Java中把输入/输出(input/output)操作称为流(Stream)。
流:即为起点到接收点有序的数据序列。
流的分类:
1.按照流的方向分为:
输入流:只读,只会从流中读取数据;
输出流:只写,只会向流中写入数据;
2.按照处理的数据分:
字节流(InputStream/OutputStream):读或写的时候以字节为单位;
字符流(Reader/Writer):读或写的时候以字符为单位;
一般情况下(排除特殊情况),一个汉字占一个字符,一个字符占两个字节,如果读或写的时候只读或写一个字节的话,那么就会出现乱码。
3.按照功能分为:
低级流:直接从数据的源头读取数据或者直接把数据写到目标位置的流,称为低级流,也称为节点流;
高级流:对一个已经存在的流的连接和封装,称为高级流,也称为处理流;
先从字节流中的FileInputStream和FileOutputStream说起:以下是两者的模型


代码如下:
package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
public class ByteStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//readFile1();
//readFile2();
//writeFile1();
writeFile2();
}
/**
* 用FileInputStream读取文件的内容,一个一个字节的读取(出现中文乱码问题)
*/
public static void readFile1() {
FileInputStream fin = null;
try {
//文件的完整路径有三部分组成:路径名称+分隔符+文件名称;
//如果指定文件不存在,或者他是一个目录,而不是一个常规文件,抑或因为其他原因无法打开进行读取,则抛出FileNotFoundException;
//注意:FileInputStream只能读取并显示纯文本文件的内容(也就是能用记事本打开的文件)
fin = new FileInputStream("d:\\aa.txt");
int i = 0;
//从文件中读取一个字节以int值返回,当读到文件末尾没有数据时返回-1;
while((i=fin.read()) != -1){
//byte->int->char
System.out.print((char)i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//流打开之后,必须进行关闭
try {
if(fin != null){
fin.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 用FileInputStream读取文件的内容,一次读取多个字节的内容(有些中文没有乱码,有些乱码;并且还多读了一些内容)
*/
public static void readFile2() {
FileInputStream fin = null;
try {
fin = new FileInputStream("d:\\aa.txt");
int i = 0;
byte[] b = new byte[100];
//从文件中读取100个字节,放大数组中,i返回的是读取到的字节的数量,当读到文件末尾没有数据时返回-1;
while((i=fin.read(b)) != -1){
//byte[] -> char[] -> String
String str = new String(b);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//流打开之后,必须进行关闭
try {
if(fin != null){
fin.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 用FileOutputStream写String到文件
*/
public static void writeFile1(){
FileOutputStream fout = null;
try {
//当目标文件不存在时,JVM会自动创建这个文件,若已存在,则将内容写到这个文件中;
fout = new FileOutputStream("d:\\bb.txt",true); //true表示追加写文件
String str = "2.用FileOutputStream写String到文件";
//将String转换为byte[]
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
fout.write(b);
System.out.println("文件写入完成");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//流打开之后,必须进行关闭
try {
if(fout != null){
fout.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 用FileOutputStream写String到文件,解决换行
*/
public static void writeFile2(){
FileOutputStream fout = null;
try {
//当目标文件不存在时,JVM会自动创建这个文件,若已存在,则将内容写到这个文件中;
fout = new FileOutputStream("d:\\bb.txt",true); //true表示追加写文件
for(int i=0;i<=10;i++){
//由于FileOutputStream不会处理换行,需要我们在String结尾加入\n
//记事本不能识别\n,能够识别\r\n;
String str = i+".用FileOutputStream写String到文件\r\n";
//将String转换为byte[]
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
fout.write(b);
}
System.out.println("文件写入完成");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//流打开之后,必须进行关闭
try {
if(fout != null){
fout.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}然后将FileInputStream和FileOutputStream拼接起来,就组成了拷贝粘贴的功能;

但是这样直接使用低级流去读和写文件显然不是我们想要的,因为效率有点低,于是我们需要在低级流上接上一个高级流,像这样:

下面有代码来实现上面的过程,也即是拷贝文件的过程:
package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 文件拷贝器
*/
public class FileCoper {
private FileCoper(){
}
/**
* 拷贝文件的操作
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyFile(String srcFile,String desPath){
//从源文件的String中取出文件名称,也就是从例如:"D:\\tools\\Navicat.rar"中取到"Navicat.rar";
String[] arr = srcFile.split("\\\\");
String fileName = arr[arr.length-1];
//组织目标文件:路径名称+分隔符+文件名称
String desFile = desPath+"\\"+fileName;
