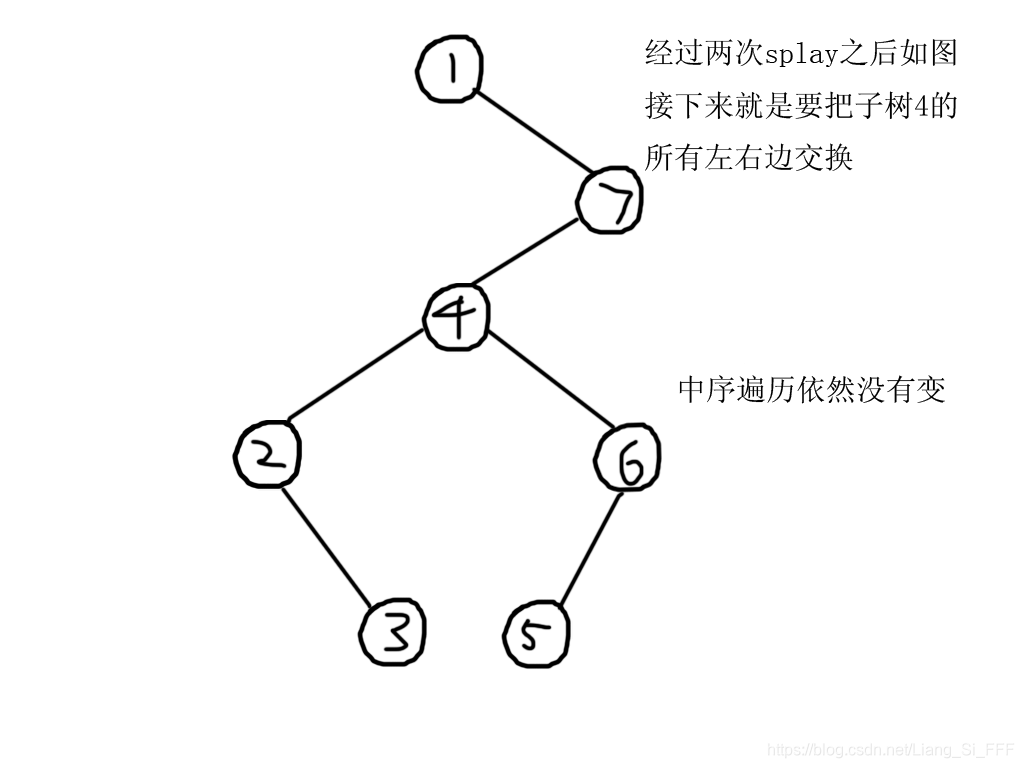
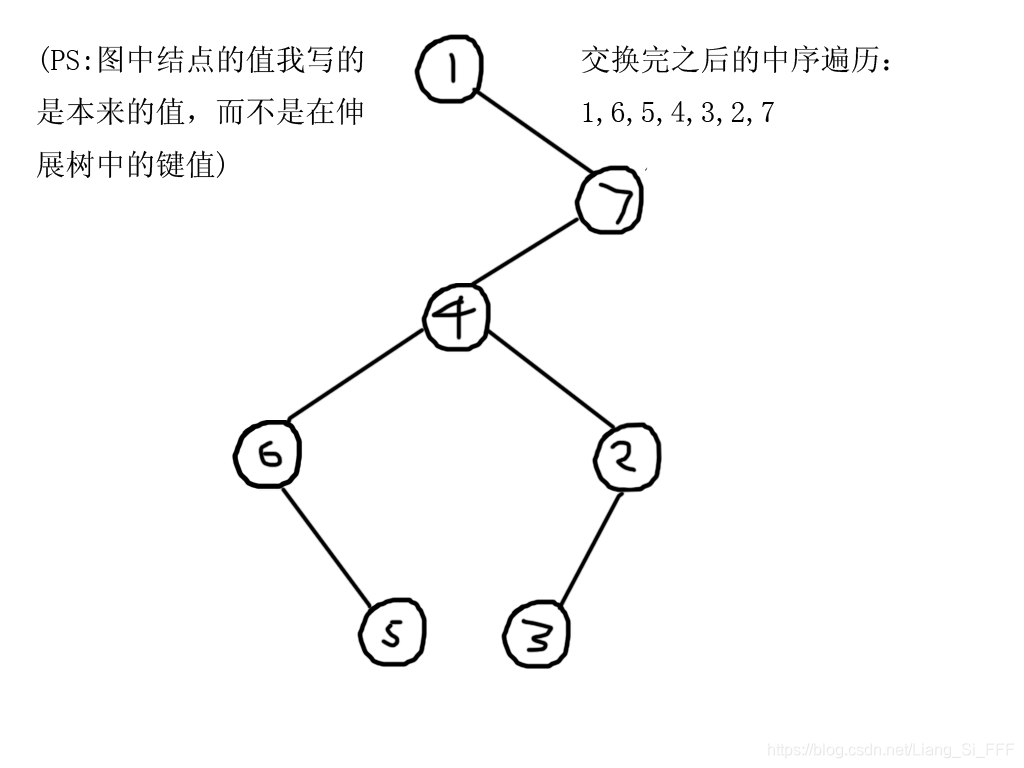
思路
第一种简陋的想法
- 以1,2,3,4…n为键值插入splay树(或者直接构建一棵平衡树就行,因为你已经知道会有哪些元素插入树中)。之后,我们对树的所有操作都不需要用到键值,直接根据zip和zap不会改变中序遍历的特性进行改变。
- 翻转区间的时候,先splay(l-1,root),splay(r+1,root->right_child),然后再把r+1这个结点的左子树的所有左右孩子交换即可。
虽然这么做确实可以做对题目,但是这样会有几个需要注意的地方。
1 . 假如要reserve(1,n),那么我们将会splay(0,root)和splay(n+1,root->left_child),但是树中没有0和n+1这两个结点。因此一开始的时候我们就应该加入INF和-INF,充当卫兵的作用。
2 . 交换子树中所有结点的速度实在是太慢了,和o(n)压根没有区别。这样根本就没有变快。
优化的方法
- 翻转树的时候不需要把整个子树都交换,只要采取线段树的懒标记的方法做一个标记即可。
- 标记完之后,假如等一下再标记同样的区间,只要异或一下1就可以了
- 假如要splay的点在已经翻转过的子树里面,那么我们到时候只要在寻找结点的过程中进行push_down就可以了。
- 在输出整棵splay树的时候,也注意一下push_down就可以了。
具体方法
- 把所有的元素都塞进splay里面。由于一开始就是有序的,所以你既可以一个一个地insert进去,也可以直接就构建一个十分平衡的splay树
- 对于每一个翻转操作,首先splay(l-1,root),splay(r+1,root->right_child),然后再把r+1的左子树打上标记即可
- 要点:每次在find一个结点的时候,一定要先push_down,然后再进行操作。
- 最后输出整棵树的时候也注意一下push_down
下面是我的代码,可能不是很看得明白。
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N=100010;
const int INF=100000000;
struct node
{
int lc,rc,fa,size,val,mark;//mark就是懒标记,val是本来的值,size是子树(包括自己)的大小
node()
{
lc=rc=fa=size=val=mark=0;
}
}tree[N];
int root=1,tot=1,FIRST=1;
void build(int,int,int,int);//直接用递归在刚开始的时候建立一棵比较平衡的树
void push_down(int);
void zip(int);//左旋
void zap(int);//右旋
void initailize();//放入INT和-INF作为卫兵
void splay(int,int);
int find(int);//用于寻找splay树中的第几大的数。毕竟在序列中排第k的数就是在splay中第k大的数
void reverse(int,int);
void print(int);//用递归输出整棵树
