文章目录
NFS介绍
- NFS是Network File System的缩写
- NFS最早由Sun公司开发,分2,3,4三个版本,2和3由Sun起草开发,4.0开始Netapp公司参与并主导开发,最新为4.1版本
- NFS数据传输基于RPC协议,RPC为Remote Procedure Call的简写。
- NFS应用场景是:A,B,C三台机器上需要保证被访问到的文件是一样的,A共享数据出来,B和C分别去挂载A共享的数据目录,从而B和C访问到的数据和A上的一致


总结:NFC服务需要借助RPC协议实现通信
NFS服务端安装配置
实验需要2台机器,一台作为服务端,一台作为客户端。两台机器需要支持互相可以ping通。
服务端,安装2个包
nfs-utils和rpcbind
# yum install -y nfs-utils rpcbind
省略。。。。
Installed:
nfs-utils.x86_64 1:1.3.0-0.54.el7 rpcbind.x86_64 0:0.2.0-44.el7
客户端,安装包nfs-utils
# yum install -y nfs-utils
省略。。。。
Installed:
nfs-utils.x86_64 1:1.3.0-0.54.el7
编辑配置文件
#编辑exports文件
# vim /etc/exports
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.1.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000) //指定共享的机器ip地址段
:wq
创建分享的目录,给创建的目录赋予777的权限。
# mkdir /home/nfstestdir
# chmod 777 /home/nfstestdir
服务端启动rpcbind并查看监听端口情况
# systemctl start rpcbind
# netstat -lnpt
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 9092/rpcbind
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 967/sshd
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:443 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1002/nginx: master
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:32000 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 888/java
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 9092/rpcbind
tcp6 0 0 :::3306 :::* LISTEN 2884/mysqld
111端口已经启动了
客户端启动rpcbind并查看监听端口情况
# systemctl start rpcbind
# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 22898/rpcbind
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 878/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1113/master
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 22898/rpcbind
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 878/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1113/master
# ps aux |grep rpc
rpc 22898 0.0 0.0 64956 1048 ? Ss 20:39 0:00 /sbin/rpcbind -w
root 23120 0.0 0.0 112660 968 pts/0 R+ 20:39 0:00 grep --color=auto rpc
服务端启动NFS
# systemctl start nfs
# ps aux |grep nfs
root 9205 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 20:26 0:00 [nfsd4_callbacks]
root 9211 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9212 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9213 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9214 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9215 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9216 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9217 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9218 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S 20:26 0:00 [nfsd]
root 9225 0.0 0.0 112660 968 pts/2 R+ 20:26 0:00 grep --color=auto nfs
# ps aux |grep rpc
rpc 9092 0.0 0.1 64956 1412 ? Ss 20:18 0:00 /sbin/rpcbind -w
rpcuser 9174 0.0 0.1 42376 1752 ? Ss 20:26 0:00 /usr/sbin/rpc.statd
root 9181 0.0 0.0 0 0 ? S< 20:26 0:00 [rpciod]
root 9185 0.0 0.0 43816 544 ? Ss 20:26 0:00 /usr/sbin/rpc.idmapd
root 9195 0.0 0.0 42564 948 ? Ss 20:26 0:00 /usr/sbin/rpc.mountd
root 9229 0.0 0.0 112660 968 pts/2 R+ 20:27 0:00 grep --color=auto rpc
服务端开机启动NFS
# systemctl enable nfs
Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/nfs-server.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/nfs-server.service.
