Java提供了多种输入输出流用于对数据进行操作,其中管道流pipeStream是一种特殊的流,用于在不同线程间直接传送数据。
pis.read的时候,如果管道内没有数据,会阻塞。
public class PipeStreamMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PipedInputStream pis=new PipedInputStream();
PipedOutputStream pos=new PipedOutputStream();
pos.connect(pis);
TaskReader tr=new TaskReader(pis);
TaskWriter tw=new TaskWriter(pos);
tr.start();
tw.start();
}
static class TaskWriter extends Thread{
private final PipedOutputStream pos;
TaskWriter(PipedOutputStream pos){
this.pos=pos;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("writer开始写");
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pos.write(i);
}
System.out.println("写完了");
pos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
static class TaskReader extends Thread{
private final PipedInputStream pis;
TaskReader(PipedInputStream pis){
this.pis=pis;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("reader ");
byte[] bytes=new byte[5];
try {
int len=pis.read(bytes);
while (len!=-1){
System.out.println(bytes[0]+" "+bytes[1]+" "+bytes[2]+" ");
len=pis.read(bytes);
}
pis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
pos的write方法,会调用pis的receive方法
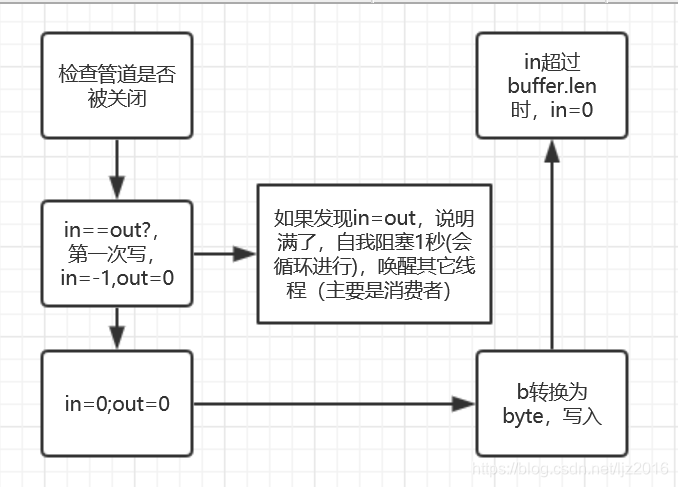
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
if (sink == null) {
throw new IOException("Pipe not connected");
}
sink.receive(b);
}
writeSide = Thread.currentThread();
pos的close方法,调用pis的receivedLast方法
public void close() throws IOException {
if (sink != null) {
sink.receivedLast();
}
}
pis的read方法:
首先会尝试读取一个字节,没读取到则阻塞并每隔1秒尝试读取一次,读取到了,再判断还有没有内容,如果有则读到buf中,直到没有可读内容或者buf读满了,则返回buf给用户。
public synchronized int read(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
if (b == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
} else if (off < 0 || len < 0 || len > b.length - off) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException();
} else if (len == 0) {
return 0;
}
/* possibly wait on the first character */
int c = read();
if (c < 0) {
return -1;
}
b[off] = (byte) c;
int rlen = 1;
while ((in >= 0) && (len > 1)) {
int available;
if (in > out) {
available = Math.min((buffer.length - out), (in - out));
} else {
available = buffer.length - out;
}
// A byte is read beforehand outside the loop
if (available > (len - 1)) {
available = len - 1;
}
System.arraycopy(buffer, out, b, off + rlen, available);
out += available;
rlen += available;
len -= available;
if (out >= buffer.length) {
out = 0;
}
if (in == out) {
/* now empty */
in = -1;
}
}
return rlen;
}
每次从buffer中读取一个字节,如果in==out,说明读取完了。
如果in<0,说明没有可读内容,会阻塞1秒(不断重复)。
public synchronized int read() throws IOException {
if (!connected) {
throw new IOException("Pipe not connected");
} else if (closedByReader) {
throw new IOException("Pipe closed");
} else if (writeSide != null && !writeSide.isAlive()
&& !closedByWriter && (in < 0)) {
throw new IOException("Write end dead");
}
readSide = Thread.currentThread();
int trials = 2;
while (in < 0) {
if (closedByWriter) {
/* closed by writer, return EOF */
return -1;
}
if ((writeSide != null) && (!writeSide.isAlive()) && (--trials < 0)) {
throw new IOException("Pipe broken");
}
/* might be a writer waiting */
notifyAll();
try {
wait(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException ex) {
throw new java.io.InterruptedIOException();
}
}
int ret = buffer[out++] & 0xFF;
if (out >= buffer.length) {
out = 0;
}
if (in == out) {
/* now empty */
in = -1;
}
return ret;
}