一: 字符串练习
(1) String的获取功能:
int length():获取字符串长度
public char charAt(int index):获取指定索引处的字符
public int indexOf(int ch)返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引,这里的参数不是char类型因为一个字符对应了一个ASCCLL码的值;int和char区别不大。
public int indexOf(String str):子字符串在大字符串中第一次出现的索引
public int lastIndexOf(int ch)返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引
public String substring(int beginIndex):从指定位置开始截取,默认截取到末尾
public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex):从指定位置开始截取,截取到指定位置结束(包前,不包后)
举例:public class StringDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个字符串
String str = "helloworld" ;
// int length():获取字符串长度
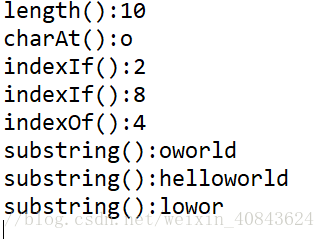
System.out.println("length():"+str.length());
//public char charAt(int index):获取指定索引处的字符
System.out.println("charAt():"+str.charAt(4)); //可以去遍历字符串
//public int indexOf(int ch)返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引
System.out.println("indexIf():"+str.indexOf('l'));
System.out.println("indexIf():"+str.lastIndexOf('l'));
//public int indexOf(String str):子字符串在大字符串中第一次出现的索引
System.out.println("indexOf():"+str.indexOf("owo"));
//public String substring(int beginIndex)
System.out.println("substring():"+str.substring(4));
System.out.println("substring():"+str.substring(0));
//public String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex)
System.out.println("substring():"+str.substring(3, 8));//lowor 包括前面不包括后面
}
}结果如下
(2)String 的类型转化功能
String类型的转换功能:
byte[] getBytes() :将字符串转换成字节数组
public char[] toCharArray():将字符串转换为字符数组
valueOf(XXX 变量名) ;可以将任意类型转换为String类型
public String toLowerCase() :将字符串转换小写
public String toUpperCase():将字符串转换成大写
代码:package org.www;
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sc="hello world";
char[] a = sc.toCharArray();
String sc1=" java";
byte[] bys = sc1.getBytes();
System.out.println(bys);
for(int i=0;i<bys.length;i++) {
System.out.print(bys[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
for(int i=0;i<bys.length;i++) {
System.out.print(" "+a[i]);
}
System.out.println("-----------------");
System.out.println(sc.concat(sc1));
System.out.println("");
System.out.println(sc1.toLowerCase());
System.out.println(sc1.toUpperCase());
}
}
结果:

例题: 需求:把一个字符串的首字母转成大写,其余为小写。(只考虑英文大小写字母字符) 举例:helloWORLD 结果:Helloworld
实现功能:
代码:public class zhuanhuan {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建键盘录入对象
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in) ;
//接收数据
System.out.println("请您输入一个字符串:");
String str = sc.nextLine() ;
//截取字符串中第一个字母
String s1 = str.substring(0, 1) ;
//将s1转转成大写
String s2 = s1.toUpperCase() ;
//截取第一个字母外的其他字符串
String s3 = str.substring(1) ;
//将s3转换称小写
String s4 = s3.toLowerCase() ;
//拼接
String result = s2.concat(s4) ;
System.out.println("result:"+result);
System.out.println("------------------------------------");
//链式编程
String result2 = str.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase().
concat(str.substring(1).toLowerCase()) ;
System.out.println("result2:"+result2);
}
}
输入 java
结果如下:

(3)字符串的替换功能:
字符串中的其他功能:
替换功能:
String replace(char oldChar, char newChar) :将指定的字符替换以前的字符
String replace(String oldString, String newString):将以前的子字符串替换新的子字符串
public String trim() 去除两端空格
例如:
public class StringDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String sc=”毛主席万岁”;
String rp = sc.replace(“毛主席”, “*“);
System.out.println(sc);
System.out.println(rp);
String sc1=” hello world “;
System.out.println(“去除空格之后”+ sc1.trim());
String sc3=”haha”;
String sc4=”hello”;
System.out.println(“比较之后的结果为”+sc3.compareTo(sc4));
}
}
结果:

public class StringTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
string的compare用法:
String s1 = "hello" ;
String s2 ="hel" ;
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2));//2
}
}
练习题:
按照指定的格式将数组拼接成一个字符串
int arr = {1,2,3} ;
输出结果:String [1, 2, 3]
实现功能的代码:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//定义一个数组,静态初始化
int[] arr = {1,2,3} ;
String result = arrayToString(arr) ;
System.out.println("result:"+result);
}
//定义功能
private static String arrayToString(int[] arr) {
//定义一个空字符串:
String s = "" ;
//拼接左中括号
s += "[" ;
//遍历数组
for(int x = 0; x < arr.length ; x ++) {
if(x == arr.length-1) {
s += arr[x] ;
s +="]" ;
}else {
s+= arr[x] ;
s+= ", " ;
}
}
return s ;
}
}
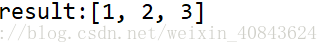
二 stringBuffer 的用法和与String的区别
(1)StringBuffer与String的区别;
前者是线程安全的类,可变的字符序列,内存中提供字符串缓冲区;后者是不可变的字符序列
从内存角度考虑:前者优于后者: String类型:在方法区中开辟空间--->占内存
(2)StringBuffer的具体用法:
StringBuffer :里面存在初始容量
里面不断的追击字符串(append)
StringBuffer的构造方法:
public StringBuffer()构造一个其中不带字符的字符串缓冲区,其初始容量为 16 个字符。
public StringBuffer(int capacity):指定容量大小
public StringBuffer(String str):构造一个字符串缓冲区:里面的容量(字符 串内容英文)大小:字符串长度+16初始容量
获取功能: public int capacity():初始容量
int length():返回字符串长度
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sc = new StringBuffer();
System.out.println("sc.capacity()="+sc.capacity());
System.out.println("sc.length()="+sc.length());
StringBuffer sc2 = new StringBuffer(50);
System.out.println("sc2.capacity()="+sc2.capacity());
System.out.println("sc2.length=()"+sc2.length());
StringBuffer sc3 = new StringBuffer("haha");
System.out.println("sc3.length=()"+sc3.length());
System.out.println("sc3.capacity()="+sc3.capacity());
}
}
结果: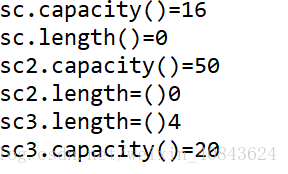
(3)StringBuffer的删除功能:
StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) :删除指定位置出的字符,返回字符串缓冲区本身
StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) :删除从指定位置开始到指定位置结束,返回值字符串缓冲区本身
举例:
public class StringTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer sc = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer a = sc.append("hello").append("world");
System.out.println(a);
StringBuffer delete = sc.delete(3, 5);
System.out.println(delete);
System.out.println(sc.deleteCharAt(3));
}结果:
(4)StringBuffer的替换功能:
public StringBuffer replace(int start,int end,String str)
从指定位置开始到指定位置结束,用给定的str字符串替换指定的字符内容
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer append = buffer.append("姚明是足球运动员");
System.out.println("替换之前的效果是:"+buffer);
System.out.println("替换过后的效果是:"+buffer.replace(3, 5, "篮球"));
}结果:
(5)StringBuffer的反转功能:
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
StringBuffer append = buffer.append("我爱java");
System.out.println("原来的字符串为:"+append);
StringBuffer reverse = append.reverse();
System.out.println("现在的字符串为:"+reverse);
}
结果:
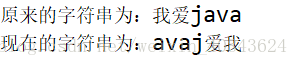
(6)
StringBuffer的截取功能:
String substring(int start) :从指定位置默认截取到末尾,返回一个新的字符串
String substring(int start,int end):从指定位置开始截取到指定位置结束
举例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
buffer.append("hello").append("java");
System.out.println("经过截取的字符为:"+buffer.substring(3));
}结果:
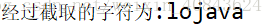
三StringBuffer与String的转化
(1)为什么要转化?
B类--->A类:有时候需要取使用A类的功能
A类--->B类:有时候的需求需要A类型
String类型转换为String类型:
(1)通过构造方法进行转化:
String s="abc";
StringBuffer buffer=new StringBuffer(s);
(2)通过无参构造再调用apend方法进行转化:
String s="abc":
StringBuffer buffer=new StringBuffe();
buffer.append(s);
StringBuffer类型转化为String类型:
(1)String的构造方法:
String s=new String(buffer);
(2)StringBuffer的调用toString方法:
String s=buffer.toString(buffer);
四:StringBuild与StringBuffer的区别
StringBuffer特点: 线程安全--->同步---->执行效率低
StringBulid的特点:线程不安全(单线程中:使用StringBulider代替StringBuffer)--->不同步---->执行效率高