//声明输入流:
FileInputStream fin = null;
BufferedInputStream bin = null;
//声明输出流:
FileOutputStream fout = null; //低级输出流
BufferedOutputStream bout = null; //高级输出流
try {
//创建输入流:
fin = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
bin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);
//创建输出流:首先初始化低级流,然后初始化高级流
fout = new FileOutputStream(desFile);
bout = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);
int i=0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024];
while((i=bin.read(b))!=-1){
bout.write(b,0,i);
}
/**
* 如果关闭低级流,那么会导致小于8k的文件滞留在bout的缓冲区,所以要刷新缓存区
* 拷贝过程中,只要文件的大小大于8k,则无需刷新缓存
*/
//bout.flush();
//由于采用了正确的流的关闭方式,所以无论文件大小,无需刷新缓存
System.out.println("文件拷贝完成,"+srcFile+"拷贝到目标文件"+desFile+"完成");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//错误的关闭方式
//if(fin != null){
// try {
// fin.close();
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//}
//if(fout != null){
// try {
// fout.close();
// } catch (IOException e) {
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
//}
//正确的关闭方式
//高级流在关闭的时候:1.会自动关闭低级流;2.会自动刷新缓存
try {
if(bin != null){
bin.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//bout关闭的时候,会自动刷新缓冲区
if(bout != null){
bout.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String file = "D:\\tools\\aa.txt";
//String file = "D:\\tools\\Navicat.rar";
copyFile(file,"d:\\");
}
}但是上面的代码有点问题,问题出在取文件名和拼接目标文件路径上,采用了"\\"和"\\\\"这两种分隔符,但是不同操作系统上的分隔符是不一样的,这样写的话就写死了,违背java的可移植性特点,所以我们采用java.io.File来解决这个问题:
package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 文件拷贝器
*/
public class FileCoper {
private FileCoper(){
}
/**
* 拷贝文件的操作
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyFile(String srcFile,String desPath){
//从源文件的String中取出文件名称
//File file = new File(srcFile);
//copyFile(file,desPath);
//继续简化
copyFile(new File(srcFile),desPath);
}
/**
* 拷贝文件的操作
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyFile(File srcFile,String desPath){
//从源文件的String中取出文件名称
String fileName = srcFile.getName();
//组织目标文件:路径名称+分隔符+文件名称
String desFile = desPath+File.separator+fileName;
//声明输入流:
FileInputStream fin = null;
BufferedInputStream bin = null;
//声明输出流:
FileOutputStream fout = null; //低级输出流
BufferedOutputStream bout = null; //高级输出流
try {
//创建输入流:
fin = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
bin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);
//创建输出流:首先初始化低级流,然后初始化高级流
fout = new FileOutputStream(desFile);
bout = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);
int i=0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024];
while((i=bin.read(b))!=-1){
bout.write(b,0,i);
}
System.out.println("文件拷贝完成,"+srcFile+"拷贝到目标文件"+desFile+"完成");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//正确的关闭方式
//高级流在关闭的时候:1.会自动关闭低级流;2.会自动刷新缓存
try {
if(bin != null){
bin.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//bout关闭的时候,会自动刷新缓冲区
if(bout != null){
bout.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String file = "D:\\tools\\aa.txt";
//String file = "D:\\tools\\Navicat.rar";
copyFile(file,"d:\\");
}
}但是这里还有一个问题,一个相对较大的文件拷贝是需要时间的,如果在拷贝的这段时间内,程序突然停下来的,文件看似拷贝下来了,但是这个文件是不完整的,那么该如何解决这个问题呢?下面代码演示:
package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 文件拷贝器
*/
public class FileCoper {
private FileCoper(){
}
/**
* 拷贝文件的操作
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyFile(String srcFile,String desPath){
//从源文件的String中取出文件名称
//File file = new File(srcFile);
//copyFile(file,desPath);