NFS配置选项
# cat /etc/exports
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.106.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000)
含义:
- rw: 读写
- ro: 只读
- sync: 同步模式,内存数据实时写入磁盘
- async :非同步模式
- no_root_squash: 客户端挂载NFS共享目录后,root用户不受约束,权限很大
- root_squash: 与上面选项相对,客户端上的root用户收到约束,被限定成某个普通用户
- all_squash: 客户端上所有用户在使用NFS共享目录时都被限定为一个普通用户
- anonuid/anongid: 和上面几个选项搭配使用,定义被限定用户的uid和gid
客户端挂载
# showmount -e 192.168.106.128
clnt_create: RPC: Port mapper failure - Unable to receive: errno 113 (No route to host)
有报错,检查客户端服务端服务都已经启动,端口也已经开放,如果网络都能ping通,那就需要关闭防火墙,服务端客户端都关闭。
服务端
# systemctl stop firewalld
# setenforce 0
setenforce: SELinux is disabled
客户端
# systemctl stop firewalld
# getenforce
Enforcing
# setenforce 0
连接服务端IP成功
# showmount -e 192.168.106.128
Export list for 192.168.106.128:
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.106.0/24
挂载服务端共享的目录,用df -h测试,挂载成功
# mount -t nfs 192.168.106.128:/home/nfstestdir /mnt
# df -h
Filesystem Size Used Avail Use% Mounted on
/dev/sda3 28G 1011M 27G 4% /
devtmpfs 907M 0 907M 0% /dev
tmpfs 916M 0 916M 0% /dev/shm
tmpfs 916M 8.8M 908M 1% /run
tmpfs 916M 0 916M 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
/dev/sda1 197M 113M 85M 58% /boot
tmpfs 184M 0 184M 0% /run/user/0
192.168.106.128:/home/nfstestdir 28G 7.3G 21G 27% /mnt //最后一行为远程服务端
由于配置文件上设置了属主和属组,可以看到文件的属主和属组都为1000
客户端:创建文件,创建的文件的属主和属组都为1000,由于没有该用户,都用1000代替
[root@linux-02 mnt]# touch zyshanlinux.111
[root@zyshanlinux-02 mnt]# ls -l
total 0
-rw-r--r--. 1 1000 1000 0 Jul 15 21:20 zyshanlinux.111
[root@linux-02 mnt]# id 1000
id: 1000: no such user
服务端:客户端创建的文件在服务端查看,属主是user1,属组是1000
[root@linux-001 ~]# ls -l /home/nfstestdir
total 0
-rw-r--r-- 1 user1 1000 0 Jul 15 21:20 zyshanlinux.111
[root@linux-001 ~]# id user1
uid=1000(user1) gid=1001(user1) groups=1001(user1)
exportfs命令
常用选项
- a 全部挂载或者全部卸载
- r 重新挂载
- u 卸载某个目录
- v 显示共享目录
如果要服务端要关闭或重启NFS,需要先把客户端挂载服务端的目录先卸载
[root@linux-02 mnt]# umount /mnt
umount.nfs4: /mnt: device is busy
[root@linux-02 mnt]# cd
[root@linux-02 ~]# umount /mnt
[root@linux-02 ~]#
由于服务端不能随意关闭或重启nfs,会导致客户端正在挂载的目录读写会出现问题。引入了exportfs命令,不许重启NFS服务,配置文件也会生效。
修改配置文件
[root@linux-001 ~]#vim /etc/exports
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.106.0/24(rw,sync,all_squash,anonuid=1000,anongid=1000)
//新增配置内容,记得IP是允许的客户端IP
/tmp 192.168.106.130(rw,sync,no_root_squash)
服务端,全部共享目录重新挂载并显示,不用重启nfs服务,配置文件就会生效
[root@linux-001 ~]# exportfs -arv
exporting 192.168.106.130:/tmp
exporting 192.168.106.0/24:/home/nfstestdir
客户端也生效了
[root@linux-02 ~]# showmount -e 192.168.106.128
Export list for 192.168.106.128:
/home/nfstestdir 192.168.106.0/24
/tmp 192.168.106.130
客户端挂载
[root@linux-02 ~]# mount -t nfs 192.168.106.128:/tmp/ /mnt/
[root@linux-02 ~]# cd /mnt
[root@linux-02 mnt]# ls
mysql2.sql systemd-private-d14aa6709ba64c9ca559b305bd7b0b86-chronyd.service-Tpa4NU
mysql_all.sql systemd-private-d14aa6709ba64c9ca559b305bd7b0b86-vgauthd.service-iHfxUd
mysql.sock systemd-private-d14aa6709ba64c9ca559b305bd7b0b86-vmtoolsd.service-mSuqtC
mysql.sql test.com.log
pear test.com.log-20180704
php_errors.log-20180704 user.sql
php-fcgi.sock
由于配置文件中写了no_root_squash,所以客户端和服务端属主属组的差异
[root@linux-02 mnt]# vi 1212.txt
[root@linux-02 mnt]# ls -l 1212.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 28 Jul 15 22:21 1212.txt
[root@linux-001 tmp]# ls -l 1212.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 root root 28 Jul 15 22:21 1212.txt
在客户端挂载目录下,就像在服务端使用root一样,是不受限制的。
NFS客户端问题
问题
- NFS 4版本会有该问题
- 客户端挂载共享目录后,不管是root用户还是普通用户,创建新文件时属主、属组为nobody
解决方法
- 客户端挂载时加上 -o nfsvers=3
- 客户端和服务端都需要 vim /etc/idmapd.conf
// 把#Domain = local.domain.edu改为Domain = xxx.com(这里的xxx.com,随意定义) - 再重启rpcidmapd服务
FTP介绍
-
FTP 是File Transfer Protocol (文件传输协议,简称文传协议)的英文简称,用于在Internet上控制文件的双向传输。
-
FTP的主要作用就是让用户连接一个远程计算机(这些计算上运行着FTP服务器程序),并查看远程计算机中的文件,然后把文件从远程计算机复制到本地计算机,或把本地计算机的文件传送到远程计算机。
-
小公司用的多,大企业不用FTP ,因为不安全
rz和sz传文件受限制比较大
rz:window–>linux
sz:linux–>window 文件超过4GB则不管用)