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
build(1,1,n,0);
initailize();
while(m--)
{
int l,r;
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
reverse(l+1,r+1);//由于有-INF的存在,所以翻转[l,r]区间的时候,其实是翻转[l+1,r+1]区间
}
print(root);
return 0;
}
void build(int x,int l,int r,int father)
{
tree[x].fa=father;
tree[x].size=1;
if(l==r)
{
tree[x].val=l;
return;
}
int mid=(l+r)/2;
tree[x].val=mid;
if(mid==l)
{
tree[x].rc=++tot;
build(tot,r,r,x);
tree[x].size+=tree[tree[x].rc].size;
}
else
{
tree[x].lc=++tot;
build(tot,l,mid-1,x);
tree[x].rc=++tot;
build(tot,mid+1,r,x);
tree[x].size+=tree[tree[x].lc].size+tree[tree[x].rc].size;
}
}
void initailize()
{
int p=root;
while(tree[p].lc!=0) tree[p].size++,p=tree[p].lc;
tree[p].size++;
tree[p].lc=++tot;
tree[tot].fa=p;
tree[tot].size=1;
tree[tot].val=-INF;
p=root;
while(tree[p].rc!=0) tree[p].size++,p=tree[p].rc;
tree[p].size++;
tree[p].rc=++tot;
tree[tot].fa=p;
tree[tot].size=1;
tree[tot].val=INF;
}
void inline push_down(int x)
{
if(tree[x].mark)
{
int L=tree[x].lc,R=tree[x].rc;
tree[L].mark^=1;
tree[R].mark^=1;
tree[x].mark=0;
tree[x].lc=R;
tree[x].rc=L;
}
}
void zip(int x)
{
int y=tree[x].fa;
tree[y].rc=tree[x].lc;
tree[x].lc=y;
tree[x].fa=tree[y].fa;
tree[y].fa=x;
if(tree[x].fa)
if(tree[tree[x].fa].lc==y)
tree[tree[x].fa].lc=x;
else tree[tree[x].fa].rc=x;
else root=x;
if(tree[y].rc)
tree[tree[y].rc].fa=y;
tree[y].size=tree[tree[y].lc].size+tree[tree[y].rc].size+1;
