版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/JavaZWT/article/details/81267068
前言
栈(Stack)是限定只能在一段进行插入和删除操作的线性表。
进行插入和删除操作的一端称为“栈顶”(top),另一端称为“栈底”(bottom)。
栈的插入操作称为“入栈”(push),栈的删除 操作称为“出栈”(pop)。
栈具有后进先出(LIFO),先进后出(FILO)的特性。
Stack类
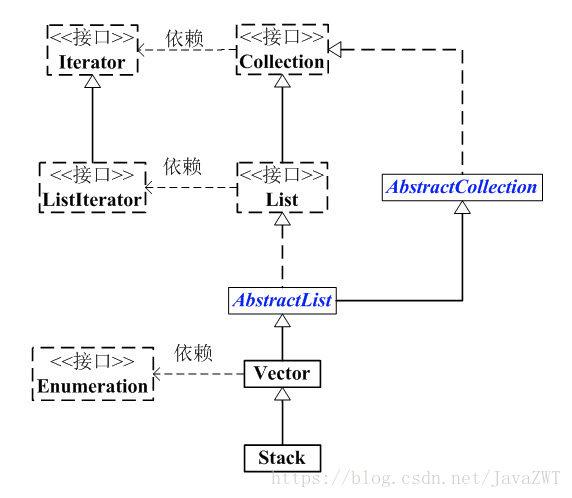
Java工具包下的Stack类继承于Vector,由此可见Stack底层是由数组实现的。
Stack和Collection的关系如下图:
我们来看下Stack的源码:
package java.util;
public
class Stack<E> extends Vector<E> {
/**
* 构造函数
*/
public Stack() {
}
/**
* 将一个元素压入栈顶
*/
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}
/**
* 取出栈顶的一个元素,并删除
*/
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}
/**
* 取出栈顶元素,不删除
*/
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
/**
* 判断栈是不是空
*/
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* 查找元素在栈的位置,没有返回-1
*/
public synchronized int search(Object o) {
int i = lastIndexOf(o);
if (i >= 0) {
return size() - i;
}
return -1;
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1224463164541339165L;
}
根据源码,可以发现Stack的方法调用了Vector类的方法,实现了线程安全。
我们主要看一下Vector里的下面三个方法:
//添加一个元素
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
//确认容量,不够会扩容
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
//移除指定位置的元素
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
//赋空,便于垃圾回收
elementData[elementCount] = null;
}
//找出在指定位置的元素
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
关联方法如下:
//
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
如果长度超了就扩容
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
//扩容方法
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新的容量定义:如果有容量增量且大于0,取增量,否则执行2倍扩容
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
//扩容后容量比传入容量还小,就取传入容量。
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
//新容量比数组最大长度还大
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
//计算容量
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
//计算容量
private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity < 0)
throw new OutOfMemoryError();
return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ?
Integer.MAX_VALUE :
MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}实践
我们如何用数组实现自己的一个stack呢?
public class Stack {
//栈元素组
private Object[] members;
//指针
private int size;
//自定义初始栈长度
public Stack(int initCapacity) throws Exception{
if(initCapacity<=0) {
throw new Exception();
}
this.members=new Object[initCapacity];
}
//默认栈长度为10
public Stack() {
this.members=new Object[10];
}
//元素入栈
public synchronized void push(Object o){
ensureCapacity(size+1);
members[size++]=o;
}
//元素出栈
public synchronized Object pop() throws Exception{
if(size<=0) {
throw new Exception();
}
return members[--size];
}
//查看栈顶元素
public synchronized Object peek() throws Exception{
if(size<=0) {
throw new Exception();
}
return members[size-1];
}
//确认容量
private synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
//size+1比数组长度要长,扩容
if(minCapacity-members.length>0) {
int oldCapacity = members.length;
Object oldMembers=members;
//扩容到二倍
int newCapacity = 2 * oldCapacity ;
//扩容后还不够或者超过int最大值,就直接赋值size+1
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
members=new Object[newCapacity];
//拷贝数组
System.arraycopy(oldMembers, 0, members, 0, size);
oldMembers=null;
}
}
}以上代码就是一个简易的Stack的实现方式。
代码见: https://github.com/JavaZWT/sakuratears
总结
Stack类在编程过程中用到的不是很多,但是计算机栈内存机制遵循先进后出原则,学习Stack类,可以帮助我们加深对程序及数据结构的理解。