个人理解:Arrays.copyOf()调用了基于本地方法和机器码的System.arrayCopy()方法,从原数组拷贝到一个临时新建数组并返回,返回数组长度取参数和原数组的较小值。也就是,传入长度太短时截取,太长了取原长。
得出结论:如果多次扩容,要选定一个合适的大小,太小频繁扩容有创建数组开销,太大占用内存。
-
package com.demo.main; import java.util.Arrays; /** * <ol>复制数组的4种方法 * <li>for</li> * <li>clone</li> * <li>Arrays.copyOf(original, newLength)</li> * <li>System.arraycopy(src, srcPos, dest, destPos, length)</li> * </ol> */ public class ArrayCopyDemo { private static final byte[] buffer = new byte[1024*10]; static { for (int i = 0; i < buffer.length; i++) { buffer[i] = (byte) (i & 0xFF); } } private static long startTime; public static void main(String[] args) { startTime = System.nanoTime(); methodFor(); calcTime("methodFor"); startTime = System.nanoTime(); methodClone(); calcTime("methodClone"); startTime = System.nanoTime(); methodArraysCopyOf(); calcTime("methodArraysCopyOf"); startTime = System.nanoTime(); methodSystemArraycopy(); calcTime("methodSystemArraycopy"); } private static void methodFor() { byte[] newBuffer = new byte[buffer.length]; for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++) { newBuffer[i] = buffer[i]; } } private static void methodClone() { byte[] newBuffer = buffer.clone(); } private static void methodArraysCopyOf() { byte[] newBuffer = Arrays.copyOf(buffer, buffer.length); } private static void methodSystemArraycopy() { byte[] newBuffer = new byte[buffer.length]; System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, newBuffer, 0, buffer.length); } private static void calcTime(String method) { long endTime = System.nanoTime(); System.out.println(method + " cost " +(endTime-startTime)+ " nanosecond"); } }
总结:
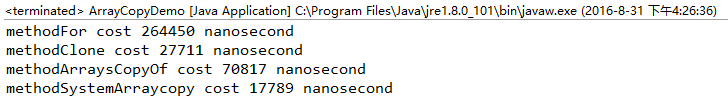
(1)从速度上看:System.arraycopy > clone > Arrays.copyOf > for
(2)for的速度之所以最慢是因为下标表示法每次都从起点开始寻位到指定下标处(现代编译器应该对其有进行优化,改为指针),另外就是它每一次循环都要判断一次是否达到数组最大长度和进行一次额外的记录下标值的加法运算。
(3)查看Arrays.copyOf的源码可以发现,它其实本质上是调用了System.arraycopy。之所以时间差距比较大,是因为很大一部分开销全花在了Math.min函数上了。
public static byte[] copyOf(byte[] original, int newLength) { byte[] copy = new byte[newLength]; System.arraycopy(original, 0, copy, 0, Math.min(original.length, newLength)); return copy; }
(4)查看System.arraycopy的源码,可以发现它实质上是通过Jni调用本地方法,及c/c++已经编译成机器码的方法,所以快。
public static native void arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length);
(5)clone的源码不详,鄙人无法比较,有知道的希望不吝赐教。
版权声明:转载请注明出处——http://blog.csdn.net/chy555chy/article https://blog.csdn.net/chy555chy/article/details/52386608