内容:
第一章:
- 内存管理
- IL
- 框架
- C# 7和6的特性
第二章: C#基础
- 编译
- 避免keyword冲突
- 类型
- 数字类型
- Bool
- String
- Array
- 变量和参数Null
- Statement
- Namespace
第一章 介绍C#和 .NET Framework
内存管理
C# 依赖runtime来执行自动内存管理。比如.NET Framework中的 Common Language Runtime(CLR)。 同时C#也没有完全不允许使用指针, 对于性能要求高的地方,也可以使用unsafe来表示自己进行内存管理。
IL
C#语言的 managed code 叫做Intermediate Language(IL) , CLR通常是在执行前,将IL转换成native machien code,这叫做 Just-In-Time(JIT)编译。 也有提前编译用来增加性能。
IT是被叫做 assembly包含的, assembly可以是一个 .exe 也可以是一个dll。 assembly包含IL还有其他的 metadata。
框架
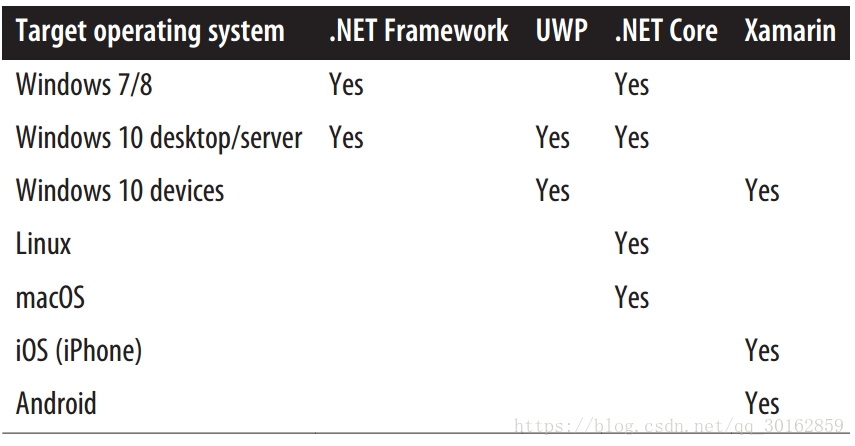
- .NET Framework
- Universal Windows Platform(UWP)
- .NET Core + ASP.NET Core
- Xamarin
四个框架的主要区别他们支持的平台不同、上层library不同,还有使用目的不同。
近期版本语言新增特点
C# 7.0
1.数字字面量
int million = 1_000_000; // 数字中间加上 下划线增加可读性
var b = 0b1010_1011_1100_1101_1110_1111; // 0b 开头表示二进制2.Out变量创建和丢弃
bool successful = int.TryParse ("123", out int result); //不需要提前创建变量来使用out
SomeBigMethod (out _, out _, out _, out int x, out _, out _, out _); //对于不关心的值,可以使用 _ 来丢弃
3.Pattern Variable
void Foo (object x)
{
if (x is string s) // 使用is,通过判断来创建变量
Console.WriteLine (s.Length);
}
switch (x)
{
case int i:
Console.WriteLine ("It's an int!");
break;
case string s:
Console.WriteLine (s.Length); // We can use the s variable
break;
case bool b when b == true: // Matches only when b is true
Console.WriteLine ("True");
break;
case null: // 可以和null比较
Console.WriteLine ("Nothing");
break;
}4.local methods
void WriteCubes()
{
Console.WriteLine (Cube (3));
Console.WriteLine (Cube (4));
Console.WriteLine (Cube (5));
int Cube (int value) => value * value * value; //在方法中创建方法
}5.箭头语法的扩展
public class Person
{
string name;
public Person (string name) => Name = name; //构造函数
public string Name
{
get => name;
set => name = value ?? ""; //set的支持
}
~Person () => Console.WriteLine ("finalize"); //析构函数
}6.Deconstructor
从类对象中抽取值
public void Deconstruct (out string firstName, out string lastName)
{
int spacePos = name.IndexOf (' ');
firstName = name.Substring (0, spacePos);
lastName = name.Substring (spacePos + 1);
}
var joe = new Person ("Joe Bloggs");
var (first, last) = joe; // Deconstruction7.Tuples
var bob = ("Bob", 23); //System.ValueTuple<...> 的语法糖
Console.WriteLine (bob.Item1); // Bob
var tuple = (Name:"Bob", Age:23);
Console.WriteLine (tuple.Name); // Bob8.throw 表达式
throw可以不必要一定是一条完整的语句了,可以作为一个表达式。
public string Foo() => throw new NotImplementedException();
value == null ? throw new ArgumentException ("value") : "";
C# 6.0
1.Roslyn编译器
2.null-conditional
string result = sb?.ToString(); // result is null
3.Expression-bodied functions
public int TimesTwo (int x) => x * 2;
public string SomeProperty => "Property value";4.Index initializers
对有索引的类型都可以直接进行初始化
var dict = new Dictionary<int,string>()
{
[3] = "three",
[10] = "ten"
};5.String interpolation
string s = $"It is {DateTime.Now.DayOfWeek} today";
6.Exception filters
try
{
html = new WebClient().DownloadString ("http://asef");
}
catch (WebException ex) when (ex.Status == WebExceptionStatus.Timeout) // 对catch的情况进一步筛选
{
...
