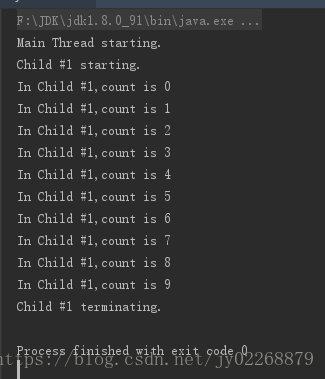
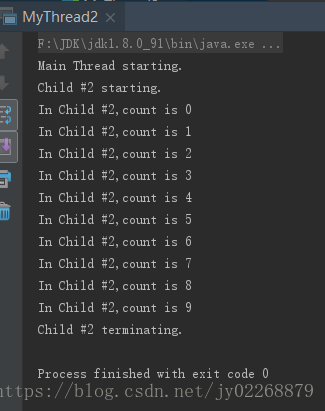
1.实现Runable接口
public class MyThread implements Runnable{
int count;
String thrdName;
MyThread(String name){
count = 0;
thrdName = name;
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(thrdName+" starting.");
try {
do {
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("In "+thrdName+",count is "+count);
count++;
}while (count<10);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(thrdName+" interrupted.");
}
System.out.println(thrdName+" terminating.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Main Thread starting.");
MyThread mt = new MyThread("Child #1");
//创建一个Thread对象
Thread t1 = new Thread(mt);
//开始运行线程
t1.start();
}
}
2.继承Thread类
public class MyThread2 extends Thread{
int count;
String thrdName;
MyThread2(String name){
count = 0;
thrdName = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(thrdName+" starting.");
try {
do {
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("In "+thrdName+",count is "+count);
count++;
}while (count<10);
}catch (Exception e){
System.out.println(thrdName+" interrupted.");
}
System.out.println(thrdName+" terminating.");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Main Thread starting.");
//创建一个Thread对象
Thread t2 = new MyThread2("Child #2");
//开始运行线程
t2.start();
}
}