使用vsftpd搭建ftp服务
安装
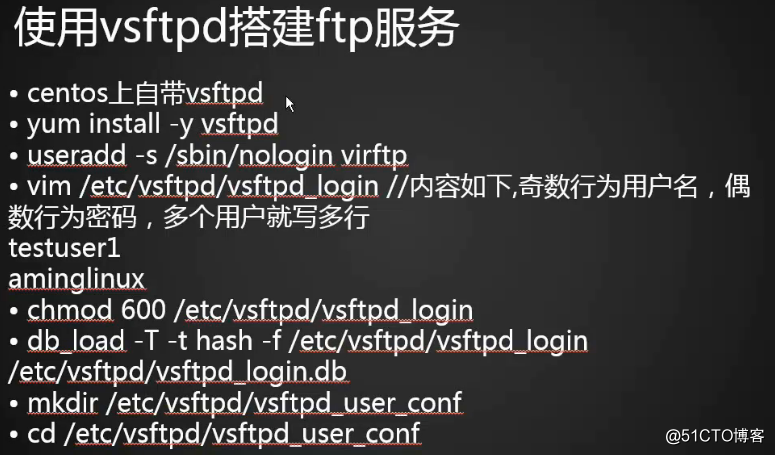
安装服务
# yum install -y vsftpd
省略。。。
已安装:
vsftpd.x86_64 0:3.0.2-22.el7
创建一个普通用户
# useradd -s /sbin/nologin virftp //指定用户的shell为nologin,不允许登录
vsftpd软件是允许系统用户以ftp方式(非SSH)登录系统的,登录后会进入用户家目录,为了安全起见,我们使用虚拟ftp用户映射到真实系统用户的方式,使用ftp服务,从而避免ftp用户直接登录系统。
创建虚拟ftp用户配置文件
# vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_login
user1 //奇数行 写用户名
12345678 //偶数行 写密码
user2 //多个用户就写多组,中间不能有空行和空格
12345678
更改权限
# chmod 600 /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_login
将文本文件转换成二进制文件
# db_load -T -t hash -f /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_login /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_login.db
创建虚拟用户的配置文件目录
# mkdir /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_user_conf
# cd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_user_conf
创建虚拟用户的配置文件
# vim user1 //此处的文件名必须和/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_login文件里的用户名一致。
local_root=/home/virftp/user1 //定义虚拟用户的家目录
anonymous_enable=NO //不允许匿名用户登陆,如果允许则用YES
write_enable=YES //写权限,允许
local_umask=022 //设定umask,用来控制用户创建文件和目录的默认权限
anon_upload_enable=NO //不允许匿名用户上传
anon_mkdir_write_enable=NO //不允许匿名用户创建目录和写权限
idle_session_timeout=600 //空闲时限600秒,超时自动断开
data_connection_timeout=120 //数据连接(请求)时限120秒,超时会自动断开
max_clients=10 //客户端的最大连接数
创建虚拟ftp用户的家目录,并创建测试文件
# mkdir /home/virftp/user1
# touch /home/virftp/user1/test.txt
级联更改系统用户virftp家目录的属主属组
# chown -R virftp:virftp /home/virftp
定义密码文件
# vim /etc/pam.d/vsftpd
#%PAM-1.0
//新增如下两行,注意区分系统是32位还是64位
auth sufficient /lib64/security/pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_login //指定密码验证形式为文件形式,并指定路径路径
account sufficient /lib64/security/pam_userdb.so db=/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_login //指定账户存储形式为文件,并指定账户存储文件路径
session optional pam_keyinit.so force revoke
auth required pam_listfile.so item=user sense=deny file=/etc/vsftpd/ftpusers onerr=succeed
auth required pam_shells.so
auth include password-auth
account include password-auth
session required pam_loginuid.so
session include password-auth
配置vsftp服务
# vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
将anonymous_enable=YES 改为 anonymous_enable=NO //不允许匿名用户登录
将#anon_upload_enable=YES 改为 anon_upload_enable=NO //不允许匿名用户上传
将#anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES 改为 anon_mkdir_write_enable=NO //不允许匿名用户创建目录和写入
再增加如下内容
chroot_local_user=YES //允许切换到系统用户
guest_enable=YES //打开来宾用户
guest_username=virftp //定义来宾用户为virftp
virtual_use_local_privs=YES //允许虚拟用户映射到系统用户
user_config_dir=/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd_user_conf //定义用户配置文件目录
allow_writeable_chroot=YES //允许写权限
启动服务:查看服务启动以及监听端口
# systemctl start vsftpd
# ps aux |grep vsftpd
root 1701 0.0 0.0 53212 572 ? Ss 22:11 0:00 /usr/sbin/vsftpd /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf
root 1703 0.0 0.0 112676 984 pts/0 S+ 22:11 0:00 grep --color=auto vsftpd
# netstat -lntp
Active Internet connections (only servers)
Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State PID/Program name
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:111 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp 0 0 192.168.122.1:53 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1165/dnsmasq
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:22 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 972/sshd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:631 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 973/cupsd
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:25 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1076/master
tcp6 0 0 :::111 :::* LISTEN 1/systemd
tcp6 0 0 :::21 :::* LISTEN 1701/vsftpd
tcp6 0 0 :::22 :::* LISTEN 972/sshd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:631 :::* LISTEN 973/cupsd
tcp6 0 0 ::1:25 :::* LISTEN 1076/master
测试
安装lftp客户端
# yum install -y lftp
省略。。。
已安装:
lftp.x86_64 0:4.4.8-8.el7_3.2
完毕!