}7.using static 引入静态成员
using static System.Console;
第二章 C#语言基础
编译
C#把.cs文件编译成assembly, assembly是打包或者部署的单元, 有 可执行文件和library两种。 .dll文件就相当于没有Main这个入口函数的可执行文件。 而 .NET Framework则是由一系列的library构成。
csc MyFirstProgram.cs
csc /target:library MyFirstProgram.cs避免keyword冲突
使用@
class @class {...} // Legal,@不是名字的一部分,这个类的名字还是class
类型
- 值类型
- 引用类型
- 泛型引用类型
- 指针类型
值类型除了包含所有的数字类型、char、bool、enum、struct。 所有值类型都是的传值都是完全复制。
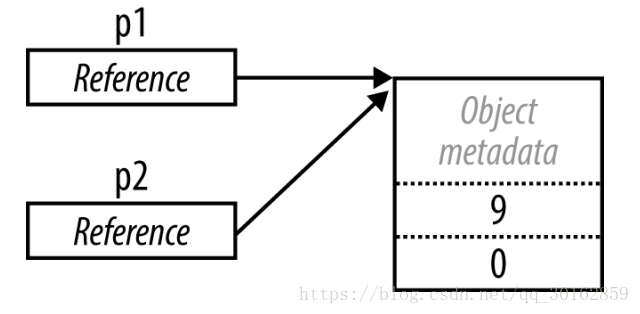
引用类型的存储包括 引用类型变量和对象,对象除了其中的字段所需要的内存外,还有额外的开销。这些开销是对.NET Runtime决定的,最起码8个bytes, 包括对象类型、锁的状态、是否被垃圾回收; 而引用类型对象的占用内存大小,取决于底层是32位还是64位平台。
除开decimal以外的值类型又叫做primitive type,因为他们编译后的结果能够直接被指令来操作。
数字类型
| C# 类型 | System类型 | 后缀 | Size | 范围 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 有符号整形 | ||||
| sbyte | SByte | 8bits | -2^7 ~ 2^7-1 | |
| short | Int16 | 16bits | -2^15 ~ 2^15-1 | |
| int | Int32 | 32bits | -2^31 ~ 2^31-1 | |
| long | Int64 | L | 64bits | -2^63 ~ 2^63-1 |
| 无符号整形 | ||||
| byte | Byte | 8bits | 0 ~ 2^8-1 | |
| ushort | UInt16 | 16bits | 0 ~ 2^16-1 | |
| uint | UInt32 | U | 32bits | 0 ~ 2^32-1 |
| ulong | UInt64 | L | 64bits | 0 ~ 2^64-1 |
| 实数 | ||||
| float | Single | F | 32bits | ± (~10^–45 to 10^38) |
| double | Double | D | 64bits | ± (~10^–324 to 10^308) |
| decimal | Decimal | M | 128bits | ± (~10^–28 to 10^28) |
整数 中,int 和long是一等公民。
overflow
overflow是在runtime时发生的,默认不报错。
int a = int.MinValue;
a--;
Console.WriteLine (a == int.MaxValue); // True使用checked来告诉runtime,如果overflow发生了就抛出OverflowException。对于Double和Float,checked不起作用,而对于decimal类型来说,它overflow永远会报错。
int c = checked (a * b); // Checks just the expression.
checked // Checks all expressions
{ // in statement block.
...
c = a * b;
...
}
int y = unchecked (x + 1); // 当对全局使用了checked时,指定不check的命令
而对于编译时,常数之间运算发生的overflow,编译器会抛出异常
int x = int.MaxValue + 1; // Compile-time error
int y = unchecked (int.MaxValue + 1); // No errorsfloat和double的特殊值
| 特殊值 | double的表示 | float的表示 |
|---|---|---|
| NaN | double.NaN | float.NaN |
| +∞ | double.PositiveInfinity | float.PositiveInfinity |
| −∞ | double.NegativeInfinity | float.NegativeInfinity |
| −0 | −0.0 | −0.0f |
非零除以0的时候,会产生 Infinity; 0除以0 或者 Inifity-Inifity会得到NaN。 使用 double.IsNaN或者float.isNaN来判断NaN
decimal
decimal底层是以10进制方式存储的,且精度很高,所以用于金钱计算。而float和double底层是二进制,所以在运算的时候经常会丢失精度。但是decimal比double慢好几倍。
Bool
bool底层占用一字节。 为了提高bool array的使用效率,System.Collections下有一个 BitArray使用一个bit表示一个bool值。
String
C#的char类型占用2个字节,表示一个Unicode字符。
String也是表示的Unicode字符串,它是引用类型,不可变。 但是对它使用==操作符,效果和对值类型使用一样。
使用@开头表示的字符串,可以占用多行。
使用+来拼接字符串不是很有效率,应该使用 StringBuilder.
