Glad You Came
Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 525 Accepted Submission(s): 161
Problem Description
Steve has an integer array a of length n (1-based). He assigned all the elements as zero at the beginning. After that, he made m operations, each of which is to update an interval of a with some value. You need to figure out ⨁ni=1(i⋅ai) after all his operations are finished, where ⨁ means the bitwise exclusive-OR operator.
In order to avoid huge input data, these operations are encrypted through some particular approach.
There are three unsigned 32-bit integers X,Y and Z which have initial values given by the input. A random number generator function is described as following, where ∧ means the bitwise exclusive-OR operator, << means the bitwise left shift operator and >> means the bitwise right shift operator. Note that function would change the values of X,Y and Z after calling.
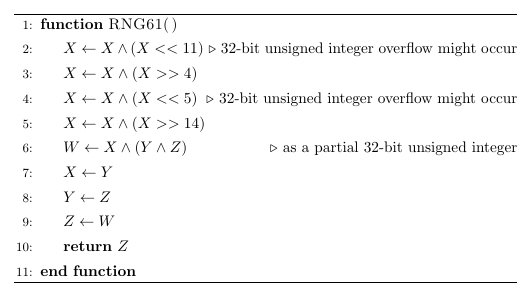
Let the i-th result value of calling the above function as fi (i=1,2,⋯,3m). The i-th operation of Steve is to update aj as vi if aj<vi (j=li,li+1,⋯,ri), where
⎧⎩⎨⎪⎪lirivi=min((f3i−2modn)+1,(f3i−1modn)+1)=max((f3i−2modn)+1,(f3i−1modn)+1)=f3imod230(i=1,2,⋯,m).
Input
The first line contains one integer T, indicating the number of test cases.
Each of the following T lines describes a test case and contains five space-separated integers n,m,X,Y and Z.
1≤T≤100, 1≤n≤105, 1≤m≤5⋅106, 0≤X,Y,Z<230.
It is guaranteed that the sum of n in all the test cases does not exceed 106 and the sum of m in all the test cases does not exceed 5⋅107.
Output
For each test case, output the answer in one line.
Sample Input
4 1 10 100 1000 10000 10 100 1000 10000 100000 100 1000 10000 100000 1000000 1000 10000 100000 1000000 10000000
Sample Output
1031463378 1446334207 351511856 47320301347
Hint
In the first sample, a = [1031463378] after all the operations. In the second sample, a = [1036205629, 1064909195, 1044643689, 1062944339, 1062944339, 1062944339, 1062944339, 1057472915, 1057472915, 1030626924] after all the operations.
Source
2018 Multi-University Training Contest 5
这个题感觉真的好强。
一开始没有看清m的大小,直接一发线段树交上去,然后成功T了,然后转念一想,分块是不是计算量会少一点点,结果写了一发分块交上去,再 T ,然后队友写了两发优先队列,也成功的T了,最后,我又排了个序,然后交了个并查集优化,结果当然也是TTTTTTT。
思路: 注意到这个题的m比n高出了一个量级,所以更好的思路是去在n上做文章,看了题解,也是真的想不到会这样做,n的范围为1e5 ,那么2的20 次方肯定够了,解决这个题就用到了一点点RMQ的小技巧,我们用 dp[i][j] 来表示以 j 开头,长度为2的i次方的的范围中的最大价值,那么每次在更新的时候其实就是更新最靠近r-l+1 这个次方上的长度,在最后查询的时候就是从高次方向低次方更新,然后直到更新到2的0次方,那么就是到长度为1 的节点了,那么这样的复杂度就是T*(m+nlogn)
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
const int N =1e5+5;
const int mod =(1<<30);
ui X,Y,Z,W;
ll a[20][N];
int Log[N];
int yi[25];
int n,m;
void init_log()
{
for(int i=2;i<N;i++){
Log[i]=Log[(i>>1)]+1;
}
}
void init_yi()
{
yi[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=20;i++) yi[i]=yi[i-1]*2;
