一、Future模式
Java 1.5开始,提供了Callable和Future,通过它们可以在任务执行完毕之后得到任务执行结果。
Future接口可以构建异步应用,是多线程开发中常见的设计模式。
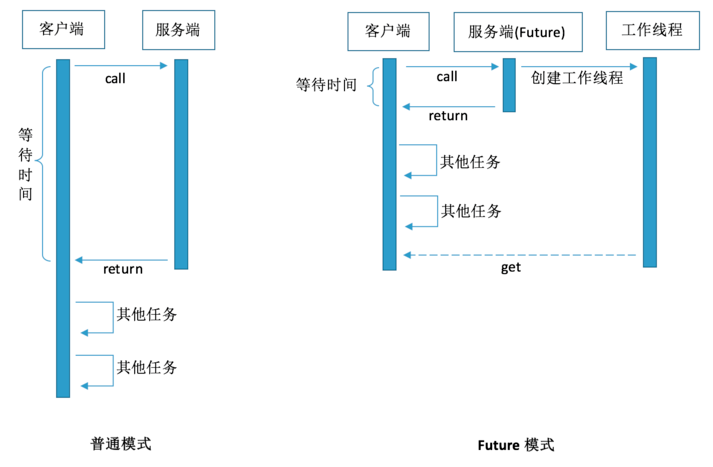
当我们需要调用一个函数方法时。如果这个函数执行很慢,那么我们就要进行等待。但有时候,我们可能并不急着要结果。
因此,我们可以让被调用者立即返回,让他在后台慢慢处理这个请求。对于调用者来说,则可以先处理一些其他任务,在真正需要数据的场合再去尝试获取需要的数据。
1、Callable与Runnable
java.lang.Runnable是一个接口,在它里面只声明了一个run()方法,run返回值是void,任务执行完毕后无法返回任何结果
public interface Runnable {
public abstract void run();
}
Callable位于java.util.concurrent包下,它也是一个接口,在它里面也只声明了一个方法叫做call(),这是一个泛型接口,call()函数返回的类型就是传递进来的V类型
public interface Callable<V> {
V call() throws Exception;
}
2、Future + Callable
Future就是对于具体的Runnable或者Callable任务的执行结果进行取消、查询是否完成、获取结果。必要时可以通过get方法获取执行结果,该方法会阻塞直到任务返回结果
public interface Future<V> {
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
boolean isCancelled();
boolean isDone();
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException; }
怎么使用Future和Callable呢?一般情况下是配合ExecutorService来使用的,在ExecutorService接口中声明了若干个submit方法的重载版本
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task); <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result); Future<?> submit(Runnable task);
Future+Callable,使用示例如下(采用第一个方法):
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @program: callable
* @description: Test
* @author: Mr.Wang
* @create: 2018-08-12 11:37
**/
public class MyTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Future<Integer> result = executor.submit(new Callable<Integer>() {
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return new Random().nextInt();
}
});
executor.shutdown();
try {
System.out.println("result:" + result.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
其它方式:
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @program: callable
* @description: testfuture
* @author: Mr.Wang
* @create: 2018-08-12 12:11
**/
public class Testfuture {
public static void main(String[] args){
//第一种方式
FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<Integer>(new Callable<Integer>() {
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
return new Random().nextInt();
}
});
new Thread(task).start();
//第二种方方式
// ExecutorService executor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
// FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<Integer>(new Callable<Integer>() {
// @Override
// public Integer call() throws Exception {
// return new Random().nextInt();
// }
// });
// executor.submit(task);
try {
System.out.println("result: "+task.get());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
3、Future 接口的局限性
了解了Future的使用,这里就要谈谈Future的局限性。Future很难直接表述多个Future 结果之间的依赖性,开发中,我们经常需要达成以下目的:
- 将两个异步计算合并为一个(这两个异步计算之间相互独立,同时第二个又依赖于第一个的结果)
- 等待 Future 集合中的所有任务都完成。
- 仅等待 Future 集合中最快结束的任务完成,并返回它的结果。
二、CompletableFuture
首先,CompletableFuture实现了Future接口,因此你可以像Future那样使用它。
待续