对于异常的处理,Spring Boot中提供默认的一个异 常处理界面,如下图:
常处理界面,如下图:
但是在实际的运用开发中,这样的页面显然是不友好的,Spring Boot也提供了自定义异常处理的方式,如下总结三种一场处理方式
1. 实现ErrorController接口的方式
实现ErrorController接口,重写getErrorPath()方法,路径指向自定义的error页面。代码如下:
package com.wangx.boot.controller; import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.error.ErrorController; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class BaseException implements ErrorController { @Override public String getErrorPath() { return "error/error"; } @RequestMapping public String error() { return getErrorPath(); } }
页面目录结构:
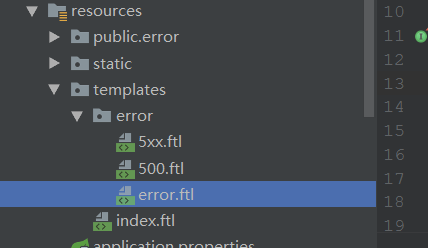
这样当出现异常时就会映射error目录下的error.ftl视图。这是所有错误都会映射该试图。
2. 静态页面和模板引擎的异常处理
静态页面直接在resources目录下添加public/error/404.html,此时如果出现路径找不到异常,就会直接映射到该页面。
运行结果为: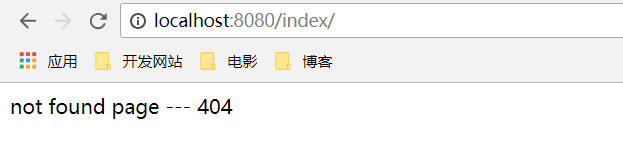
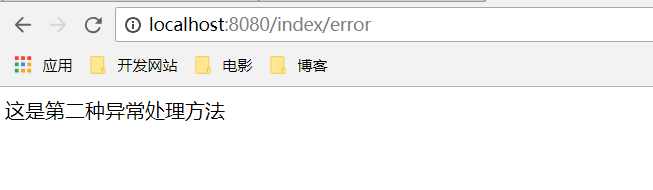
模板引擎则需要在templates目录下的添加error/5xx.ftl视图,如1中的5xx.ftl,Spring Boot也会自动根据状态码映射该试图,如这里的5xx.ftl可以改为500.ftl,这样报500时也会映射该试图,运行结果如下:
3. 使用@ControllerAdvice、@ExceptionHandler、@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK)处理异常
这种方式可以@ExceptionHandler({RuntimeException.class})处理不同的异常
代码如下:
package com.wangx.boot.controller; import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseStatus; import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView; @ControllerAdvice public class BizExceptionHander { @ExceptionHandler({RuntimeException.class}) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public ModelAndView processException(RuntimeException r) { ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.addObject("exceptions", r.getMessage()); modelAndView.setViewName("error/500"); return modelAndView; } @ExceptionHandler({Exception.class}) @ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.OK) public String xception(Exception r) { ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.addObject("exceptions", r.getMessage()); return "error/500"; } }
在出现RuntimeException时执行第一个方法,Exception时执行第二个方法,拦截处理什么样的异常由ExceptionHandler注解中的异常类的字节码文件决定,设置异常路径为error/500,在error/500下新建500.ftl视图
500.ftl
<body>这是第三种种异常处理方法.异常信息:${exceptions}
</body>
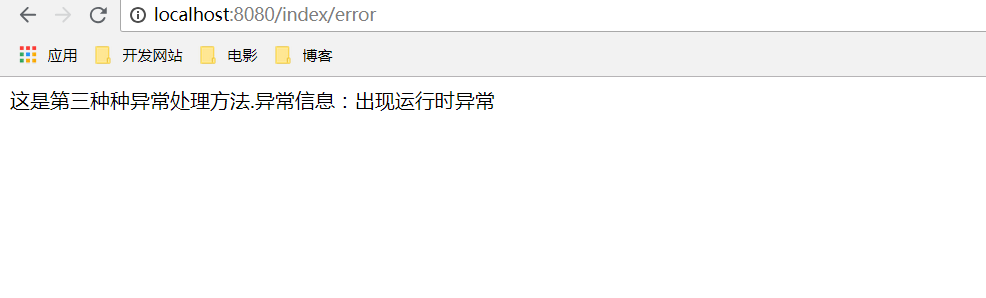
在IndexController.java中使方法抛出运行时一场(2中的异常也是此方式测试的,抛出500状态码)
IndexController.java
package com.wangx.boot.controller; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import java.util.Map; @Controller @RequestMapping("/index") public class IndexController { @RequestMapping("/index") public String hello(Map<String,Object> map){ //传递数据到freemaker模板中 map.put("name", "[Angel -- 守护天使]"); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/error") public String erroe(Map<String,Object> map){ throw new RuntimeException("出现运行时异常"); } }
运行结果:
这里只是简单的异常处理使用方式测试示例,可以根据自己的需求,选择不同的异常处理方式。