}
inline ui get()
{
X=X^(X<<11);
X=X^(X>>4);
X=X^(X<<5);
X=X^(X>>14);
W=X^(Y^Z);
X=Y;
Y=Z;
Z=W;
return Z;
}
inline void getlrv(int &l,int &r,ll &val)
{
ui f1,f2,f3;
f1=get(); f2=get(); f3=get();
l=(int)min((f1%n)+1,(f2%n)+1);
r=(int)max((f1%n)+1,(f2%n)+1);
val=1ll*(f3%mod);
}
int main()
{
init_log();
init_yi();
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
scanf("%d %d %u %u %u",&n,&m,&X,&Y,&Z);
int l,r;
ll val;
while(m--)
{
getlrv(l,r,val);
//cout<<"l "<<l<<" r "<<r<<" val "<<val<<endl;
int log=Log[r-l+1];
//cout<<"log "<<log<<endl;
a[log][l]=max(a[log][l],val);
a[log][r-yi[log]+1]=max(a[log][r-yi[log]+1],val);
}
for(int i=19;i>=1;i--){
for(int j=1;j+yi[i]-1<=n;j++){
a[i-1][j]=max(a[i-1][j],a[i][j]);
a[i-1][j+yi[i-1]]=max(a[i-1][j+yi[i-1]],a[i][j]);
}
}
ll ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
ll tmp=i*a[0][i];
ans=ans^tmp;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
赛后看见人家线段树也有过的,自己太傻逼了。。。
线段树:
代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define lson (i<<1)
#define rson (i<<1|1)
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef unsigned ui;
const int N =1e5+5;
const ll mm=(1<<30);
struct node
{
ll l,r;
ll val;
ll lz;
}tr[N<<2];
ll a[N];
ui X,Y,Z,W;
ll n,m;
inline void push_down(ll i)
{
if(tr[i].lz){
tr[lson].lz=max(tr[lson].lz,tr[i].lz);
tr[rson].lz=max(tr[rson].lz,tr[i].lz);
tr[i].lz=0;
}
}
inline void build(ll i,ll l,ll r)
{
tr[i].l=l; tr[i].r=r; tr[i].lz=0; tr[i].val=0;
if(l==r) return ;
int mid=(l+r)>>1;
build(lson,l,mid);
build(rson,mid+1,r);
}
inline void update(ll i,ll l,ll r,ll val)
{
if(tr[i].lz>val) return ;
if(tr[i].l==l&&tr[i].r==r){
tr[i].lz=max(tr[i].lz,val);
return ;
}
push_down(i);
int mid=(tr[i].l+tr[i].r)>>1;
if(r<=mid) update(lson,l,r,val);
else if(l>mid) update(rson,l,r,val);
else{
update(lson,l,mid,val);
update(rson,mid+1,r,val);
}
}
inline void query(ll i,ll l,ll r)
{
if(tr[i].l==tr[i].r&&tr[i].l==l){
a[tr[i].l]=tr[i].lz;
return ;
}
push_down(i);
int mid=(tr[i].l+tr[i].r)>>1;
if(r<=mid) query(lson,l,mid);
else if(l>mid) query(rson,mid+1,r);
else{
query(lson,l,mid);
query(rson,mid+1,r);
}
}
inline ui get()
{
X=X^(X<<11);
X=X^(X>>4);
X=X^(X<<5);
X=X^(X>>14);
W=X^(Y^Z);
X=Y;
Y=Z;
Z=W;
return Z;
}
inline void getlrv(ll &l,ll &r,ll &val)
{
ui f1,f2,f3;
f1=get(); f2=get(); f3=get();
l=1ll*min((f1%n)+1,(f2%n)+1);
r=1ll*max((f1%n)+1,(f2%n)+1);
val=1ll*(f3%mm);
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%lld %lld %u %u %u",&n,&m,&X,&Y,&Z);
build(1,1,n);
ll l,r,val;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
getlrv(l,r,val);
update(1,l,r,val);
}
query(1,1,n);
/*
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<a[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
*/
ll ans=0;
for(ll i=1;i<=n;i++){
ll tmp=i*a[i];
ans=ans^tmp;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}