描述
After the long vacation, the maze designer master has to do his job. A tour company gives him a map which is a rectangle. The map consists of N \times MN×M little squares. That is to say, the height of the rectangle is NN and the width of the rectangle is MM. The master knows exactly how the maze is going to use. The tour company will put a couple in two different squares in the maze and make them seek each other. Of course,the master will not make them find each other easily. The only thing the master does is building some wall between some little squares. He knows in that way, wherever the couple is put, there is only one path between them. It is not a difficult thing for him, but he is a considerate man. He also knows that the cost of building every wall between two adjacent squares is different(Nobody knows the reason). As a result, he designs the maze to make the tour company spend the least money to build it.
Now, here’s your part. The tour company knows you’re the apprentice of the master, so they give you a task. you’re given QQ qustions which contain the information of where the couple will be put. You need to figure out the length of the shortest path between them.
However,the master doesn’t tell you how he designs the maze, but he believes that you, the best student of himself, know the way. So he goes on vacation again.
Input
The first line of the input contains two integers NN and MM (1 \le N,M \le 5001≤N,M≤500), giving the number of rows and columns of the maze.
The next N \times MN×M lines of the input give the information of every little square in the maze, and their coordinates are in order of (1,1)(1,1) , (1,2)(1,2) \cdots⋯ (1,M)(1,M) , (2,1)(2,1) , (2,2)(2,2) , \cdots⋯ , (2,M)(2,M) , \cdots⋯ ,(N,M)(N,M).
Each line contains two characters DD and RR and two integers aa , bb (0 \le a,b \le 20000000000≤a,b≤2000000000 ), aa is the cost of building the wall between it and its lower adjacent square, and bb is the cost of building the wall between it and its right adjacent square. If the side is boundary, the lacking path will be replaced with X 00.
The next line contains an integer QQ (1 \le Q \le 1000001≤Q≤100000 ), which represents the number of questions.
The next QQ lines gives four integers, x_1x1, y_1y1, x_2x2, y_2y2 ( 1 \le x_11≤x1 , x_2 \le Nx2≤N , 1 \le y_11≤y1 , y_2 \le My2≤M ), which represent two squares and their coordinate are (x_1x1 , y_1y1) and (x_2x2 , y_2y2).
(xx,yy) means row xx and column yy.
It is guaranteed that there is only one kind of maze.
Output
For each question, output one line with one integer which represents the length of the shortest path between two given squares.
样例输入
3 3
D 1 R 9
D 7 R 8
D 4 X 0
D 2 R 6
D 12 R 5
D 3 X 0
X 0 R 10
X 0 R 11
X 0 X 0
3
1 1 3 3
1 2 3 2
2 2 3 1样例输出
4
2
2题目来源
思路