//继续简化
copyFile(new File(srcFile),desPath);
}
/**
* 拷贝文件的操作
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyFile(File srcFile,String desPath){
//从源文件的String中取出文件名称
String fileName = srcFile.getName();
//判断目标路径是否存在,如果不存在,就把他创造出来;
File dpath = new File(desPath);
if(!dpath.exists()){
dpath.mkdirs();
}
//组织目标文件:路径名称+分隔符+文件名称
String desFile = desPath+File.separator+fileName;
String tempFile = desFile + ".td"; //拷贝过程中的临时文件名称
//声明输入流:
FileInputStream fin = null;
BufferedInputStream bin = null;
//声明输出流:
FileOutputStream fout = null; //低级输出流
BufferedOutputStream bout = null; //高级输出流
try {
//创建输入流:
fin = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
bin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);
//创建输出流:首先初始化低级流,然后初始化高级流
fout = new FileOutputStream(tempFile);
bout = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);
int i=0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024];
while((i=bin.read(b))!=-1){
bout.write(b,0,i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//正确的关闭方式
//高级流在关闭的时候:1.会自动关闭低级流;2.会自动刷新缓存
try {
if(bin != null){
bin.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//bout关闭的时候,会自动刷新缓冲区
if(bout != null){
bout.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//当文件拷贝完成之后,把临时文件名称改成目标文件名称
//这里注意:需要在流关闭的时候才可以重命名,要不然流将线程锁住,无法改名
File file1 = new File(desFile);
File file2 = new File(tempFile);
if(file2.renameTo(file1)){
System.out.println("文件拷贝完成,"+srcFile+"拷贝到目标文件"+desFile+"完成");
}else{
System.err.println("拷贝失败");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//String file = "D:\\tools\\aa.txt";
String file = "D:\\tools\\Navicat.rar";
copyFile(file,"d:\\abc");
}
}但是这里还有一个问题,以上只是解决了拷贝一个文件到任意指定的文件夹中,但是实际还有将任意文件夹(包括其中的文件)拷贝到任意文件夹中,这个又该如何实现呢?一下代码演示:
package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.*;
/**
* 文件拷贝器
*/
public class FileCoper {
private FileCoper(){
}
/**
* 拷贝文件的操作
* @param srcFile 源文件
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyFile(File srcFile,String desPath){
//从源文件的String中取出文件名称
String fileName = srcFile.getName();
//判断目标路径是否存在,如果不存在,就把他创造出来;
File dpath = new File(desPath);
if(!dpath.exists()){
dpath.mkdirs();
}
//组织目标文件:路径名称+分隔符+文件名称
String desFile = desPath+File.separator+fileName;
String tempFile = desFile + ".td"; //拷贝过程中的临时文件名称
//声明输入流:
FileInputStream fin = null;
BufferedInputStream bin = null;
//声明输出流:
FileOutputStream fout = null; //低级输出流
BufferedOutputStream bout = null; //高级输出流
try {
//创建输入流:
fin = new FileInputStream(srcFile);
bin = new BufferedInputStream(fin);
//创建输出流:首先初始化低级流,然后初始化高级流
fout = new FileOutputStream(tempFile);
bout = new BufferedOutputStream(fout);
int i=0;
byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024];
while((i=bin.read(b))!=-1){
bout.write(b,0,i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
//正确的关闭方式
//高级流在关闭的时候:1.会自动关闭低级流;2.会自动刷新缓存
try {
if(bin != null){
bin.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
//bout关闭的时候,会自动刷新缓冲区
if(bout != null){
bout.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//当文件拷贝完成之后,把临时文件名称改成目标文件名称
//这里注意:需要在流关闭的时候才可以重命名,要不然流将线程锁住,无法改名
File file1 = new File(desFile);
File file2 = new File(tempFile);
if(file2.renameTo(file1)){
System.out.println("文件拷贝完成,"+srcFile+"拷贝到目标文件"+desFile+"完成");
}else{
System.err.println("拷贝失败");
}
}
}
/**
* 拷贝文件夹的功能
* @param srcPath 原文件夹
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyDir(String srcPath,String desPath){
copyDir(new File(srcPath),desPath);
