第一次写计算几何题,要判断2个线段是否相交。
借鉴了刘汝佳《算法竞赛入门经典里面的》代码,但是没做(我实在是太菜了)
我的思想是相交有以下3种情况
- 规范相交(2个线段恰好有一个公共点,且不在任何一条线段上)
可转化为 叉积的符号不同 - 两线段在端点处相交
- 一个线段中的端点在另一个线段上
撕了一会代码,Wrong Answer(绝望了。。)
然后google了一下过了的代码,发现一个很简洁的思路
顺带复习了一下向量的叉积和点积
两向量的点积
点积是一个值,表示二者的长度再乘上它们夹角的余弦。
如果夹角大于90度,那么点击就是负数。
两向量的叉积
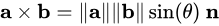
叉积是一个向量,其方向垂直于2个向量确定的平面,再进一步的方向由右手规则确定。
其中右手食指指向A的方向,右手中指指向B的方向,拇指方向即为叉积确定向量方向
可用如下代码计算:
// 叉积
double Cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
判断两线段相交的方法
判断两线段是否相交:
我们分两步确定两条线段是否相交:
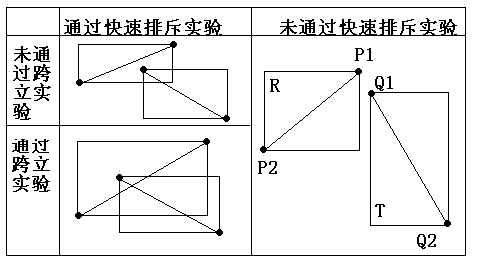
(1)快速排斥试验
设以线段 P1P2 为对角线的矩形为R, 设以线段 Q1Q2 为对角线的矩形为T,如果R和T不相交,显然两线段不会相交。
(2)跨立试验
如果两线段相交,则两线段必然相互跨立对方。若P1P2跨立Q1Q2 ,则矢量 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和( P2 - Q1 )位于矢量( Q2 - Q1 ) 的两侧,即( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( P2 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) < 0。上式可改写成( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) > 0。当 ( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) = 0 时,说明 ( P1 - Q1 ) 和 ( Q2 - Q1 )共线,但是因为已经通过快速排斥试验,所以 P1 一定在线段 Q1Q2上;同理,( Q2 - Q1 ) ×(P2 - Q1 ) = 0 说明 P2 一定在线段 Q1Q2上。所以判断P1P2跨立Q1Q2的依据是:( P1 - Q1 ) × ( Q2 - Q1 ) * ( Q2 - Q1 ) × ( P2 - Q1 ) >= 0。同理判断Q1Q2跨立P1P2的依据是:( Q1 - P1 ) × ( P2 - P1 ) * ( P2 - P1 ) × ( Q2 - P1 ) >= 0。具体情况如下图所示:
My Wrong Answer Code And Online AC Code
/*
核心:判断2线段是否相交(需要考虑端点的情况)
*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//using namespace std;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const int maxn=105;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
//构造函数
//Point(double x=0,double y=0 ):x(x),y(y){}
Point(double x,double y ):x(x),y(y){}
Point():x(0),y(0){}
};
typedef Point Vector;// 别名
const double eps=1e-10;
Vector operator + (Vector A,Vector B)
{
return Vector(A.x+B.x,A.y+B.y);
}
Vector operator - (Point A,Point B)
{
return Vector(A.x-B.x,A.y-B.y);
}
Vector operator * (Point A,double p)
{
return Vector(A.x*p,A.y*p);
}
Vector operator / (Point A,double p)
{
return Vector(A.x/p,A.y/p);
}
bool operator <(const Point&a,const Point &b)
{
return a.x<b.x||(a.x==b.x&&a.y<b.y);
}
//向量判断符号
int dcmp(double x)
{
if(fabs(x)<eps)
return 0;
else
return x<0?-1:1;
}
bool operator ==(const Point&a,const Point &b)
{
return dcmp(a.x-b.x)==0 &&dcmp(a.y-b.y)==0;
}
//点积
double Dot(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.x+A.y*B.y;
}
// 叉积
double Cross(Vector A,Vector B)
{
return A.x*B.y-A.y*B.x;
}
// 判断线段相交,忽略两端点
bool SegmentProperIntersection(Point a1,Point a2,Point b1,Point b2)
{
double c1=Cross(a2-a1,b1-a1), c2=Cross(a2-a1,b2-a1),
