时间模块
三种格式
时间戳时间 浮点数 秒为单位
1970.1.1 0:0:0 英国伦敦时间 1970.1.1 8:0:0 东八区
结构化时间 元组
格式化时间 str数据类型

1 import time 2 print(time.time()) #1536044649.2858107 3 #时间戳时间,计算机能够识别的时间 4 5 struct_time = time.localtime() 6 print(struct_time) 7 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2018, tm_mon=9, tm_mday=4, tm_hour=15, tm_min=4, tm_sec=9, tm_wday=1, tm_yday=247, tm_isdst=0) 8 #结构化时间,用来操作时间的 9 10 fmt1 = time.strftime('%H:%M:%S') 11 fmt2 = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') 12 fmt3 = time.strftime('%y-%m-%d') 13 print(fmt1) #15:04:09(当前的时间) 14 print(fmt2) #1999-09-09(当前的日期) 15 print(fmt3) #99-09-09(大小写y的区别) 16 #格式化时间,人能够看懂的时间
三种格式的相互转化
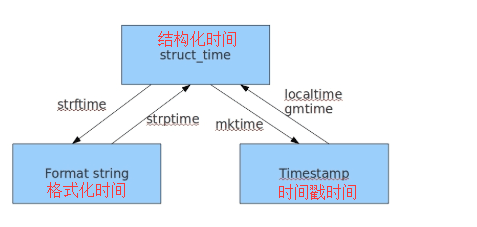

1 import time 2 str_time = '2008-8-8' 3 4 struct_time = time.strptime(str_time, '%Y-%m-%d') 5 print(struct_time) #格式化时间转化成结构化时间 6 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2008, tm_mon=8, tm_mday=8, tm_hour=0, tm_min=0, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=4, tm_yday=221, tm_isdst=-1) 7 8 timestamp = time.mktime(struct_time) 9 print(timestamp) #结构化时间转出成时间戳时间 10 #1218124800.0 11 12 timestamp = 3000000000 13 14 struct_time = time.localtime(timestamp) 15 print(struct_time) #时间戳时间转化成结构化时间 16 #time.struct_time(tm_year=2065, tm_mon=1, tm_mday=24, tm_hour=13, tm_min=20, tm_sec=0, tm_wday=5, tm_yday=24, tm_isdst=0) 17 18 fmt_time = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', struct_time) 19 print(fmt_time) #结构化时间转化成格式化时间 20 #2065-01-24 13:20:00 21 ###格式化时间一定不要忘记格式化输出

1 #写函数,计算本月一号的时间戳时间 2 import time 3 def get_timestamp(): 4 fmt_time = time.strftime('%Y-%m-1') 5 struct_time = time.strptime(fmt_time,'%Y-%m-%d') 6 timestamp = time.mktime(struct_time) 7 return timestamp 8 ret = get_timestamp() 9 print(ret)
随机数模块
import random

1 import random 2 #取随机小数 3 print(random.random()) 4 #默认在0—1之间随机取小数 5 print(random.uniform(2, 3)) 6 #在2—3之间随机去小数 7 8 #取随机整数 9 print(random.randint(1, 2)) 10 #1和2随机取一个,两边都有可能被取到 11 print(random.randrange(1, 2)) 12 #取头不取尾,只取1 13 print(random.randrange(1, 100, 2)) 14 #1—100随机取一个单数 15 16 #从一个列表中饭随机抽取 17 lst = [1,2,3,4,5,6,('a','b'),'cc','dd'] 18 ret = random.choice(lst) 19 print(ret) 20 #列表中随机取一个 21 ret1 = random.choice(range(100)) 22 print(ret1) 23 #1—100随机取一个 24 ret2 = random.sample(lst,3) 25 print(ret2) 26 #在列表中随机取三个 27 28 #乱序 29 lst1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,('a','b'),'cc','dd'] 30 random.shuffle(lst1) 31 print(lst1) 32 #在原有列表的里打乱顺序重新输出

1 def get_code(n=6): #n=6 默认参数 2 code = '' 3 for i in range(n): 4 num = random.randint(0,9) 5 code += str(num) 6 return code 7 8 9 ret = get_code() 10 ret1 = get_code(4) #四位随机验证码 11 print(ret, ret1)

1 def get_code(n=6,alph_flag = True): 2 code = '' 3 for i in range(n): 4 s = str(random.randint(0, 9)) 5 if alph_flag: 6 alpha_upper = chr(random.randint(65, 90)) #所有大写随机抽一个 7 alpha_lower = chr(random.randint(97, 122)) #所有小写随机抽一个 8 s = random.choice([s, alpha_lower, alpha_upper]) 9 code += s 10 return code 11 ret = get_code(6,alph_flag =False) #alph_flag为False,则只有数字随机验证码 12 print(ret) 13 #chr() 内置函数,根据输入位置数字返回相应的unicode字符 14 #65-90 ==A-Z 97-122 == a-z
os模块

1 os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录 2 os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推 3 os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname 4 os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname 5 os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印 6 os.remove() 删除一个文件 7 os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录 8 os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息 9 10 os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示 11 os.popen("bash command).read() 运行shell命令,获取执行结果 12 os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径 13 os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd 14 15 os.path 16 os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径 17 os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回 18 os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素 19 os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素 20 os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False 21 os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True 22 os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False 23 os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False 24 os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略 25 os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后访问时间 26 os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间 27 os.path.getsize(path) 返回path的大小
操作系统命令
python代码
os.system('dir') #以字符串的形式来执行操作系统的命令
exec #以字符串的形式来执行python代码
eval #以字符串的形式来执行python代码,并且返回结果
sys模块
sys.argv:命令行参数list,第一个元素是程序本身路径
sys.path:一个模块能否被导入,就看这个模块所在的目录在不在sys.path路径中
内置模块和第三方扩展模块都不需要我们处理sys.path就可以直接使用
自定义的模块的导入工作需要自己手动的修改sys.path
sys.modules:查看当前内存空间中所有的模块,和这个模块的内存空间
