On a N * N grid, we place some 1 * 1 * 1 cubes that are axis-aligned with the x, y, and z axes.
Each value v = grid[i][j] represents a tower of v cubes placed on top of grid cell (i, j).
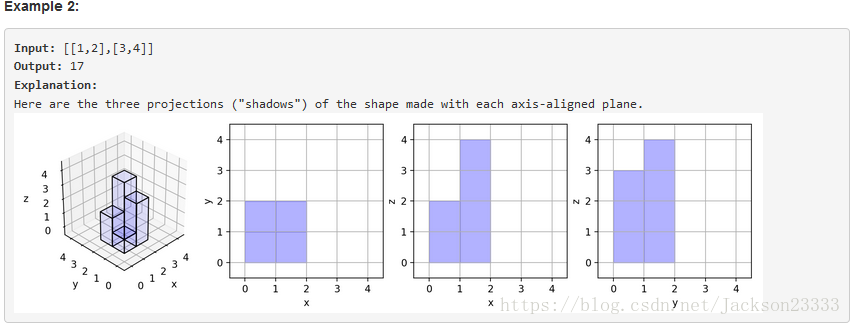
Now we view the projection of these cubes onto the xy, yz, and zx planes.
A projection is like a shadow, that maps our 3 dimensional figure to a 2 dimensional plane.
Here, we are viewing the "shadow" when looking at the cubes from the top, the front, and the side.
Return the total area of all three projections.
Example 1:
Input: [[2]]
Output: 5
Example 3:
Input: [[1,0],[0,2]]
Output: 8
Example 4:
Input: [[1,1,1],[1,0,1],[1,1,1]]
Output: 14
Example 5:
Input: [[2,2,2],[2,1,2],[2,2,2]]
Output: 21
Note:
1 <= grid.length = grid[0].length <= 500 <= grid[i][j] <= 50
大概的意思就是求三维立体投影面积,从顶部(xy),正面(yz),侧面(zx),观看在3D坐标上堆积的正方形所形成的图形面积,然后三个面积相加求和。其中每个正方形的边长是1.
代码如下(还是js写的,提交用时76ms):
大家可以参考下思路,有更好意见的大佬,欢迎骚扰。