1. 方案选择
最近发现好久不看算法了,自己的能力有些松懈和退步了,便捡起 LeetCode 刷刷题,在选择IDE时发现:Vim 太简陋,Eclipse 操作太繁杂,VS Code 正合适。我把 VS Code 用于编写小小型C++项目的配置方式记录下来。
VS Code 提供 C/C++ for VS Code 插件,提供下面 C++ 语言方面的支持(Language service):
- Code Formatting (clang-format) 代码格式化
- Auto-Completion (experimental) 自动完成
- Symbol Searching 符号搜索
- Go to Definition/Declaration 定义跳转
- Peek Definition/Declaration 定义预览
- Class/Method Navigation 类/方法 导航
- Signature Help 帮助提示
- Quick Info (Hover) 鼠标浮动提示
- Error Squiggles 错误曲线标识
下面开始配置,仅记录 Linux 环境下的配置:
2. 编译配置
在 VS Code 中打开工具窗口 (Ctrl+Shift+P) ,输入 C/CPP: Edit Configurations 来生成配置文件 c_cpp_properties.json 可以添加一些自定义 include 路径,如果不使用外部的第三方库,默认配置可以直接使用。
C++ 是需要编译的,VS Code 把代码的 linting, building, packaging, testing , deploying 都归结为 Tasks 我们需要配置一个或者多个 Tasks 来完成编译任务
打开工具窗口 (Ctrl+Shift+P) → 输入 Tasks: Configure Task Runner,弹出窗口中选择 Others 在新打开的tasks.json中配置如下:
{
// See https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=733558
// for the documentation about the tasks.json format
"version": "2.0.0",
"tasks": [
{
"label": "build-release",
"type": "shell",
"command": "g++",
"args": [
"*.cpp",
"-o${workspaceRootFolderName}"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc"
]
},
{
"label": "build-debug",
"type": "shell",
"command": "g++",
"args": [
"-g",
"*.cpp",
"-o${workspaceRootFolderName}"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc"
]
},
{
"label": "make default",
"type": "shell",
"command": "make",
"args": [
"default"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
}
},
{
"label": "make all",
"type": "shell",
"command": "make",
"args": [
"all"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc"
]
},
{
"label": "make clean",
"type": "shell",
"command": "make",
"args": [
"clean"
],
"group": {
"kind": "build",
"isDefault": true
},
"problemMatcher": [
"$gcc"
]
}
]
}
3. 调试配置
配置完成后可以使用 Ctrl+Shift+B 快捷键来执行编译,编译成功后就是调试运行(debug) ,VS Code 的调试有专用的模块,进入调试模块,选择 C++(GDB/LLDB) 此时会生成调试配置文件 launch.json,输入下面的配置信息:
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch direct",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/${workspaceRootFolderName}",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
},
{
"name": "(gdb) Launch makefile",
"type": "cppdbg",
"request": "launch",
"program": "${workspaceFolder}/debug/${workspaceRootFolderName}",
"args": [],
"stopAtEntry": false,
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}",
"environment": [],
"externalConsole": true,
"MIMode": "gdb",
"setupCommands": [
{
"description": "Enable pretty-printing for gdb",
"text": "-enable-pretty-printing",
"ignoreFailures": true
}
]
}
]
}
然后就可以使用快捷键 F5 进行调试了。
4. Makefile 模板
下面列出了一个简易的 Makefile 模板:
# Fork from https://github.com/TheNetAdmin/Makefile-Templates
# tool marcros
CC := g++
CCFLAG := -std=c++14
DBGFLAG := -g
CCOBJFLAG := $(CCFLAG) -c
# path marcros
BIN_PATH := bin
OBJ_PATH := obj
LIB_PATH := lib
SRC_PATH := src
DBG_PATH := debug
# compile marcros
TARGET_NAME := $(shell pwd | awk -F '/' '{printf $$(NF)}')
ifeq ($(OS),Windows_NT)
TARGET_NAME := $(addsuffix .exe,$(TARGET_NAME))
endif
TARGET := $(BIN_PATH)/$(TARGET_NAME)
TARGET_DEBUG := $(DBG_PATH)/$(TARGET_NAME)
# src files & obj files
SRC := $(foreach x, $(SRC_PATH), $(wildcard $(addprefix $(x)/*,.c*)))
OBJ := $(addprefix $(OBJ_PATH)/, $(addsuffix .o, $(notdir $(basename $(SRC)))))
OBJ_DEBUG := $(addprefix $(DBG_PATH)/, $(addsuffix .o, $(notdir $(basename $(SRC)))))
# clean files list
DISTCLEAN_LIST := $(OBJ) \
$(OBJ_DEBUG)
CLEAN_LIST := $(TARGET) \
$(TARGET_DEBUG) \
$(DISTCLEAN_LIST)
# default rule
default: arch
# non-phony targets
$(TARGET): $(OBJ)
$(CC) $(CCFLAG) -o $@ $?