}
/**
* 拷贝文件夹的功能
* @param srcPath 原文件夹
* @param desPath 目标路径
*/
public static void copyDir(File srcPath,String desPath){
//判断srcPath是文件还是文件夹:
if(srcPath.isFile()){
//是文件,那么调用之前拷贝文件的方法:
copyFile(srcPath,desPath);
}else{
//是文件夹:
//从原文件中获取要拷贝的文件夹名称,例如,我要拷贝jdk源代码"D:\\file\\src",从中获取src
String pathName = srcPath.getName();
//在目标路径中创建要拷贝的目录,例如在"d:\\"创建"src"目录:
String dPath = desPath+File.separator+pathName; //"d:\\src"
File file = new File(dPath);
file.mkdirs();
//获取原文件夹中所有子文件(夹)
File[] files = srcPath.listFiles();
//遍历存放子文件的数组,一个个的拷贝到目标路径中,也就是dPath
for(File file1:files){
copyDir(file1,dPath); //递归调用
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
//String file = "D:\\tools\\aa.txt";
//String file = "D:\\tools\\Navicat.rar";
//copyFile(file,"d:\\abc");
String file = "D:\\file\\src";
copyDir(file,"d:\\");
}
}这里文件或文件夹拷贝告一段落了,反观之前的FileOutputStream这个低级流在实现写的时候,有一些瑕疵,模型如下:

package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.*;
public class ByteStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
writeFile3();
}
/**
* 在FileOutputStream上接一个高级流PrintStream输出
*/
public static void writeFile3(){
FileOutputStream fout = null;
PrintStream ps = null;
try {
fout = new FileOutputStream("d:\\dd.txt",true);
ps = new PrintStream(fout);
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++){
String str = i+"在FileOutputStream上接一个高级流PrintStream输出";
//为了方便操作,ps.println(str)/ps.close()暂时不需要处理异常;
ps.println(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(ps != null){
ps.close();
}
}
}
}================================================================================================
以上讲的都是字节流,从这里我们开始讲讲字符流的使用。
首先是使用字符流去读取文件中的数据,模型如下:
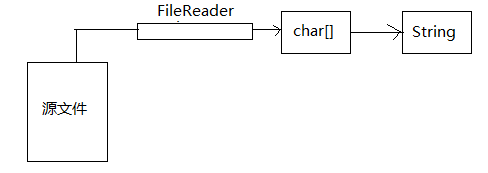
以下是代码演示:
package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharacterStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
//readFile1();
readFile2();
}
/**
* 用FileReader读取文件的内容,一个一个字符的读取
*/
public static void readFile1(){
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("d:\\aa.txt");
int i = 0;
//读取一个字符,当做int返回,直到文件末尾没有字符时返回-1;
while((i=fr.read()) != -1){
//char -> int -> char
System.out.print((char)i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(fr != null){
fr.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 用FileReader读取文件的内容,一次读取多个字符的数据
*/
public static void readFile2(){
FileReader fr = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("d:\\aa.txt");
int i = 0;
char[] c = new char[1024];
//读取多个字符,保存到数组中,i是读取到的字符的数量
while((i=fr.read(c)) != -1){
//char[] -> String
String str = new String(c,0,i);
System.out.print(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(fr != null){
fr.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}但是这样用低级流去读取文件是字符数组,然后还要手动转换为字符串,这样在读取大文件时效率不高,这时我没需要在低级流上接一个高级流,利用高级流的缓存一行一行的读取数据,效率大大提高,一下模型演示:

下面是代码演示:
package com.Jevin.io;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
public class CharacterStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
readFile3();
}
/**
* 用FileReader和BufferReader读取文件中的内容
*/
public static void readFile3() {
FileReader fr = null;
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
fr = new FileReader("d:\\aa.txt");
br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String str = null;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(str);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}这里简单的字节流和字符流就介绍到这里,接下来介绍一个有意思的流:RandomAccessFile,它可以从文件的任意位置读,也可以从文件的任意位置写。写个功能有什么用呢?换言之:可以将一个大文件切割成多个小文件分别读写。
