版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。 https://blog.csdn.net/aitangyong/article/details/53894997
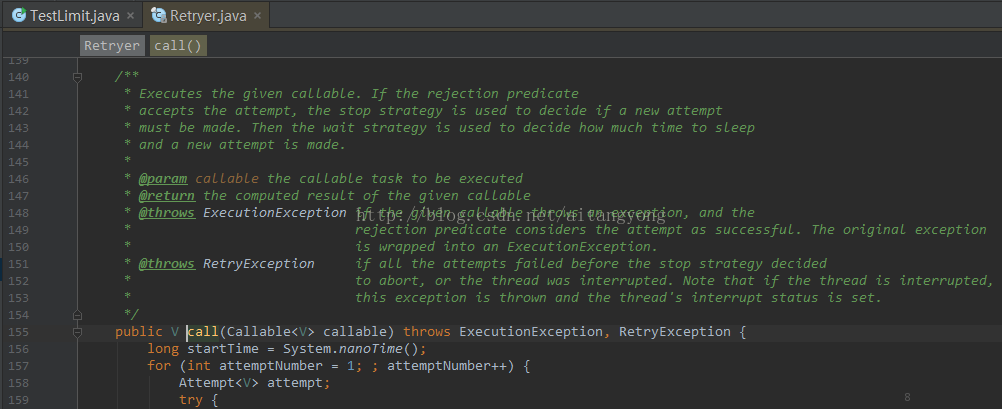
前面我们介绍了如何通过RetryerBuilder构造一个Retryer对象,现在我们学习下如何使用 Retryer.call()。这个API很重要,对于这个方法的入参、返回值、可能抛出的异常要了解清楚。
入参:很简单,就是一个实现了业务逻辑的Callable对象;返回值:某次尝试成功后,Callable的返回值。我们主要关注下可能的异常:RetryException和ExecutionException。
ExecutionException产生:传入的Callable执行过程中产生了异常,但是我们在构建Retryer对象的时候并没有考虑这种情况,就会抛出这个异常。抛出这异常,也就意味着重试终止。
private static SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss,SSS");
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Retryer<Boolean> retryer = RetryerBuilder.<Boolean>newBuilder()
.retryIfExceptionOfType(IOException.class)
.withWaitStrategy(WaitStrategies.fixedWait(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS))
.withStopStrategy(StopStrategies.stopAfterAttempt(5))
.build();
System.out.println("begin..." + df.format(new Date()));
try {
retryer.call(buildTask());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end..." + df.format(new Date()));
}
private static Callable<Boolean> buildTask() {
return new Callable<Boolean>() {
private int i = 0;
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("called");
i++;
if (i == 1) {
throw new IOException();
} else {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
};
}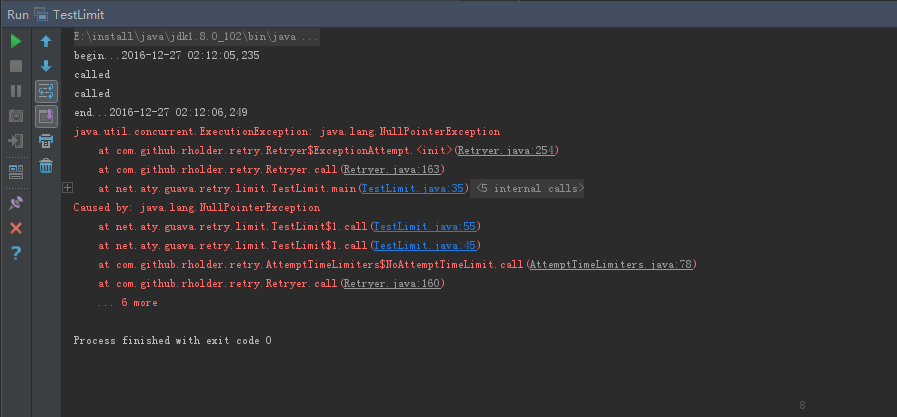
RetryException就很简单了,当所有重试介绍后,依然不能成功,那么就会抛这异常。
private static SimpleDateFormat df = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss,SSS");
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Retryer<Boolean> retryer = RetryerBuilder.<Boolean>newBuilder()
.retryIfException()
.withWaitStrategy(WaitStrategies.fixedWait(1,TimeUnit.SECONDS))
.withStopStrategy(StopStrategies.stopAfterAttempt(5))
.build();
System.out.println("begin..." + df.format(new Date()));
try {
retryer.call(buildTask());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end..." + df.format(new Date()));
}
private static Callable<Boolean> buildTask() {
return new Callable<Boolean>() {
private int i = 0;
@Override
public Boolean call() throws Exception {
System.out.println("called");
i++;
if (i == 1) {
throw new IOException();
} else {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
}
};
}