前言
SqlSession是Mybatis最重要的构建之一,可以简单的认为Mybatis一系列的配置目的是生成类似 JDBC生成的Connection对象的SqlSession对象,这样才能与数据库开启“沟通”,通过SqlSession可以实现增删改查(当然现在更加推荐是使用Mapper接口形式),那么它是如何执行实现的,这就是本篇博文所介绍的东西,其中会涉及到简单的源码讲解。
了解SqlSession的运作原理是学习Mybatis插件的必经之路,因为Mybatis的插件会在SqlSession运行过程中“插入”运行,如果没有很好理解的话,Mybatis插件可能会覆盖相应的源码造成严重的问题。鉴于此,本篇博文尽量详细介绍SqlSession运作原理!
建议:在我之前的博文《Mybatis缓存(1)--------系统缓存及简单配置介绍》中介绍到SqlSession的产生过程,可以先理解后再读此博文可能会更加好理解!
注:本篇博文也是我最近真正理解Mybatis才开始编写的,可能有些地方不太准确,如果有错误之处敬请指出,另外创作不易,望转载告之,谢谢!
参数资料:《深入浅出Mybatis基础原理与实践》(我这里只有电子版PDF,需要的朋友可以联系我)
1、SqlSession简单介绍
(1)SqlSession简单原理介绍
SqlSession提供select/insert/update/delete方法,在旧版本中使用使用SqlSession接口的这些方法,但是新版的Mybatis中就会建议使用Mapper接口的方法。
映射器其实就是一个动态代理对象,进入到MapperMethod的execute方法就能简单找到SqlSession的删除、更新、查询、选择方法,从底层实现来说:通过动态代理技术,让接口跑起来,之后采用命令模式,最后还是采用了SqlSession的接口方法(getMapper()方法等到Mapper)执行SQL查询(也就是说Mapper接口方法的实现底层还是采用SqlSession接口方法实现的)。
注:以上虽然只是简单的描述,但实际上源码相对复杂,下面将结合源码进行简单的介绍!
(2)SqlSession重要的四个对象
1)Execute:调度执行StatementHandler、ParmmeterHandler、ResultHandler执行相应的SQL语句;
2)StatementHandler:使用数据库中Statement(PrepareStatement)执行操作,即底层是封装好了的prepareStatement;
3)ParammeterHandler:处理SQL参数;
4)ResultHandler:结果集ResultSet封装处理返回。
2、SqlSession四大对象
(1)Execute执行器:
执行器起到至关重要的作用,它是真正执行Java与数据库交互的东西,参与了整个SQL查询执行过程中。
1)主要有三种执行器:简易执行器SIMPLE(不配置就是默认执行器)、REUSE是一种重用预处理语句、BATCH批量更新、批量专用处理器
package org.apache.ibatis.session; /** * @author Clinton Begin */ public enum ExecutorType { SIMPLE, REUSE, BATCH }
2)执行器作用:Executor会先调用StatementHandler的prepare()方法预编译SQL语句,同时设置一些基本的运行参数,然后调用parameterize()方法启用ParemeterHandler设置参数,完成预编译,简单总结起来就是即先预编译SQL语句,之后设置参数
首先,以SimpleExecutor为例,查看源码我们得到如下几点重要知识点:
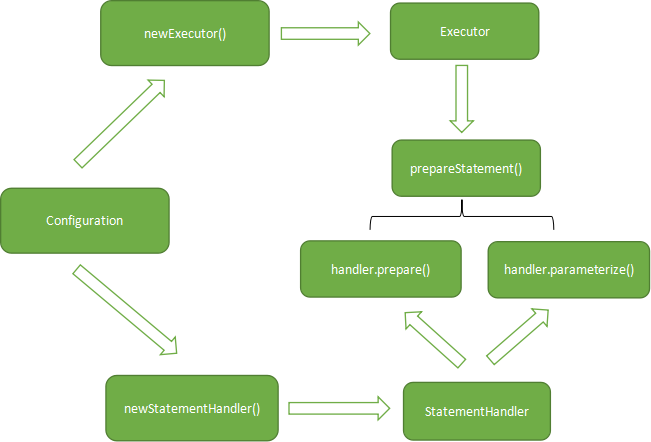
第一:Executor通过Configuration对象中newExecutor()方法中选择相应的执行器生成
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) { executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType; executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType; Executor executor; if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) { executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction); } else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) { executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction); } else { executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction); } if (cacheEnabled) { executor = new CachingExecutor(executor); } executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor); return executor; }
(注:最后interceptorChain.pluginAll()中执行层层动态代理,最后在可以在调用真正的Executor前可以修改插件代码,这也就是为什么学会Mybatis的插件必须要知道SqlSession的运行过程)
第二:在执行器中StatementHandler是根据Configuration构建的
public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) { super(configuration, transaction); } @Override public int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException { Statement stmt = null; try { Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration(); StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(this, ms, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT, null, null); stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog()); return handler.update(stmt); } finally { closeStatement(stmt); } }
第三:Executor会执行StatementHandler的prepare()方法进行预编译---->填入connection对象---->再调用parameterize()方法设置参数---->完成预编译
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) throws SQLException { Statement stmt; Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog); stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout()); handler.parameterize(stmt); return stmt; }
总结以上绘制简单思维图如下:
(2)StatementHanlder数据库会话器
由Executor的prepareStatement方法中parameterize方法引出StatementHandler
StatementHandler的生成是由Configuration方法中newStatementHandler()方法生成的,但是StatementHandler是RoutingStatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject,
RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) { StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql); statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler); return statementHandler; }
-------------------------------------------未完待续,明天继续写------------------------------------------------------