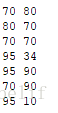经过前面一段时间的学习,简单的单词统计已经不能实现更多的需求,就连自带的一些函数方法等也是跟不上节奏了;加上前面一篇MapReduce的底层执行步骤的了解,今天学习自定义的排序、分组、分区相对也特别容易。
认为不好理解,先参考一下前面的一篇:https://blog.csdn.net/hu_belif/article/details/83007178
自定义排序
自定义的排序有许多许多,根据不同的业务需求,重写父类的方法即可。这里介绍两种常用的自定义排序:
一、自定义普通的正、倒排序
Mapper文件不需要太多的修改,首先创建一个自定义的排序类,继承一个Comparator(IntWritable.Comparator是子类),重写里面的compare方法即可。
eg:
Mymaper
package sort_2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, LongWritable,Text> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String values = value.toString();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(values);
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
/*
*MapReduce对自动对map阶段的输出数据进行分组、排序、归并等操作;
*所以我们这里需要把key与value值反过来传给reducer;
*然后在reducer阶段的时候再把位置调换回来即可。
*注意:这里的st.nextToken()的位置,第一次调用就能获取到第一个值,以此类推。
*/
key= new Text(st.nextToken());
value = new LongWritable(Long.parseLong(st.nextToken()));
context.write(value,key);
}
}
}
Reducer类
package sort_2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MySortReduce extends Reducer<LongWritable,Text, Text, LongWritable> {
/*让reduce默认分组排序*/
@Override
protected void reduce(LongWritable key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (Text value : values) {
context.write(new Text(value),key);
}
}
}
MySort类
package sort_2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
public class MySort extends IntWritable.Comparator {
@Override
public int compare(Object a, Object b) {
return super.compare(a, b);//结果正序
// return -super.compare(a, b);//结果倒序
}
@Override
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
return super.compare(b1, s1, l1, b2, s2, l2);//结果正序
// return -super.compare(b1, s1, l1, b2, s2, l2);//结果倒序
}
}
Runner类
这个就不粘出来了,就是正常的写,多加一句 job.setSortComparatorClass(MySort.class);
可以参考:https://blog.csdn.net/hu_belif/article/details/82595361里面的runner类写法多加一句话。
注意:重写后需要正序的话不需要动任何的参数,倒序的话把返回值改成倒数即可。最后需要在Runner中加上一句
job.setSortComparatorClass(MySort.class);//把自定义排序类的地址给job(很重要,不加等于没有排序)
二、自定义二次排序的正、倒排序
这个的话凭空想象就有些难理解,我们来用一道题讲解。
二次排序的需求说明:
按第一列进行正序排序,若有相同的数据按照第二列数据的大小正序排序;我们可以把这些数据看做一个一个的键值对或组,前后两个数是一体的,一个变位置前后一行一同换位置。
先来看代码演示:
Mapper类
package sort_2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/*
*让我们的自定义排序MySort作为Map阶段的最终输出
*/
public class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, MySort, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String values = value.toString();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(values);
while (st.hasMoreTokens()) {
MySort mySort = new MySort(Long.parseLong(st.nextToken()), Long.parseLong(st.nextToken()));//把需要排序的数据给我们的自定义排序
context.write(mySort, new LongWritable(Long.parseLong(mySort.secondNum.toString())));//输出到reducer
}
}
}
Reducer类
package sort_2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import javax.xml.soap.Text;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyReducer extends Reducer<MySort, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable> {
/**
* 接收到Map阶段传输的MySort类的key后,遍历values,输出最终结果
* 这里需要注意的是:输出的key值是一个longWritable型数据,不是一个MySort对象,需要取出对象中的属性
*/
@Override
protected void reduce(MySort key, Iterable<LongWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (LongWritable value : values) {
context.write(new LongWritable(key.firstNum),value);
}
}
}
MySort类
package sort_2;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MySort implements WritableComparable<MySort> {
public Long firstNum;
public Long secondNum;
public MySort() {//无参构造必须提供,不然报错
}
public MySort(Long firstNum, Long secondNum) {
this.firstNum = firstNum;
this.secondNum = secondNum;
}
/**
* 比较两个数的前后大小,有三种情况:
* 1:-1--第一列的当前数小于当前列的上一个数
* 2:1--第一列的当前数大于当前列的上一个数
* 3:0--相等,两个数相减等于零,这时就会比较第二列的数据大小,这时也会有三种情况,同上;
