版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/lsf1025995457/article/details/52628030
Retrofit 是 Square 公司出品的 HTTP 请求库, 同时是 Square 是最早开源项目之一, Retrofit 是目前 Android 最流行的 Http Client 库之一, 目前版本是 Retrofit2.0 Beta4, 越来越多 Android 开发者开始使用这个请求库了
1、配置环境
在build.gradle文件中导入依赖包,一个为retrofit包,还有一个为Json转换包
compile 'com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:2.1.0'
compile 'com.squareup.retrofit2:converter-gson:2.1.0'在AndroidManifest.xml文件中加入网络请求权限
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />例子详细地址:
http://int.dpool.sina.com.cn/iplookup/iplookup.php?format=json&ip=218.4.255.255
public interface ApiService {
//获取详情数据
@GET("iplookup/iplookup.php?")
Call<LocationBean> getLocationData(@Query("format") String format, @Query("ip") String ip);
@POST("iplookup/iplookup.php?")
Call<LocationBean> postLocationData(@Query("format") String format, @Query("ip") String ip);
}@GET为Http中的get请求,后面请求的参数表示请求的路径但是不包含域名。
@Post为Http中的post请求,参数与get请求相同,在Post请求上添加@FormUrlEncoded注解,表示以表单的方式来提交参数。
@Query后面表示参数,前面是键后面参数为值。
3、定义实体类public class LocationBean {
/**
* ret : 1
* start : -1
* end : -1
* country : 中国
* province : 江苏
* city : 苏州
* district :
* isp :
* type :
* desc :
*/
private int ret;
private int start;
private int end;
private String country;
