https://yq.aliyun.com/articles/272405#27
本文代码摘录的时候,将一些与本流程无关的内容去掉了,如有需要请看源码。
一、闲言碎语
使用rpc框架已经多年了,虽然之前有研究过rpc的过程,但是却不曾详细阅读过dubbo的源码,探究过其中的设计思路与亮点。所以抽时间阅读了一下dubbo的源码,分享出来和大家一起学习。
二、目标与示例
1. 目标
l  探究dubbo rpc实现原理。
l  探究rpc从发出请求到收到返回结果这整个过程的详细过程。
l  学习rpc的负载均衡原理。
l  学习服务暴露、服务发现的原理以及实现细节。
l  多线程中dubbo是如何做到将返回结果和每个线程一一对应的。
本文重点为源码分析和模型实现分析,如果对dubbo的概念和使用不熟悉,情移步官网。
本文的所有分析均基于dubbo 2.5.3版本。
本文假定使用zookeeper管理服务。
2. 示例代码
以下的分析基于以下配置方式。不同的配置方式并不会影响本文所需要解决的几个问题,只是一下方式配置会比较便于理解,所以这里依次做为示例。
1) consumer
<bean id="rpcServiceRef" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.ReferenceBean"> <property name="interface" value="com.wzf.service.RpcService"/> <property name="application" ref="dubboApplicationConfig"/> <property name="registry" ref="dubboRegistryConfig"/> <property name="version" value="dev"/> <property name="timeout" value="3000"/> <property name="retries" value="0"/> <property name="check" value="false"/> </bean>2) provider
<bean id="rpcServiceExport" class="com.alibaba.dubbo.config.spring.ServiceBean"> <property name="interface" value="com.wzf.funny.service.RpcService"/> <property name="ref" ref="rpcServiceImpl"/> <property name="application" ref="dubboApplicationConfig"/> <property name="registry" ref="dubboRegistryConfig"/> <property name="protocol" ref="dubboProtocolConfig"/> <property name="version" value="dev"/> <property name="timeout" value="0"/> <property name="retries" value="0"/> </bean>三、 模型
1. dubbo的模块模型
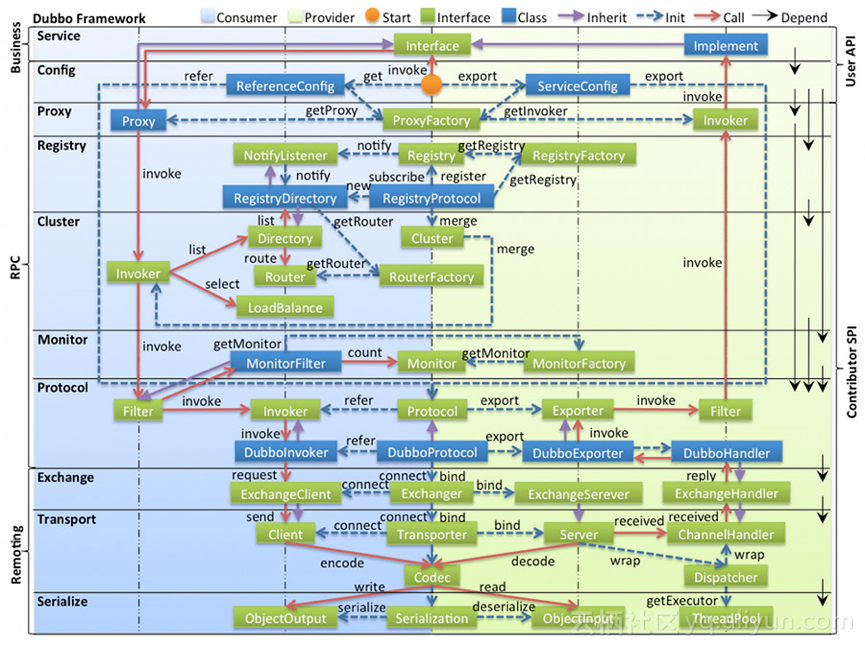
dubbo的模块模型有些复杂,不太容易看懂,如果你也有同感的话,可以看一下本文后面的几部分,他们详细讲述了dubbo中rpc的调用链,其中包括了核心的几个类,比较便于理解。
2. 服务调用关系模型
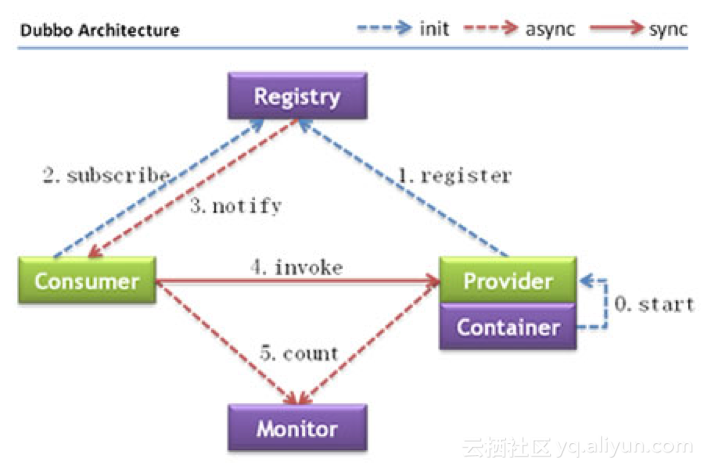
如图所示,dubbo的RPC调用模型分为registry、provider、consumer、monitor这几个部分。此图展示了从服务注册、发现、调用的全过程,但dubbo是如何做到的呢?其实这个问题包括了以下几个问题:provider如何注册服务到zookeeper;consumer如何从zookeeper拉取provider信息;provider变化以后,zookeeper如何告知consumer;consumer如何调用provider。另外,监控逻辑很简单本文暂时不做分析。
3. Provider
从源码上看ServiceBean主要完成以下几件工作:服务暴露,取消暴露服务。
1) 暴露服务
服务暴露开始于ServiceBean的afterPropertiesSet方法,此方法在ServiceBean的所有属性都被赋值以后被BeanFactory调用。服务暴露的调用链是: ServiceConfig#export -> ServiceConfig#doExport -> ServiceConfig#doExportUrls -> ServiceConfig#doExportUrlsFor1Protocol -> ServiceConfig#exportLocal(URL url)。 暴露服务其实包括两个类容:
l  将Invoker存入AbstractProtocol#exporterMap,调用服务时从次map中取出Invoker直接使用。
protected final Set<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ConcurrentHashSet<Invoker<?>>();其中key为:com.wzf.funny.service.ArticleService:dev, value为invoker对象
l  将url注册到zookeeper。
此过程的入口在RegistryProtocol#export方法中,调用链为:
RegistryProtocol#export -> FailbackRegistry#register -> AbstractRegistry#register -> ZookeeperRegistry#doRegister -> ZookeeperClient#create -> AbstractZookeeperClient#create