* 接下来就不属于我们的工作了,WritableComparable默认继承了Writable, Comparable<T>两个类,剩下的工作就交给他们了。
* @param o
* @return
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(MySort o) {
int result = 0;
int num = (int) (this.firstNum-o.firstNum);
if (num != 0){
result = num;
}else{
result = (int) (this.secondNum-o.secondNum);
}
return result;//正序
//return -result;//倒序
}
/**
* 序列化
* @param out
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(firstNum);
out.writeLong(secondNum);
}
/**
* 反序列化
* @param in
* @throws IOException
*/
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.firstNum = in.readLong();
this.secondNum = in.readLong();
}
}
WritableComparable的源码:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
//
package org.apache.hadoop.io;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceAudience.Public;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceStability.Stable;
@Public
@Stable
public interface WritableComparable<T> extends Writable, Comparable<T> {
//默认的继承了Writable,Comparable类
}
Runner类不演示了,需要注意的是把Mapper与Reducer的输入输出类型改成自定义的MySort排序类型,不需要添加job.setSortComparatorClass();我们使用默认的MapReduce的key排序分组加上自定义排序完成就足够了。
结果:
70 70
70 80
70 90
80 70
95 10
95 34
95 90接下来就是对以上详细的解释了:
在mapreduce操作时,shuffle阶段会多次根据key值排序。但是在shuffle分组后,相同key值的values序列的顺序是不确定的(如下图)。如果想要此时value值也是排序好的,这种需求就是二次排序。

测试的文件数据:
a 1
a 5
a 7
a 9
b 3
b 8
b 10
未经过二次排序的输出结果:
a 9
a 7
a 5
a 1
b 10
b 8
b 3
实现思路:
将map端输出的<key,value>中的key和value先传入自定义的排序类中做比较处理,处理之后在重新拉取出来。这里就变成<第一列,第二列>,在针对newKey(第一列)排序的时候,如果newKey相同,就再对value(第二列)进行排序。
- 需要自定义的地方
- 自定义数据类型实现组合key
实现方式:继承WritableComparable
注意:(容易被“坑”)
在reduce端对values进行迭代的时候,不要直接存储value值或者key值,因为reduce方法会反复执行多次,但key和value相关的对象只有两个,reduce会反复重用这两个对象。需要用相应的数据类型.get()取出后再存储。
自定义分区:
就使用简单的词频统计来设置一个需求:
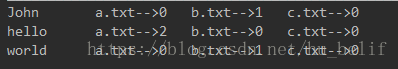
现在有三个文件{a.txt,b.txt,c.txt}(代表三个分区),需要利用MapReduce的自定义分区计算出每一个分区中的词频统计结果。并将带有“Hello”字段的统计结果放入编号为‘1’的分区中,将带有“World”字段的统计结果放入编号为‘2’的分区中,其余的放入编号为‘0’的分区中。
三个文件中的内容为:
这个的话直接上演示代码,再解释:
Mapper类:
package go_over.Map;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/**
* @Author H.rosy
* @Create 2018-09-16 21:46
*/
public class MyMap extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, Text> {
void check(String text, String FName, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {//检查数据所属文件的方法
Text k = new Text(text);
Text v = new Text(FName);
context.write(k, v);
}
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String values = value.toString();
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(values);
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) context.getInputSplit();//创建文件切割对象
while (st.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = split.getPath().getName();//利用文件切割对象获取文件的名字
if ("a.txt".equals(name)) {
check(st.nextToken(), "a", context);//调用传参的方法
} else if ("b.txt".equals(name)) {
check(st.nextToken(), "b", context);
} else{
check(st.nextToken(), "c", context);
}
}
}
}
Reducer类:
package go_over.Reduce;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyReduce extends Reducer<Text, Text, Text, Text> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<Text> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
/**
* 定义三个累加器分别代表三个文件的词频统计结果
*/
int countA = 0;
int countB = 0;
int countC = 0;
/**
* 遍历数据集开始统计
*/
for (Text value : values) {
if ("a".equals(value.toString())) {
countA++;
} else if ("b".equals(value.toString())) {
countB++;
} else {
countC++;
}
}
//手动拼接一下统计的结果
String result = " a.txt-->" + countA + " b.txt-->" + countB + " c.txt-->" + countC;
context.write(key, new Text(result));//输出到文件
}
}
MyPartition类
package go_over.Partition;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
public class MyPartition extends Partitioner<Text, Text> {
/**
* 继承一个Partitioner的抽象类
* 重写getPartition方法
* @return
*/
