IntentService定义
IntentService继承与Service,用来处理异步请求。客户端可以通过startService(Intent)方法传递请求给IntentService。IntentService在onCreate()函数中通过HandlerThread单独开启一个线程来依次处理所有Intent请求对象所对应的任务。
这样以免事务处理阻塞主线程(ANR)。执行完所一个Intent请求对象所对应的工作之后,如果没有新的Intent请求达到,则**自动停止**Service;否则执行下一个Intent请求所对应的任务。
IntentService在处理事务时,还是采用的Handler方式,创建一个名叫ServiceHandler的内部Handler,并把它直接绑定到HandlerThread所对应的子线程。 ServiceHandler把处理一个intent所对应的事务都封装到叫做onHandleIntent的虚函数;因此我们直接实现虚函数onHandleIntent,再在里面根据Intent的不同进行不同的事务处理就可以了。
另外,IntentService默认实现了Onbind()方法,返回值为null。
使用IntentService需要实现的两个方法:
-
构造函数
IntentService的构造函数一定是参数为空的构造函数,然后再在其中调用super(“name”)这种形式的构造函数。因为Service的实例化是系统来完成的,而且系统是用参数为空的构造函数来实例化Service的
-
实现虚函数onHandleIntent
在里面根据Intent的不同进行不同的事务处理。
好处:处理异步请求的时候可以减少写代码的工作量,比较轻松地实现项目的需求。
IntentService与Service的区别
Service不是独立的进程,也不是独立的线程,它是依赖于应用程序的主线程的,不建议在Service中编写耗时的逻辑和操作,否则会引起ANR。
IntentService 它创建了一个独立的工作线程来处理所有的通过onStartCommand()传递给服务的intents(把intent插入到工作队列中)。通过工作队列把intent逐个发送给onHandleIntent()。
不需要主动调用stopSelft()来结束服务。因为,在所有的intent被处理完后,系统会自动关闭服务。
默认实现的onBind()返回null。
IntentService实例介绍
首先是myIntentService.java
public class myIntentService extends IntentService {
//------------------必须实现-----------------------------
public myIntentService() {
super("myIntentService");
// 注意构造函数参数为空,这个字符串就是worker thread的名字
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
//根据Intent的不同进行不同的事务处理
String taskName = intent.getExtras().getString("taskName");
switch (taskName) {
case "task1":
Log.i("myIntentService", "do task1");
break;
case "task2":
Log.i("myIntentService", "do task2");
break;
default:
break;
}
}
//--------------------用于打印生命周期--------------------
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i("myIntentService", "onCreate");
super.onCreate();
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i("myIntentService", "onStartCommand");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i("myIntentService", "onDestroy");
super.onDestroy();
}
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
然后记得在Manifest.xml中注册服务
<service android:name=".myIntentService">
<intent-filter >
<action android:name="cn.scu.finch"/>
</intent-filter>
</service>- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
最后在Activity中开启服务
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//同一服务只会开启一个worker thread,在onHandleIntent函数里依次处理intent请求。
Intent i = new Intent("cn.scu.finch");
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("taskName", "task1");
i.putExtras(bundle);
startService(i);
Intent i2 = new Intent("cn.scu.finch");
Bundle bundle2 = new Bundle();
bundle2.putString("taskName", "task2");
i2.putExtras(bundle2);
startService(i2);
startService(i); //多次启动
}
}- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
运行结果:
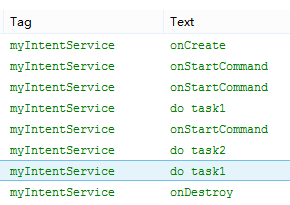
IntentService在onCreate()函数中通过HandlerThread单独开启一个线程来依次处理所有Intent请求对象所对应的任务。
通过onStartCommand()传递给服务intent被依次插入到工作队列中。工作队列又把intent逐个发送给onHandleIntent()。
注意:
它只有一个工作线程,名字就是构造函数的那个字符串,也就是“myIntentService”,我们知道多次开启service,只会调用一次onCreate方法(创建一个工作线程),多次onStartCommand方法(用于传入intent通过工作队列再发给onHandleIntent函数做处理)。