以user1用户的身份访问ftp服务器,并输入密码
# lftp [email protected]
口令:
lftp [email protected]:~> ls //执行命令ls,看是否正常输出
-rw-r--r-- 1 1000 1000 0 Oct 06 14:02 test.txt
lftp [email protected]:/> ? //问号可以查看它可以使用哪些命令
lftp [email protected]:/> get test.txt //将test.txtget到当前目录下
lftp [email protected]:/> quit //退出
[root@linux7-128 vsftpd_user_conf]# ls //查看当前目录是否有test.txt
test.txt user1
若不正常查看日志/var/log/messages和/var/log/secure
windows下安装filezilla客户端软件,进行测试
使用Xshell以SFTP协议登录到系统
新建会话,定义会话名称,选择SFTP协议,输入服务器地址和端口,和ssh协议端口一致即可

在左侧SFTP选项这里定义本地文件目录和远程文件目录,用来保存文件

确定保存,使用系统用户登录

xshell使用xftp传输文件
在xshell的窗口里,同时按ctrl+alt+f 组合键,会弹出xftp的下载链接按照指引下载家庭与学校用的那个版本,并安装打开xshell客户端,使用系统用户登录到服务器,然后使用ctrl+alt+f 组合键打开xftp窗口,左边是本地目录,右边是服务器目录,双击鼠标可以快速复制文件到另一端去,也可以选中文件使用右键选项。

必须要先登录到系统,才可以使用xftp,否则会弹出窗口让你配置远程服务器信息,无论使用ssh还是sftp协议登录都可以使用xftp功能。
使用pure-ftpd搭建ftp服务

安装
安装软件包
# yum install -y epel-release
# yum install -y pure-ftpd
配置pure-ftpd服务
# vim /etc/pure-ftpd/pure-ftpd.conf
PureDB /etc/pure-ftpd/pureftpd.pdb //将这行前面的#去掉
关闭vsftpd服务,开启pure-ftpd服务
# systemctl stop vsftpd
# systemctl start pure-ftpd
# ps aux |grep ftp
root 2503 0.0 0.1 202480 1204 ? Ss 23:28 0:00 pure-ftpd (SERVER)
root 2505 0.0 0.0 112676 980 pts/0 S+ 23:28 0:00 grep --color=auto ftp
创建测试目录并建系统用户和用户组,指定uid,gid
[root@linux7-128 ~]# mkdir /data/ftp
[root@linux7-128 ~]# groupadd -g 1010 pure-ftp
[root@linux7-128 ~]# useradd -u 1010 -g pure-ftp pure-ftp
级联更改文件共享目录属主属组
# chown -R pure-ftp:pure-ftp /data/ftp
使用pure-pw命令创建虚拟ftp用户并指定映射的系统用户和家目录
# pure-pw useradd ftp_user1 -u pure-ftp -d /data/ftp
Password:
Enter it again:
- 使用
pure-pw help命令,查看pure-pw命令的使用说明; - 使用
pure-pw list命令,查看所有ftp用户和所在目录; - 使用
pure-pw mkdb命令,生成pure-ftp识别的密码文件;
测试
# pure-pw mkdb
# touch /data/ftp/123.txt
# lftp [email protected]
口令:
lftp [email protected]:~> ls
drwxr-xr-x 2 1010 pure-ftp 21 Oct 6 23:42 .
drwxr-xr-x 2 1010 pure-ftp 21 Oct 6 23:42 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 0 0 0 Oct 6 23:42 123.txt
lftp [email protected]:/> quit
[root@linux7-128 ~]# chown pure-ftp:pure-ftp /data/ftp/123.txt
[root@linux7-128 ~]# lftp [email protected]
口令:
lftp [email protected]:~> ls
drwxr-xr-x 2 1010 pure-ftp 21 Oct 6 23:42 .
drwxr-xr-x 2 1010 pure-ftp 21 Oct 6 23:42 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 1010 pure-ftp 0 Oct 6 23:42 123.txt