ScheduledExecutorService的主要作用就是可以将定时任务与线程池功能结合使用。今天我们来学习一下ScheduledExecutorService的用法。
ScheduledExecutorService的简单使用
一、使用scheduleAtFixedRate()方法实现周期性执行
public class ScheduledExecutorServiceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
executorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run "+ System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}, 0, 100, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
运行的结果如下:立刻执行,而且每隔100毫秒执行一次。
run 1501051231331 run 1501051231427 run 1501051231527 run 1501051231628 run 1501051231726 run 1501051231827 run 1501051231926 run 1501051232026 run 1501051232127 .......
二、ScheduledExecutorService使用Callable延迟运行
package com.linux.thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
public class CallableRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
List<Callable> callableList = new ArrayList<>();
callableList.add(new MyCallableA());
callableList.add(new MyCallableB());
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
ScheduledFuture futureA = executorService.schedule(callableList.get(0), 4L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
ScheduledFuture futureB = executorService.schedule(callableList.get(1), 4L, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(" X = " + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("返回值A:" + futureA.get());
System.out.println("返回值B:" + futureB.get());
System.out.println(" Y = " + System.currentTimeMillis());
executorService.shutdown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
static class MyCallableA implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception{
try {
System.out.println("callA begin " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", " + System.currentTimeMillis());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3); // 休眠3秒
System.out.println("callA end " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", " + System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return "returnA";
}
}
static class MyCallableB implements Callable<String> {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception{
System.out.println("callB begin " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", " + System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println("callB end " + Thread.currentThread().getName() + ", " + System.currentTimeMillis());
return "returnB";
}
}
}
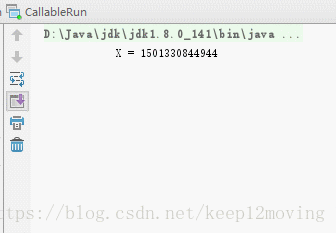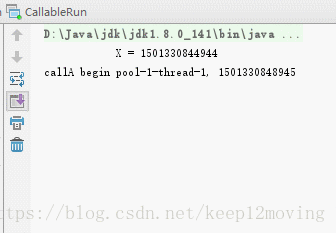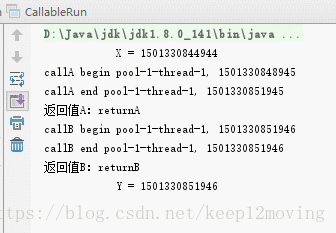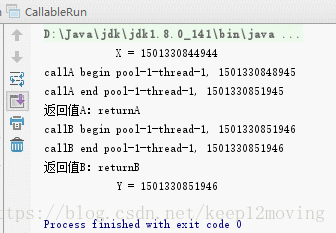
运行的结果如下:
三、使用scheduleWithFixedDelay()方法实现周期性执行
package com.linux.thread;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.ScheduledExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class RunMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScheduledExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadScheduledExecutor();
System.out.println(" x = " + System.currentTimeMillis());
executorService.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new MyRunable(), 1, 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println(" y = " + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
static class MyRunable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println(" begin = " + System.currentTimeMillis() + ", name: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(4);
System.out.println(" end = " + System.currentTimeMillis() + ", name: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行的结果如下:
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/huhx/p/baseusejavaScheduledExecutorService.html