先说题意,你需要设计一个矩形的迷宫,这个迷宫是 的,这个迷宫是给情侣设计的,旅游公司会把这对情侣放在迷宫的某两个位置,让他们相互寻找,现在要在迷宫中建造一些墙壁,使得这对情侣之间只有一条路,让他们能够相互找到,在迷宫的两个相邻的格子建造墙壁会有不同花费。旅游公司想花费最少的钱来建造这个迷宫,然后有q个询问,询问你在建立若干堵墙后,使得任意两点间的路径都唯一且花费最少的情况下,两个点之间的距离。
样例给出是首先给出
和
,然后给出
行,每行的D x代表花费x元可以向下建造一个墙壁,R x代表向右建造墙壁的花费,X 0这样代表不能建造。
因为题目要保证只有一条路径可以到达,那么这肯定是一棵树,任意两点路径唯一且花费最少,也就是需要求一下最大生成树,最后求两点之间距离时,求lca即可。
如样例,建图后为:
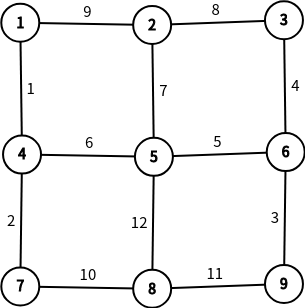
最大生成树为:
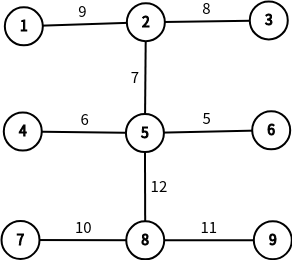
首先建图跑一下最大生成树,在最大生成树上跑lca,我的代码是通过树链剖分实现的,求出最近公共祖先后,两个点和他们的lca的差的绝对值之和就是答案。
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define mem(a, b) memset(a, b, sizeof(a))
typedef long long ll;
const ll N = 1e6 + 10;
ll tot1, n, m;
ll fa[N], dep[N], siz[N], son[N], top[N];
ll first[N], tot, cnt;
ll pre[N];
struct edge
{
ll v, next;
} e[N * 2];
void init()
{
mem(first, -1);
tot = 0;
cnt = 0;
tot1 = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i <= n * m; i++)
pre[i] = i;
}
void add_edge(ll u, ll v)
{
e[tot].v = v;
e[tot].next = first[u];
first[u] = tot++;
}
void dfs1(ll u, ll f, ll deep)
{
fa[u] = f;
dep[u] = deep;
siz[u] = 1;
son[u] = 0;
ll maxson = -1;
for (ll i = first[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
ll v = e[i].v;
if (v == f)
continue;
dfs1(v, u, deep + 1);
siz[u] += siz[v];
if (siz[v] > maxson)
{
son[u] = v;
maxson = siz[v];
}
}
}
void dfs2(ll u, ll topf)
{
top[u] = topf;
if (!son[u])
return;
dfs2(son[u], topf);
for (ll i = first[u]; ~i; i = e[i].next)
{
ll v = e[i].v;
if (v == fa[u] || v == son[u])
continue;
dfs2(v, v);
}
}
ll qlca(ll x, ll y)
{
while (top[x] != top[y])
{
if (dep[top[x]] < dep[top[y]])
swap(x, y);
x = fa[top[x]];
}
return dep[x] < dep[y] ? x : y;
}
struct kedge
{
ll u, v, w;
} ke[N];
ll find(ll x)
{
return x == pre[x] ? x : pre[x] = find(pre[x]);
}
ll mix(ll x, ll y)
{
ll fx = find(x), fy = find(y);
if (fx != fy)
{
pre[fy] = fx;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
bool cmp(kedge a, kedge b)
{
return a.w > b.w;
}
ll kruskal()
{
sort(ke + 1, ke + tot1 + 1, cmp);
ll sum = 0, num = 0;
for (ll i = 1; i <= tot1; i++)
{
if (mix(ke[i].u, ke[i].v))
{
add_edge(ke[i].u, ke[i].v);
add_edge(ke[i].v, ke[i].u);
num++;
sum += ke[i].w;
}
if (num == n * m - 1)
break;
}
return sum;
}
ll abs(ll x, ll y)
{
if (x > y)
return x - y;
return y - x;
}
int main()
{
// freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
char d[2], r[2];
ll a, b;
scanf("%lld%lld", &n, &m);
init();
for (ll i = 1; i <= n * m; i++)
{
scanf("%s%lld%s%lld", d, &a, r, &b);
if (d[0] != 'X')
{
ke[++tot1].u = i;
ke[tot1].v = i + n;
ke[tot1].w = a;
}
if (r[0] != 'X')
{
ke[++tot1].u = i;
ke[tot1].v = i + 1;
ke[tot1].w = b;
}
}
kruskal();
dfs1(1, 0, 1);
dfs2(1, 1);
ll q;
scanf("%lld", &q);
while (q--)
{
ll x1, y1, x2, y2;
scanf("%lld%lld%lld%lld", &x1, &y1, &x2, &y2);
ll x = (x1 - 1) * m + y1, y = (x2 - 1) * m + y2;
ll lca = qlca(x, y);
printf("%lld\n", abs(dep[lca], dep[x]) + abs(dep[lca], dep[y]));
}
return 0;
}