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, Text value, int i) {
int falg = 0;//分区编号(标志)
if(key.find("Hello")==0){
falg = 1;
}else if(key.find("World")==0){
falg = 2;
}
return falg;//返回的int数值代表着分区的编号
}
}
Runner类:
package go_over.demo;
import com.bw.map.countMap;
import com.bw.map.sortMap;
import com.bw.reduce.countReduce;
import com.bw.reduce.sortReduce;
import com.bw.sort.MySort;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.URI;
/**
* This is my test
*
* @Author
* @Create 2018-09-09 19:43
*/
public class MyDemo {
/**
* 首先创建一个静态变量区
*
* @param args
*/
static Configuration conf = new Configuration();
static Job job = null;
static FileSystem fs = null;
static String uri = "hdfs://192.168.132.130:9000";
static {//静态代码块
try {
conf.setBoolean("dfs.support.append", true);
fs = FileSystem.get(URI.create(uri), conf);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
//公共变量区
String input = uri.concat("/test");//本人需要做处理的文件都在这个目录下
String output = uri.concat("/output");//统计好结果后的文件存放目录
{//初始化job任务区
job = Job.getInstance(conf);//定义一个job任务
job.setJobName("wordCount");//添加工作名字
job.setMapperClass(countMap.class);//添加map类映射
job.setReducerClass(countReduce.class);//添加reduce映射
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Text.class);//设置map阶段的输出key类型
job.setMapOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);//设置map阶段的输出value类型
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);//设置最终阶段的输出key类型
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);//设置最终阶段的输出value类型
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartition.class);//设置分区的自定义类地址
job.setNumReduceTasks(3);//设置分区数量
checkFileExists(new Path[]{new Path(output)});//检测文件是否存在
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(input));//指定操作路径
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(output));//指定操作路径
job.waitForCompletion(true);//提交任务
}
{//结果展示模块
{//统计结果展示块
String alert = "-------------------------------下面是统计结果--------------------------";
getResult(new Path(sortInput), alert);
}
}
{
fs.close();//关闭资源
}
}
synchronized static boolean getResult(Path path, String alert) throws IOException {
FSDataInputStream open = fs.open(path);//打开目标路径的文件
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(open, "utf-8"));//设置缓冲区
String res = "";
System.err.println(alert);//输出提示信息
while ((res = reader.readLine()) != null) {//循环按行读取文本内容并赋值给res
System.out.println(res);//输出统计后的结果
}
reader.close();//关闭资源
return true;
}
static void checkFileExists(Path... paths) throws IOException {//查看文件是否存在,避免出现文件重复存在的错误
for (Path path : paths) {
boolean exists = fs.exists(path);
if (exists) {
fs.delete(path, true);
}
}
}
最后的输出结果为:
在HDFS的分区文件中的效果为:
Found 4 items
-rw-r--r-- 3 supergroup 0 2018-10-23 20:48 /output/_SUCCESS
-rw-r--r-- 3 supergroup 128 2018-10-23 20:48 /output/part-r-00000
-rw-r--r-- 3 supergroup 43 2018-10-23 20:48 /output/part-r-00001
-rw-r--r-- 3 supergroup 43 2018-10-23 20:48 /output/part-r-00002
//最后一位代表的就是我们自定义的那个分区编号自定义分组:
这是实现效果图:
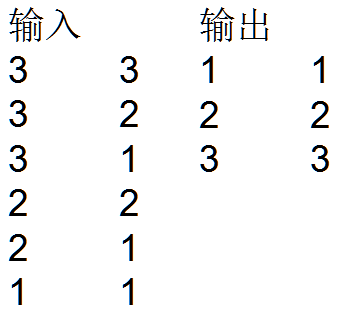
需求分析:根据第一列进行归并分组后正序排序,并找出对应第二列每组中的最大值
技术实现:
(1).自定义分组比较器继承RawComparator,实现compare()方法。
(2).在设置作业是设置job.setGroupingComparatorClass()。
Mapper、Reducer与Runner类
public class MyGroupTest {
// 定义输入路径
private static final String INPUT_PATH = "hdfs://liaozhongmin:9000/data";
// 定义输出路径
private static final String OUT_PATH = "hdfs://liaozhongmin:9000/out";
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 创建配置信息
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
// 创建文件系统
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(new URI(OUT_PATH), conf);
// 如果输出目录存在,我们就删除
if (fileSystem.exists(new Path(OUT_PATH))) {
fileSystem.delete(new Path(OUT_PATH), true);
}
// 创建任务
Job job = new Job(conf, MyGroupTest.class.getName());