c3=Cross(b2-b1,a1-b1), c4=Cross(b2-b1,a2-b1);
return dcmp(c1)*dcmp(c2)<0 && dcmp(c3)*dcmp(c4)<0;
}
// 点是否在线段上
bool OnSegment(Point p,Point a1,Point a2)
{
return dcmp(Cross(a1-p,a2-p))==0&&dcmp(Dot(a1-p,a2-p))<0;
}
std::vector<Point> vec[maxn];
int main()
{
int t;
while(scanf("%d",&t)!=EOF)
{
if(t==0)
break;
double x1,y1,x2,y2;
for(int i=0;i<t;i++)
{
scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x1,&y1,&x2,&y2);
vec[i].push_back(Point(x1,y1));
vec[i].push_back(Point(x2,y2));
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<t;i++)
{
for(int j=i+1;j<t;j++)
{
if(vec[i][0]==vec[j][0]||vec[i][0]==vec[j][1]||vec[i][1]==vec[j][0]||vec[i][1]==vec[j][1])
{
cnt++;
continue;
}
if(OnSegment(vec[i][0],vec[j][0],vec[j][1])||OnSegment(vec[i][1],vec[j][0],vec[j][1]))
{
cnt++;
continue;
}
if(OnSegment(vec[j][0],vec[i][0],vec[i][1])||OnSegment(vec[j][1],vec[i][0],vec[i][1]))
{
cnt++;
continue;
}
if(SegmentProperIntersection(vec[i][0],vec[i][1],vec[j][0],vec[j][1]))
{
cnt++;
continue;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",cnt);
}
return 0;
}
/*
//网络上AC的代码
//参考了http://dev.gameres.com/Program/Abstract/Geometry.htm#%E8%AE%A1%E7%AE%97%E7%82%B9%E5%88%B0%E7%BA%BF%E6%AE%B5%E7%9A%84%E6%9C%80%E8%BF%91%E7%82%B9
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
#include <set>
//#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <utility>
#include <iomanip>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <ctime>
#include <ctype.h>
using namespace std;
#define L __int64
struct point{ //点结构
double x, y;
point (double a = 0, double b = 0) {x = a, y = b;}
};
struct line{ //线段结构
point s, e;
line (point a, point b) {s = a, e = b;}
line (){}
}l[105];
double multi (point a, point b, point c) //叉积判断点线关系
{
double x1, y1, x2, y2;
x1 = b.x - a.x;
y1 = b.y - a.y;
x2 = c.x - b.x;
y2 = c.y - b.y;
return x1*y2 - x2*y1;
}
bool intersect (line a, line b) //判断两线段是否相交
{
if (max (a.s.x, a.e.x) >= min (b.s.x, b.e.x) && //快速排斥试验
max (b.s.x, b.e.x) >= min (a.s.x, a.e.x) &&
max (a.s.y, a.e.y) >= min (b.s.y, b.e.y) &&
max (b.s.y, b.e.y) >= min (a.s.y, a.e.y) &&
multi (a.s, b.s, b.e)*multi (a.e, b.s, b.e) <= 0 && //跨立试验
multi (b.s, a.s, a.e)*multi (b.e, a.s, a.e) <= 0)
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
int n, i, res, j;
while (scanf ("%d", &n), n)
{
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
scanf ("%lf%lf%lf%lf", &l[i].s.x, &l[i].s.y, &l[i].e.x, &l[i].e.y);
res = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++)
if (intersect (l[i], l[j]))
res++;
printf ("%d\n", res);
}
return 0;
}
*/