interpolated string
后面加上 : 还有格式符
string s = $"255 in hex is {byte.MaxValue:X2}"; // X2 = 2-digit Hexadecimal
string s = $@"this spans {
x} lines";Array
char[] vowels = new char[5]; // Declare an array of 5 characters
char[] vowels = new char[] {'a','e','i','o','u'};
char[] vowels = {'a','e','i','o','u'};
rectangular array
int[,] matrix = new int[3,3]; // 创建并且初始化
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.GetLength(0); i++) //使用 GetLength来获取指定维度上的长度
for (int j = 0; j < matrix.GetLength(1); j++)
matrix[i,j] = i * 3 + j;
int[,] matrix = new int[,] //初始化
{
{0,1,2},
{3,4,5},
{6,7,8}
};jagged array
int[][] matrix = new int[3][]; //指定内层长度,因为外层的长度可以不定; 内层Array会被初始化为null
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.Length; i++) // matrix本身相当于一位数组
{
matrix[i] = new int[3]; // Create inner array
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].Length; j++)
matrix[i][j] = i * 3 + j;
}
int[][] matrix = new int[][]
{
new int[] {0,1,2},
new int[] {3,4,5},
new int[] {6,7,8,9}
};化简初始化
第一种是省去new和 类型
char[] vowels = {'a','e','i','o','u'};
int[,] rectangularMatrix =
{
{0,1,2},
{3,4,5},
{6,7,8}
};
int[][] jaggedMatrix =
{
new int[] {0,1,2},
new int[] {3,4,5},
new int[] {6,7,8}
};第二种是使用var
var rectMatrix = new int[,] // rectMatrix is implicitly of type int[,]
{
{0,1,2},
{3,4,5},
{6,7,8}
};
var jaggedMat = new int[][] // jaggedMat is implicitly of type int[][]
{
new int[] {0,1,2},
new int[] {3,4,5},
new int[] {6,7,8}
};
var vowels = new[] {'a','e','i','o','u'}; // Compiler infers char[]
变量和参数
variable有4种:
- local variable
- parameter
- field
- array element
局部变量和参数在堆里, object在heap上; 且值类型如果是 字段 或者是array的元素,那么它也在heap上; heap也存储静态字段。
字段和数组的元素在创建时会自动初始化; 而局部变量需要我们自己赋值。
默认值
| 类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|
| 引用类型 | null |
| 数字和enum | 0 |
| char | ‘\0’ |
| bool | false |
查看默认值:
decimal d = default (decimal);
ref 和 out
都是按照引用传递的
params
放在参数的最后面,要指定类型,是一个array
static int Sum (params int[] ints)
optional 和 named 参数
ref local 和 ref return
Null
string s2 = s1??"string"; //短路操作
string s = sb?.ToString();Statement
C#是有块级作用域的。
lock是 Monotor类的Enter和Exit方法的快捷方式。
Namespace
namespace Outer.Middle.Inner
相当于
namespace Outer
{
namespace Middle
{
namespace Inner
{
}
}
}没有定义在任何namespace中的类,位于global namespace, 最外层的namespace也被包含于global中。
使用using static:
using static System.Console; //导入类中所有的静态成员
using static System.Windows.Visibility; //导入enum
Namespace的规则
- 调用上一级namespace 的类
namespace Outer
{
class Class1 {}
namespace Inner
{
class Class2 : Class1 {} //调用外层namespace的类,可以不用quanlified name
}
}- 调用同一级namespace的类
namespace MyTradingCompany
{
namespace Common
{
class ReportBase {}
}
namespace ManagementReporting
{
class SalesReport : Common.ReportBase {} //调用同一级namespace的类
}
}- 内外都有同一个类名,内层的掩盖外层
namespace Outer
{
class Foo { }
namespace Inner
{
class Foo { }
class Test
{
Foo f1; // = Outer.Inner.Foo
Outer.Foo f2; // = Outer.Foo
}
}
}
namespace N
{
class A
{
static void Main()
{
System.Console.WriteLine (new A.B());
System.Console.WriteLine (new global::A.B()); // 从global最外层开始指定
}
public class B {}
}
}
namespace A
{
class B {}
}- 在namespace内部使用using
namespace N1
{
class Class1 {}
}
namespace N2
{
using N1;
class Class2 : Class1 {}
}
namespace N2
{
class Class3 : Class1 {} // Compile-time error
}- 别名
using PropertyInfo2 = System.Reflection.PropertyInfo; //给类起别名
class Program { PropertyInfo2 p; } // 给namespace起别名