$(TARGET_DEBUG): $(OBJ_DEBUG)
$(CC) $(CCFLAG) $(DBGFLAG) $? -o $@
$(OBJ_PATH)/%.o: $(SRC_PATH)/%.c*
$(CC) $(CCOBJFLAG) -o $@ $<
$(DBG_PATH)/%.o: $(SRC_PATH)/%.c*
$(CC) $(CCOBJFLAG) $(DBGFLAG) -o $@ $<
# phony rules
.PHONY: arch
arch:
@mkdir -p src obj lib bin debug
.PHONY: all
all: $(TARGET) $(TARGET_DEBUG)
.PHONY: debug
debug: $(TARGET_DEBUG)
.PHONY: clean
clean:
@echo CLEAN $(CLEAN_LIST)
@rm -f $(CLEAN_LIST)
.PHONY: distclean
distclean:
@echo CLEAN $(CLEAN_LIST)
@rm -f $(DISTCLEAN_LIST)
5. 参考示例
下面是一个简易的链表逆序的算法实现,可以作为运行调试的例子:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct ListNode
{
int value;
ListNode *next;
};
void ReversePrint(ListNode *pHead) //递归实现逆序打印(不改变链表结构)
{
if (pHead != NULL)
{
if (pHead->next != NULL)
ReversePrint(pHead->next);
cout << pHead->value << " ";
}
}
ListNode *ReverseList1(ListNode *pHead) //头插法(改变链表结构)
{
if (pHead == NULL)
return NULL;
ListNode *p = pHead->next;
ListNode *newHead = pHead;
while (p != NULL)
{ //将p结点移到链表最前方
pHead->next = p->next; //头结点指向p的下一个结点
p->next = newHead; //p插入链表最前方
newHead = p; //链表新头结点更新为p
p = pHead->next; //处理下一个结点,该结点位于头结点后
}
return newHead;
}
ListNode *ReverseList2(ListNode *pHead) //依次改变指针方向(改变链表结构)
{
ListNode *prev = NULL;
ListNode *next = NULL;
while (pHead != NULL)
{
next = pHead->next; //保存剩余链表
pHead->next = prev; //断开剩余链表头结点pHead,指向pre
prev = pHead; //pre更新
pHead = next; //head更新
}
return prev;
}
int main() //主函数
{
int n;
cout << endl
<< "请输入链表元素个数: " << endl;
cin >> n; //输入元素个数
ListNode *head = NULL;
ListNode *p = NULL;
ListNode *q = NULL;
cout << endl
<< "请依次输入链表元素: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) //分配内存,依次输入元素
{
q = new ListNode;
cin >> q->value;
if (head == NULL)
{
head = q;
p = head;
}
else
{
p->next = q;
p = p->next;
}
}
if (head == NULL)
return 0;
p->next = NULL;
//验证
cout << "递归逆序打印: " << endl;
ReversePrint(head);
cout << endl
<< "头插法反转链表: " << endl;
ListNode *reverseHead;
reverseHead = ReverseList1(head);
p = reverseHead;
while (p != NULL)
{
cout << p->value << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << endl
<< "改变指针方向反转链表(将链表再次反转): " << endl;
