更多参考我的另一篇博客:
https://www.cnblogs.com/winslam/articles/8975139.html
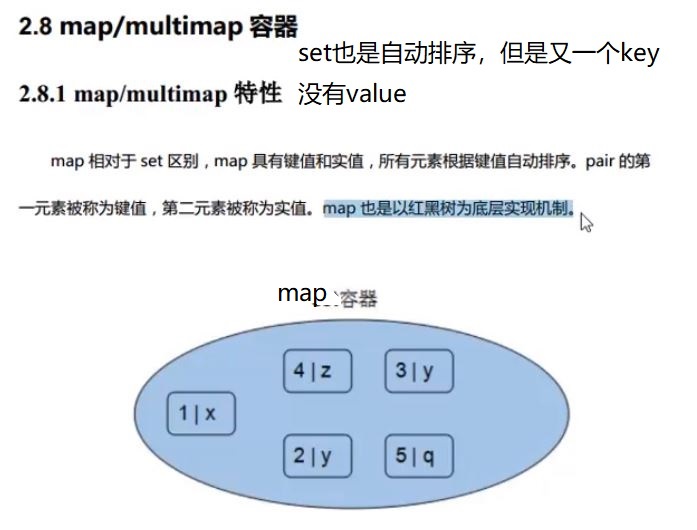
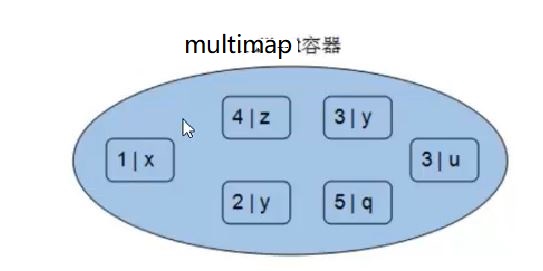
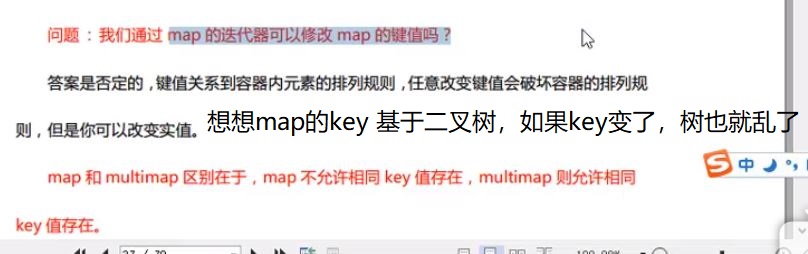


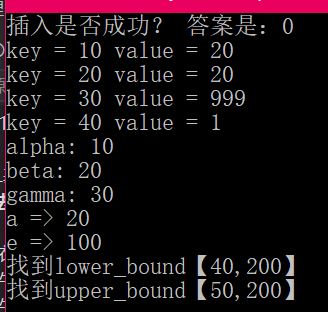
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<map> 3 4 using namespace std; 5 6 void printf(map<int, int> map_) 7 { 8 for (map<int, int>::iterator itr = map_.begin(); itr != map_.end(); itr++) 9 { 10 cout << "key = " << itr->first << " value = " << itr->second << endl; 11 } 12 } 13 14 class Student 15 { 16 public: 17 Student(int age, int num) :age_(age), num_(num) {}; 18 19 int age_; 20 int num_; 21 }; 22 23 // 仿函数写法1 24 //class MyCompare 25 //{ 26 //public: 27 // bool operator()(Student stu1, Student stu2) 28 // { 29 // return stu1.num_ > stu2.num_; 30 // } 31 //}; 32 // 仿函数写法2 33 struct MyCompare 34 { 35 36 bool operator()(Student stu1, Student stu2) 37 { 38 return stu1.num_ > stu2.num_; 39 } 40 }; 41 42 43 int main() 44 { 45 // <1>初始化 46 map<int, int> map_; 47 map_.insert(pair<int, int>(10, 20)); // 1 48 map_.insert(make_pair<int, int>(20, 20)); // 2 49 pair<map<int, int>::iterator, bool> ret = map_.insert(map<int, int>::value_type(20, 20)); // 3,返回插入成功? 50 cout << "插入是否成功? 答案是:" << ret.second << endl; 51 52 map_[30] = 30; // 4 53 map_[30] = 999;//修改已有键的值 54 map_[40]++;// key = 40 之前不存在,这里value首先默认为 0 55 printf(map_); 56 // <2> 57 // 仿函数【自定义排序规则】 58 map<Student, int, MyCompare> map1; //map/multimap本身会自动排序,所以这里无法对 class 进行排序,你必须自定义一个仿函数 59 map1.insert(make_pair(Student(10, 100), 1)); 60 map1.insert(make_pair(Student(10, 300), 1)); 61 map1.insert(make_pair(Student(10, 300), 1)); // 插入失败 62 map1.insert(make_pair(Student(10, 600), 1)); 63 64 // <3>操作符[] 与 at 65 std::map<std::string, int> mymap = 66 { 67 { "alpha", 0 }, 68 { "beta", 0 }, 69 { "gamma", 0 } 70 }; 71 mymap.at("alpha") = 10; 72 mymap.at("beta") = 20; 73 mymap["gamma"] = 30; 74 75 for (auto& x:mymap) 76 { 77 std::cout << x.first.c_str() << ": " << x.second << '\n'; 78 } 79 80 // <4>区间操作 81 { 82 // lower_bound and upper_bound 83 map<char, int> mymap; 84 map<char, int>::iterator itlow, itup; 85 86 mymap['a'] = 20; 87 mymap['b'] = 40; 88 mymap['c'] = 60; 89 mymap['d'] = 80; 90 mymap['e'] = 100; 91 92 itlow = mymap.lower_bound('b'); // itlow points to b 指向等于b 93 itup = mymap.upper_bound('d'); // itup points to e (not d!) 指向大于d 94 95 mymap.erase(itlow, itup); // erases [itlow,itup) 96 97 // print content: 98 for (std::map<char, int>::iterator it = mymap.begin(); it != mymap.end(); ++it) 99 std::cout << it->first << " => " << it->second << '\n'; 100 101 // equal_range 102 map<int, int> mymap_; 103 mymap_.insert(make_pair(10, 100)); 104 mymap_.insert(make_pair(20, 300)); 105 mymap_.insert(make_pair(30, 200)); 106 mymap_.insert(make_pair(40, 200)); 107 mymap_.insert(make_pair(50, 200)); 108 pair<map<int, int>::iterator, map<int, int>::iterator> ret; 109 ret = mymap_.equal_range(40); 110 if (ret.first->second) 111 { 112 cout << "找到lower_bound" << "【" << ret.first->first <<","<< ret.first->second << "】" << endl; 113 } 114 if (ret.second->second) 115 { 116 cout << "找到upper_bound" << "【" << ret.second->first << "," << ret.second->second << "】" << endl; 117 } 118 } 119 return 1; 120 }