版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。如文章对您有帮助,欢迎扫描上面或者头像上的二维码支持,谢谢~ https://blog.csdn.net/b2222505/article/details/79681202
ReentrantLock、CountDownLatch、CyclicBarrier
1、ReentrantLock可重入互斥锁
公平锁与非公平锁的释放锁步骤是一致的。获取锁的过程不一致,非公平锁是让当前线程优先独占,而公平锁则是让等待时间最长的线程优先,非公平的可能让其他线程没机会执行,而公平的则可以让等待时间最长的先执行,但是性能上会差点。
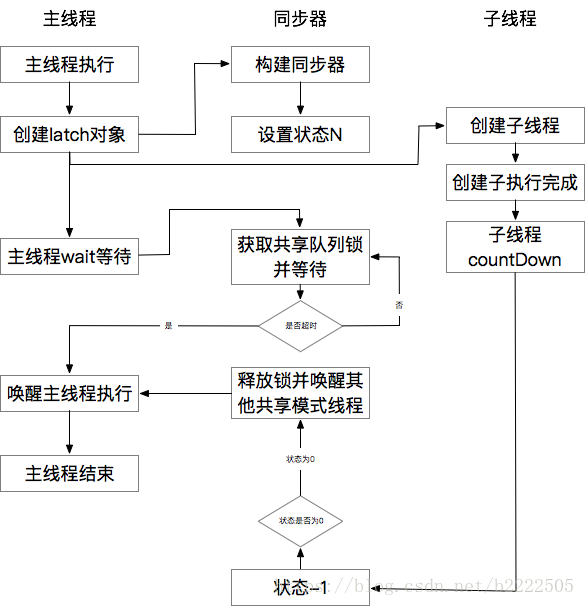
2、CountDownLatch是一个线程(或者多个线程)等待(await)多个线程(countDown),当多个线程都countDown完,await线程继续往后执行。
3、CyclicBarrier是多个线程相互等待(await),当所有都await后一起继续往后执行。
ReentrantLock Demo
class ReentrantLockDemo {
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void m() {
lock.lock();
try {
// ... method body
} finally {
lock.unlock()
}
}
}CountDownLatch Demo
public class CountDownLatchDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(10);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(5, 10, 200, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(5));
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
TestTask task=new TestTask("task_" + (i+1),latch);
executor.execute(task);
}
try {
System.out.println("等待10个子线程执行完毕...");
latch.await();
System.out.println("10个子线程已经执行完毕");
System.out.println("继续执行主线程");
}catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
executor.shutdown();
}
}
class TestTask implements Runnable{
private String name;
private CountDownLatch latch;
public TestTask(String name,CountDownLatch latch){
this.name=name;
this.latch=latch;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(name + " start running.");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(name + " start end.");
this.latch.countDown();
}
}CyclicBarrier Demo
public class CyclicBarrierDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
CyclicBarrier barrier = new CyclicBarrier(10);
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(10, 10, 200, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(5));
for(int i=0;i<10;i++){
TestTask task=new TestTask("客人_" + (i+1),barrier,i);
executor.execute(task);
}
}
}
class TestTask implements Runnable{
private String name;
private CyclicBarrier barrier;
private int index;
public TestTask(String name,CyclicBarrier barrier,int index){
this.name=name;
this.barrier=barrier;
this.index=index;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000 + this.index*1000);
System.out.println(name + " 哥已到");
Thread.sleep(1000 + this.index*2000);
System.out.println(name + " 哥已就坐,其他几个哥赶快啊,哥饿啦.");
this.barrier.await();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(name + "终于都到啦,开吃啦");
}
}