模型如下所示:

代码如下所示:
package com.Jevin.io.demo;
import java.io.File;
/**
* 文件拷贝包工头
*/
public class FileCopyContractor {
private File srcFile; //源文件
private String desFile; //目标文件
private String tempFile; //拷贝过程中的临时文件
private int splitCount; //文件切分的份数
public FileCopyContractor(){}
public FileCopyContractor(File srcFile, String desPath, int splitCount) {
super();
this.srcFile = srcFile;
this.splitCount = splitCount;
//组织目标文件:
String fileName = srcFile.getName();
this.desFile = desPath + File.separator + fileName;
this.tempFile = desFile + ".td";
}
public FileCopyContractor(String srcFile, String desPath, int splitCount) {
this(new File(srcFile),desPath,splitCount);
}
/**
* 包工头开始工作:
*/
public void start(){
//获取原文件的大小:
long fileSize = srcFile.length();
System.out.println("文件的大小是:"+fileSize);
//根据切分的份数和源文件的大小,计算每个工人的平均工作量
long perWorkerSize = fileSize/this.splitCount;
//计算第一个工人的开始位置和结束位置:
long startPost = 0L;
long endPost = perWorkerSize;
//包工头创建多个工人:
for(int i=0;i<this.splitCount;i++){
//创建工人对象:
FileCopyWorker fileCopyWorker = new FileCopyWorker("工人-"+i,srcFile,tempFile,startPost,endPost);
//工人开始工作:
fileCopyWorker.work();
//包工头计算下一个工人的开始位置和结束位置:
startPost = endPost;
endPost = startPost + perWorkerSize;
//如果是最后一个工人,则做到最后;
if(i == this.splitCount-2){
endPost = fileSize;
}
}
//所有工人完成工作之后,把临时文件名称改成目标文件名称:
File file1 = new File(this.tempFile);
File file2 = new File(this.desFile);
if(file1.renameTo(file2)){
System.out.println(this.srcFile + "拷贝到"+this.desFile+"完成");
}else{
System.out.println("重命名文件失败");
}
}
}package com.Jevin.io.demo;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
/**
* 文件拷贝工人
*/
public class FileCopyWorker {
private String name; //工人名称
private File srcFile; //源文件
private String desFile; //目标文件
private long startPost; //开始位置
private long endPost; //结束位置
private long copyedPost; //已经拷贝的位置
public FileCopyWorker(String name, File srcFile, String desFile, long startPost, long endPost) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.srcFile = srcFile;
this.desFile = desFile;
this.startPost = startPost;
this.endPost = endPost;
this.copyedPost = this.startPost; //初始化拷贝位置即为初始位置
System.out.println(name+"[开始位置是:"+this.startPost+",结束位置是:"+this.endPost+"]");
}
/**
* 工人开始工作
*/
public void work(){
RandomAccessFile rin = null; //读数据流
RandomAccessFile rout = null; //写数据流
try {
rin = new RandomAccessFile(this.srcFile,"r");
rout = new RandomAccessFile(this.desFile,"rw");
//定位读写的位置:
rin.seek(this.startPost); //开始读的位置
rout.seek(this.startPost); //开始写的位置
byte[] b = new byte[1024*1024];
int i = 0;
//当已经拷贝的位置小于结束位置,并且未拷贝到文件结尾,就一直循环拷贝下去:
while((this.copyedPost < this.endPost) && (i=rin.read(b)) != -1){
if((this.copyedPost + i) > this.endPost){
i = (int) (this.endPost - this.copyedPost);
}
rout.write(b,0,i);
this.copyedPost += i;
System.out.println(name+"正在工作,已经拷贝的位置是:"+this.copyedPost+",结束位置是:"+this.endPost);
}
System.out.println(name+"结束工作,已经拷贝的位置是:"+this.copyedPost+",结束位置是:"+this.endPost);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
try {
if(rin != null){
rin.close();
}
if(rout != null){
rout.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}package com.Jevin.io.demo;
public class MainTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
String file = "D:\\tools\\Navicat.rar";
FileCopyContractor fileCopyContractor = new FileCopyContractor(file,"d:\\",15);
fileCopyContractor.start();
}
}“流”暂时就到这里吧,又补充的再继续吧!