It was recycling day in Kekoland. To celebrate it Adil and Bera went to Central Perk where they can take bottles from the ground and put them into a recycling bin.
We can think Central Perk as coordinate plane. There are n bottles on the ground, the i-th bottle is located at position (xi, yi). Both Adil and Bera can carry only one bottle at once each.
For both Adil and Bera the process looks as follows:
- Choose to stop or to continue to collect bottles.
- If the choice was to continue then choose some bottle and walk towards it.
- Pick this bottle and walk to the recycling bin.
- Go to step 1.
Adil and Bera may move independently. They are allowed to pick bottles simultaneously, all bottles may be picked by any of the two, it's allowed that one of them stays still while the other one continues to pick bottles.
They want to organize the process such that the total distance they walk (the sum of distance walked by Adil and distance walked by Bera) is minimum possible. Of course, at the end all bottles should lie in the recycling bin.
First line of the input contains six integers ax, ay, bx, by, tx and ty (0 ≤ ax, ay, bx, by, tx, ty ≤ 109) — initial positions of Adil, Bera and recycling bin respectively.
The second line contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000) — the number of bottles on the ground.
Then follow n lines, each of them contains two integers xi and yi (0 ≤ xi, yi ≤ 109) — position of the i-th bottle.
It's guaranteed that positions of Adil, Bera, recycling bin and all bottles are distinct.
Print one real number — the minimum possible total distance Adil and Bera need to walk in order to put all bottles into recycling bin. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct if 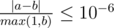 .
.
3 1 1 2 0 0
3
1 1
2 1
2 3
11.084259940083
5 0 4 2 2 0
5
5 2
3 0
5 5
3 5
3 3
33.121375178000
Consider the first sample.
Adil will use the following path:  .
.
Bera will use the following path:  .
.
Adil's path will be 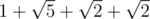 units long, while Bera's path will be
units long, while Bera's path will be 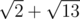 units long.
units long.
题意:
两个人捡瓶子,分别从原位置出发,捡到一个后返回垃圾箱处放垃圾,两人独立;
问最后距离之和的 min;
令最开始的距离为 sum = ∑2*dist [ i ];
两人可以同时到一个点,那么距离就是 sum - dist [ i ] + disa [ i ] + disb [ i ]-dist [ i ];
当然也可以一个人去,那么就是 sum - dist [ i ] + ( disa [ i ] || disb[ i ] );
每次维护一个最小值即可;
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstring>
#include<string>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<bitset>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<stack>
#include<functional>
#include<sstream>
//#include<cctype>
//#pragma GCC optimize("O3")
using namespace std;
#define maxn 200005
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define INF 9999999999
#define rdint(x) scanf("%d",&x)
#define rdllt(x) scanf("%lld",&x)
#define rdult(x) scanf("%lu",&x)
#define rdlf(x) scanf("%lf",&x)
#define rdstr(x) scanf("%s",x)
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef unsigned int U;
#define ms(x) memset((x),0,sizeof(x))
const long long int mod = 1e9 + 7;
#define Mod 1000000000
#define sq(x) (x)*(x)
#define eps 1e-3
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
#define pi acos(-1.0)
const int N = 1005;
#define REP(i,n) for(int i=0;i<(n);i++)
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
inline ll rd() {
ll x = 0;
char c = getchar();
bool f = false;
while (!isdigit(c)) {
if (c == '-') f = true;
c = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(c)) {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (c ^ 48);
c = getchar();
}
return f ? -x : x;
}
ll gcd(ll a, ll b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a%b);
}
ll sqr(ll x) { return x * x; }
/*ll ans;
ll exgcd(ll a, ll b, ll &x, ll &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1; y = 0; return a;
}
ans = exgcd(b, a%b, x, y);
ll t = x; x = y; y = t - a / b * y;
return ans;
}
*/
ll qpow(ll a, ll b, ll c) {
ll ans = 1;
a = a % c;
while (b) {
if (b % 2)ans = ans * a%c;
b /= 2; a = a * a%c;
}
return ans;
}
double ax, ay, bx, by, tx, ty;
struct node {
double x, y;
}indx[maxn];
double dis(double a, double b, double x, double y) {
return sqrt(1.0*(a - x)*(a - x) + 1.0*(b - y)*(b - y))*1.0;
}
double dist[maxn], disa[maxn], disb[maxn];
int main()
{
//ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
rdlf(ax); rdlf(ay); rdlf(bx); rdlf(by); rdlf(tx); rdlf(ty);
int n; rdint(n);
double ans = 0.0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
rdlf(indx[i].x), rdlf(indx[i].y);
dist[i] = 1.0*dis(indx[i].x, indx[i].y, tx, ty);
disa[i] = 1.0*dis(ax, ay, indx[i].x, indx[i].y);
disb[i] = 1.0*dis(bx, by, indx[i].x, indx[i].y);
ans += 2.0*dist[i];
}
double Max = INF * 1.0;
double Maxx = INF * 1.0;
int posa, posb;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (Max > disa[i] - dist[i]) {
Max =1.0* disa[i] - 1.0*dist[i]; posa = i;
}
if (Maxx > disb[i] - dist[i]) {
Maxx = 1.0*disb[i] - 1.0*dist[i]; posb = i;
}
}
// cout << posa << ' ' << posb << endl;
double sum = ans;
if (Maxx < 0 && Max < 0) {
if (posa != posb) {
sum = ans + Maxx * 1.0 + Max * 1.0;
}
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i != posa) {
sum = min(sum, ans - dist[posa] + disa[posa] - dist[i] + disb[i]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i != posb) {
sum = min(sum, ans - dist[posb] + disb[posb] - dist[i] + disa[i]);
}
}
}
}
else {
if (Max < Maxx) {
sum = ans + disa[posa] - dist[posa];
}
else {
sum = ans + disb[posb] - dist[posb];
}
}
printf("%.9lf\n", 1.0*sum);
return 0;
}