tree[x].size=tree[tree[x].lc].size+tree[tree[x].rc].size+1;
}
void zap(int x)
{
int y=tree[x].fa;
tree[y].lc=tree[x].rc;
tree[x].rc=y;
tree[x].fa=tree[y].fa;
tree[y].fa=x;
if(tree[x].fa)
if(tree[tree[x].fa].lc==y)
tree[tree[x].fa].lc=x;
else tree[tree[x].fa].rc=x;
else root=x;
if(tree[y].lc)
tree[tree[y].lc].fa=y;
tree[y].size=tree[tree[y].lc].size+tree[tree[y].rc].size+1;
tree[x].size=tree[tree[x].lc].size+tree[tree[x].rc].size+1;
}
void splay(int x,int aim)
{
aim=tree[aim].fa;
while(tree[x].fa!=aim)
{
int y=tree[x].fa;
int z=tree[y].fa;
if(z==aim)
if(tree[y].lc==x)
zap(x);
else zip(x);
else if(tree[z].lc==y&&tree[y].lc==x)
zap(x),zap(x);
else if(tree[z].rc==y&&tree[y].rc==x)
zip(x),zip(x);
else if(tree[z].lc==y)
zip(x),zap(x);
else zap(x),zip(x);
}
}
int find(int k)
{
int p=root;
while(1)
{
push_down(p);
if(tree[tree[p].lc].size>=k)
p=tree[p].lc;
else
{
k-=tree[tree[p].lc].size;
if(k==1) return p;
k-=1;
p=tree[p].rc;
}
}
}
void reverse(int l,int r)
{
int L=find(l-1);
splay(L,root);
int R=find(r+1);
splay(R,tree[L].rc);
tree[tree[R].lc].mark^=1;
}
void print(int x)
{
if(x==0) return;
push_down(x);
print(tree[x].lc);
if(tree[x].val!=INF&&tree[x].val!=-INF)
{
if(FIRST)
{
FIRST=0;
printf("%d",tree[x].val);
}
else printf(" %d",tree[x].val);
}
print(tree[x].rc);
}
对了,顺便说一下,为什么我看的资料书里面,不同的平衡树的zip是不一样的?有些是表示左旋,有些是表示右旋,zap也是一样,导致我现在都是按照自己的标准来了。
(对了,貌似CSDN不让发水贴,所以以后我有什么要说的就在文章的后面说一些吧)