2) 服务发现
ZookeeperRegistry是服务发现的核心类之一,实现了《服务调用关系模型》中的register、subscribe、notify。以下分析一下几个主要的方法。
l 构造函数
从以下代码中可以看到,zkClient创建成功以后,会监听RECONNECTED事件,recover方法主要做一件事:将需要暴露的url放在failedRegistered(Set<URL>)中,将需要订阅的服务放在failedSubscribed(Set<URL>)中。说明RECONNECTED时,因为所有需要暴露的服务都需要重新注册,所以其实是将需要暴露、订阅的url都放到failedRegistered、failedSubscribed中。
public ZookeeperRegistry(URL url, ZookeeperTransporter zookeeperTransporter) { super(url); //其他代码省略 this.root = group; zkClient = zookeeperTransporter.connect(url); zkClient.addStateListener(new StateListener() { public void stateChanged(int state) { if (state == RECONNECTED) { try { recover(); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error(e.getMessage(), e); } } } }); }创建zkclient的url示例如下:
zookeeper://localhost:2181/com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=funny&dubbo=2.5.3&interface=com.alibaba.dubbo.registry.RegistryService&pid=38796×tamp=1502594657663
l register(URL url)
注册url代表的服务到zookeeper
l unregister(URL url)
从zookeeper中删除之前注册的服务
l subscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener)
订阅url的服务
l unsubscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener)
取消订阅url对应的服务
l notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls)
通知
l retry()
上面提到过,在recover()中将需要暴露的服务放到failedRegistered(Set<URL>)中,将需要订阅的服务放在failedSubscribed(Set<URL>)中,并没有真正的重新暴露服务或者订阅服务,这个工作是放在retry()中的,另外notify、doUnsubscribe,failedUnregistered也都放在此方法中处理。retry()方法的主要逻辑如下(为了方便阅读,我删掉了部分代码),retry被一个定时线程调用:
protected void retry() { if (! failedRegistered.isEmpty()) { for (URL url : failed) { doRegister(url); failedRegistered.remove(url); } } if(! failedUnregistered.isEmpty()) { for (URL url : failed) { doUnregister(url); failedUnregistered.remove(url); } } if (! failedSubscribed.isEmpty()) { for (Map.Entry<URL, Set<NotifyListener>> entry : failed.entrySet()) { URL url = entry.getKey(); Set<NotifyListener> listeners = entry.getValue(); for (NotifyListener listener : listeners) { doSubscribe(url, listener); listeners.remove(listener); } } } if (! failedUnsubscribed.isEmpty()) { for (Map.Entry<URL, Set<NotifyListener>> entry : failed.entrySet()) { URL url = entry.getKey(); Set<NotifyListener> listeners = entry.getValue(); for (NotifyListener listener : listeners) { doUnsubscribe(url, listener); listeners.remove(listener); } } } if (! failedNotified.isEmpty()) { for (Map<NotifyListener, List<URL>> values : failed.values()) { for (Map.Entry<NotifyListener, List<URL>> entry:values.entrySet()) { NotifyListener listener = entry.getKey(); List<URL> urls = entry.getValue(); listener.notify(urls); values.remove(listener