p = ReverseList2(reverseHead); //改变指针方向反转链表
while (p != NULL)
{
cout << p->value << " ";
q = p;
p = p->next;
delete q; //释放内存
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
6. Windows 环境配置
Windows环境下是非常不方便进行 GNU/C++ 编译的,但是极端情况下也是可以用的,记录一下 Mingw-w64 (GCC for Windows 64 & 32 bits) 环境的搭建和 VS Code 的相关配置,使用 Mingw-builds 进行安装,如果需要配套的命令行工具可以使用 Msys2 , Cygwin是运行于Windows平台的POSIX子系统编译出来的程序需要dll依赖,这里并不推荐使用。
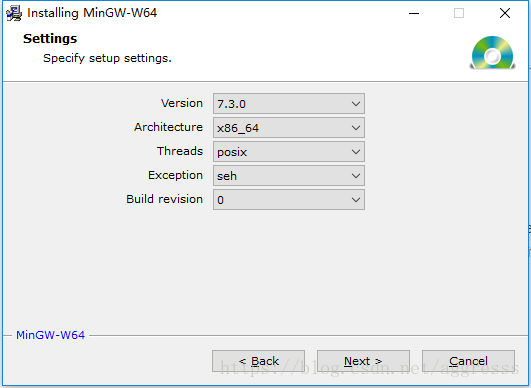
Mingw-w64安装:
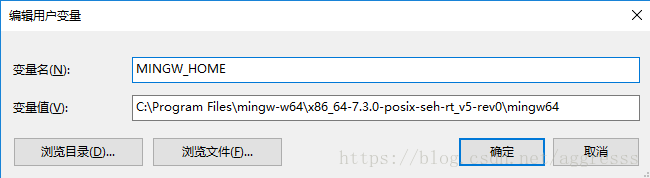
安装完成后使用 sysdm.cpl 修改环境变量
然后将 %MINGW_HOME%\bin 附加到 Path 变量后面,这样就可以在系统环境下直接调用 GNU/GCC 工具。
在 VS Code 中打开工具窗口 (Ctrl+Shift+P) ,输入 C/CPP: Edit Configurations 来生成配置文件 c_cpp_properties.json 添加 MinGW-w64 的 include 路径:
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": [
"${workspaceFolder}",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++/tr1",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++/backward",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++/x86_64-w64-mingw32",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/include"
],
"defines": [
"_DEBUG",
"UNICODE",
"_UNICODE",
"__GNUC__=5",
"__cdecl=__attribute__((__cdecl__))"
],
"intelliSenseMode": "msvc-x64",
"browse": {
"path": [
"${workspaceFolder}",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++/tr1",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++/backward",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/x86_64-w64-mingw32/include/c++/x86_64-w64-mingw32",
"${env:MINGW_HOME}/include"
],
"limitSymbolsToIncludedHeaders": true,
"databaseFilename": ""
},
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++17"
}
其他的使用就和Linux一样了,如果MinGW64体验不够好可以使用 MSVC, 这里就不介绍了。
7. 备注
下面是 VS Code 中的 预定义变量(Predefined variables) :
${workspaceRoot}当前打开的文件夹的绝对路径+文件夹的名字${workspaceRootFolderName}当前打开的文件夹的名字${file}当前打开正在编辑的文件名,包括绝对路径,文件名,文件后缀名${relativeFile}从当前打开的文件夹到当前打开的文件的路径${fileBasename}当前打开的文件名+后缀名,不包括路径${fileBasenameNoExtension}当前打开的文件的文件名,不包括路径和后缀名${fileDirname}当前打开的文件所在的绝对路径,不包括文件名${fileExtname}当前打开的文件的后缀名${cwd}同 pwd , 当前绝对路径${lineNumber}当前打开的文件,光标所在的行数