private String province;
private String city;
private String district;
private String isp;
private String type;
private String desc;
public int getRet() {
return ret;
}
public void setRet(int ret) {
this.ret = ret;
}
......
}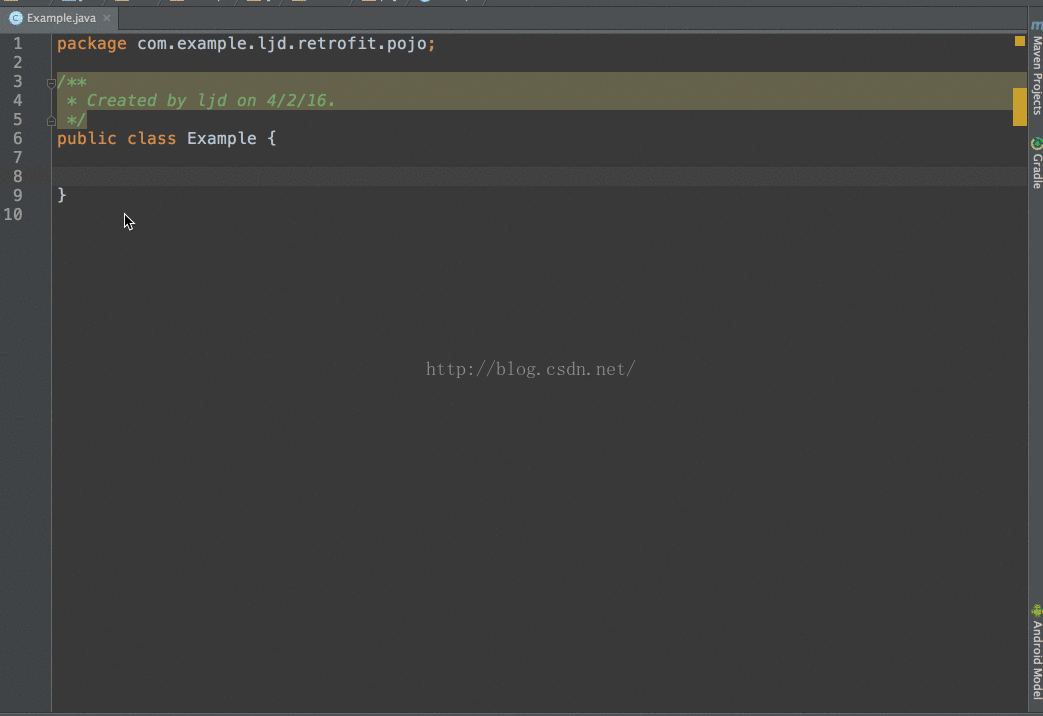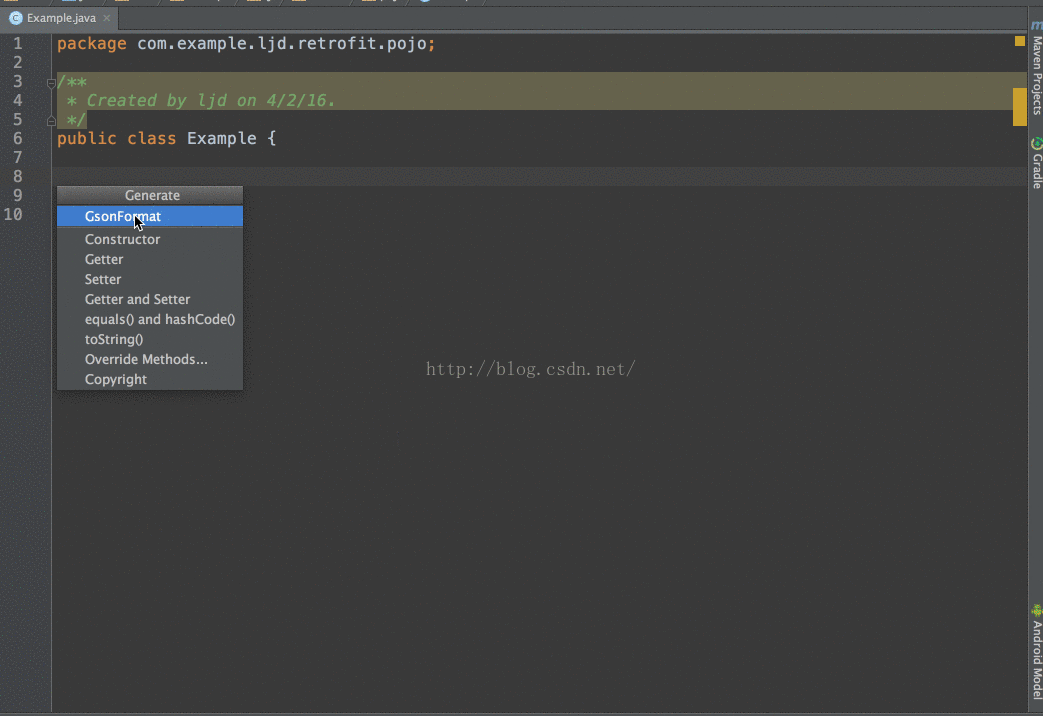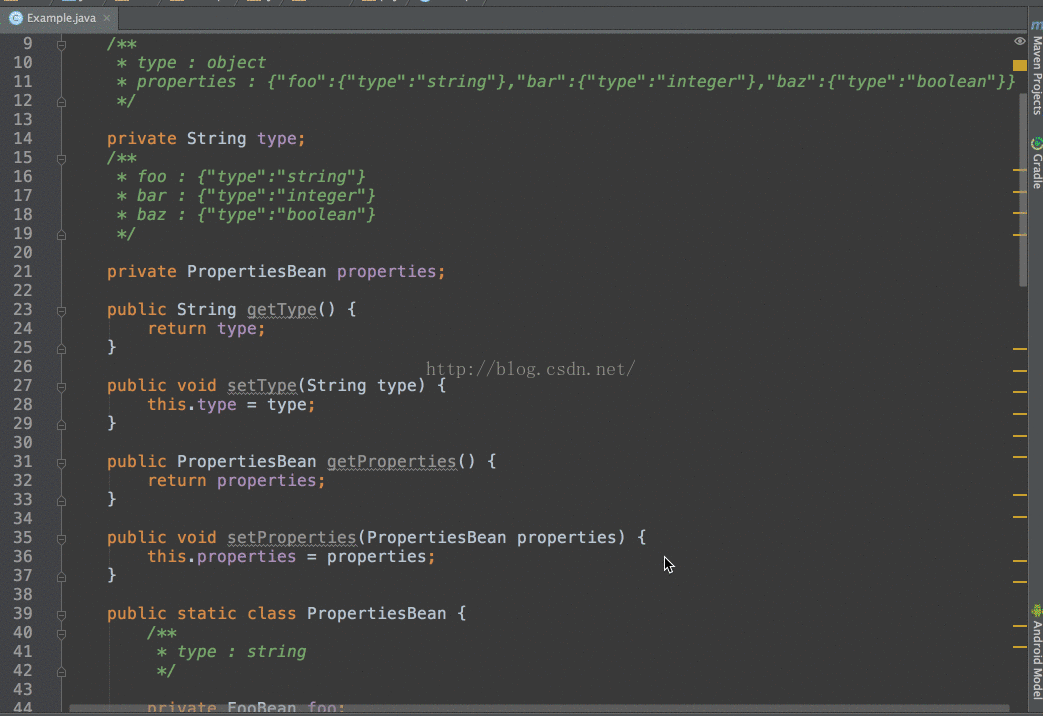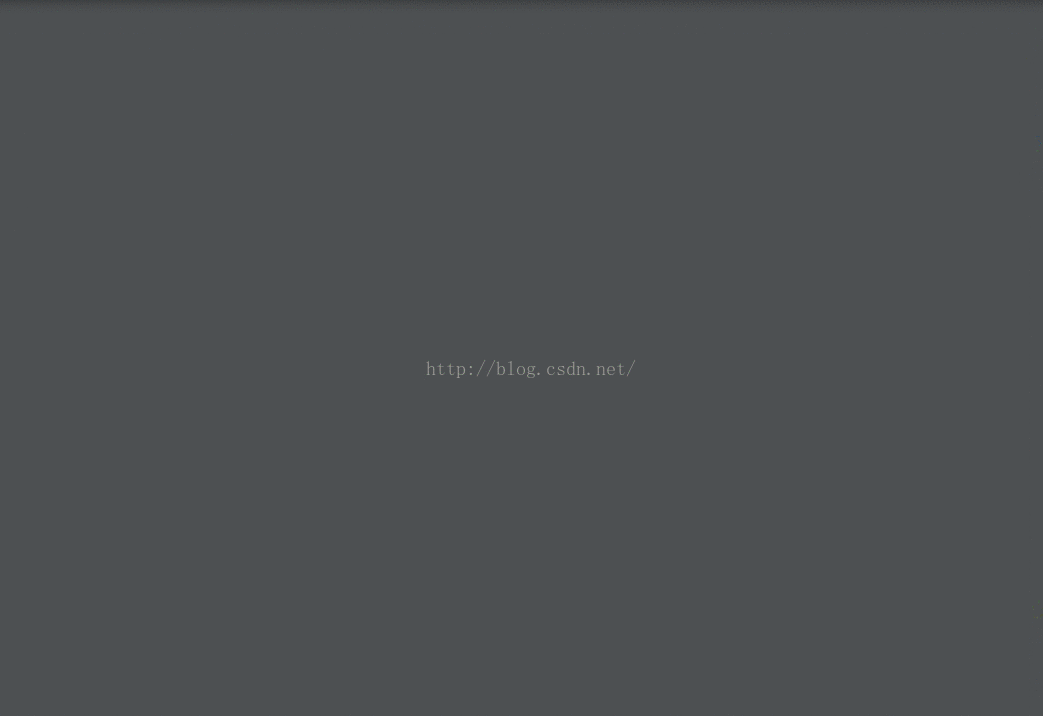
配置方法:
Android studio File->Settings..->Plugins–>Browse repositores..搜索GsonFormat
安装插件,重启android studio
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
//域名
.baseUrl("http://int.dpool.sina.com.cn/")
//增加返回值为Gson的支持(以实体类返回)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())的意思是构建一个返回值支持,后面可通过Call接收到实体类返回值。
4、网络请求
ApiService apiService = retrofit.create(ApiService.class);//这里采用的是Java的动态代理模式
Call<LocationBean> call = apiService.postLocationData("json", "218.4.255.255");//传入我们请求的键值对的值
call.enqueue(new Callback<LocationBean>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<LocationBean> call, Response<LocationBean> response) {
//服务器响应
LocationBean bean = response.body();
Log.e("TAG", "body.getMessage()===" + bean.getCity());
content.setText(bean.getCity());
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<LocationBean> call, Throwable t) {
//请求失败
}
});5、示例
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button btn;
private TextView content;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btn);
content = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.content);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
RetrofitTest();
}
});
}
private void RetrofitTest() {
Retrofit retrofit = new Retrofit.Builder()
//域名
.baseUrl("http://int.dpool.sina.com.cn/")
//增加返回值为Gson的支持(以实体类返回)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build();
ApiService apiService = retrofit.create(ApiService.class);//这里采用的是Java的动态代理模式
Call<LocationBean> call = apiService.postLocationData("json", "218.4.255.255");//传入我们请求的键值对的值
call.enqueue(new Callback<LocationBean>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(Call<LocationBean> call, Response<LocationBean> response) {
//服务器响应
LocationBean bean = response.body();
Log.e("TAG", "body.getMessage()===" + bean.getCity());
content.setText(bean.getCity());
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Call<LocationBean> call, Throwable t) {
//请求失败
}
});
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="按钮" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/content"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>