// 设置输入目录和设置输入数据格式化的类
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, INPUT_PATH);
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
// 设置自定义Mapper类和设置map函数输出数据的key和value的类型
job.setMapperClass(MyGroupMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(CombineKey.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
//一定不要忘记设置自定义分组比较器的类(这一步是关键)
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(MyGroupComparator.class);
// 设置分区和reduce数量(reduce的数量,和分区的数量对应,因为分区为一个,所以reduce的数量也是一个)
job.setPartitionerClass(HashPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(1);
// 排序、分组
// 归约
// Shuffle把数据从Map端拷贝到Reduce端。
// 指定Reducer类和输出key和value的类型
job.setReducerClass(MyGroupReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(LongWritable.class);
// 指定输出的路径和设置输出的格式化类
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(OUT_PATH));
job.setOutputFormatClass(TextOutputFormat.class);
// 提交作业 退出
System.exit(job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static class MyGroupMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CombineKey, LongWritable> {
// 创建联合的key
private CombineKey combineKey = new CombineKey();
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, CombineKey, LongWritable>.Context context) throws IOException,
InterruptedException {
// 对输入value进行分割
String[] splits = value.toString().split("\t");
// 设置联合的Key
combineKey.setComKey(Long.parseLong(splits[0]));
combineKey.setComVal(Long.parseLong(splits[1]));
// 传给reducer计算
context.write(combineKey, new LongWritable(Long.parseLong(splits[1])));
}
}
public static class MyGroupReducer extends Reducer<CombineKey, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(CombineKey combineKey, Iterable<LongWritable> values,
Reducer<CombineKey, LongWritable, LongWritable, LongWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
long max = Long.MIN_VALUE;
// 遍历比较求出每个组中的最大值
for (LongWritable val : values) {
if (val.get() > max) {
max= val.get();
}
}
// 把原始数据中的第一列中的元素分组后的组号作为key,所求的最小值为value将结果写出去
context.write(new LongWritable(combineKey.getComKey()), new LongWritable(max));
}
}
}二次排序及类
/**
* 二次排序构造一个新的Key
* @version
*/
class CombineKey implements WritableComparable<CombineKey> {
private Long comKey;
private Long comVal;
// 无参构造函数必须提供,否则Hadoop的反射机制会报错
public CombineKey() {
}
// 有参构造函数
public CombineKey(Long comKey, Long comVal) {
this.comKey = comKey;
this.comVal = comVal;
}
public Long getComKey() {
return comKey;
}
public void setComKey(Long comKey) {
this.comKey = comKey;
}
public Long getComVal() {
return comVal;
}
public void setComVal(Long comVal) {
this.comVal = comVal;
}
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeLong(this.comKey);
out.writeLong(this.comVal);
}
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.comKey = in.readLong();
this.comVal = in.readLong();
}
/**
* 第一列按升序排列,第一列相同时,第二列也按升序排列
*/
public int compareTo(CombineKey o) {
long minus = this.comKey - o.comVal;
if (minus != 0) {
return (int) minus;
}
return (int) (this.comVal - o.comVal);
}
}分组比较器类:
/**
* 自定义分组比较器
* @version
*/
class MyGroupComparator implements RawComparator<CombineKey> {
// 分组策略中,这个方法不是重点
public int compare(CombineKey o1, CombineKey o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
/**
* b1 表示第一个参与比较的字节数组
* s1 表示第一个字节数组中开始比较的位置
* l1 表示第一个字节数组中参与比较的字节长度
* b2 表示第二个参与比较的字节数组
* s2 表示第二个字节数组中开始比较的位置
* l2 表示第二个字节数组参与比较的字节长度
*/
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1, byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
// 这里是按第CombineKey中的第一个元素进行分组,因为是long类型,所以是8个字节
return WritableComparator.compareBytes(b1, s1, 8, b2, s2, 8);
}
}最终结果:
1 1
2 2
3 3参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/89f56ecb88f7和https://blog.csdn.net/lzm1340458776/article/details/42840771