一、ArrayList概述
1.特点:有序的、可重复的集合
2.ArrayList继承了Serializable,可以实现序列化传输。继承了Cloneable,可以被克隆。继承RandomAccess,可以通过下标标记快速访问。
3.ArrayList是单线程安全的集合,多线程使用Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList<>())
4.每个ArrayList实例都有一个容量,该容量是指用来存储列表元素的数组的大小。它总是至少等于列表的大小。随着向ArrayList中不断添加元素,其容量也自动增长。自动增长会带来数据向新数组的重新拷贝,因此,如果可预知数据量的多少,可在构造ArrayList时指定其容量。在添加大量元素前,应用程序也可以使用ensureCapacity操作来增加ArrayList实例的容量,这可以减少递增式再分配的数量。
二、方法源码分析
1.get():返回对应下标数据
public E get(int index) {
rangeCheck(index); //判断下标
return elementData(index); //返回数据
}2.set(int index, E element) :在index位置替换为element元素,并返回原先的数据
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
} public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1);
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
} private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
} private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) //判断如果当前数组容量不够,就需要扩充
grow(minCapacity);
} private void grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //原有的数目
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1); //将原有的数目扩大1.5倍
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) //判断新数组容量够不够
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) //判断数组容量有没有超过最大限制
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); //创建新的数组,并赋值。所以在初始化数组时候最好指定数组的容量
}4.add(int index,E element):特定位置添加元素
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}5.addAll与add类似
6.remove(int index):移出index位置的元素,并返回该元素
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0) //将移除位置之后的元素挪动一个位置
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index,
numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; // 将末尾的元素置空 null
return oldValue;
} public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) { //如果
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (elementData[index] == null) {
fastRemove(index);//移除元素
return true;
}
} else {
for (int index = 0; index < size; index++)
if (o.equals(elementData[index])) {
fastRemove(index);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}三 、LinkedList:
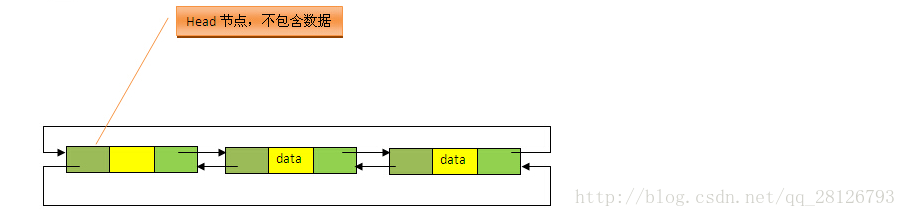
1.数据结构:LinkedList是双向循环列表
每个节点数数据结构如下:
2.属性
transient int size = 0;
transient Node<E> first;
transient Node<E> last; private static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node<E> prev;
Node(Node<E> prev, E element, Node<E> next) {
this.item = element;
this.next = next; //后指针
this.prev = prev; //前指针
}
}4. 构造函数
public LinkedList() {
}
public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this();
addAll(c); //调用上面的空构造函数,然后执行addAll函数
}5.函数
1)get(int index):获取index位置的数据
public E get(int index) {
checkElementIndex(index); //判断元素是否存在
return node(index).item; //返回元素
} Node<E> node(int index) {
if (index < (size >> 1)) { //判断元素在前半部分还是后半部分,,可以提高查询效率
Node<E> x = first;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
x = x.next;
return x;
} else {
Node<E> x = last;
for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--)
x = x.prev;
return x;
}
}2)add(E e) : 添加元素
public boolean add(E e) {
linkLast(e);
return true;
}void linkLast(E e) {
final Node<E> l = last;
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //创建新的节点
last = newNode;
if (l == null) //判断是否有数据
first = newNode;
else
l.next = newNode; //将指向新的元素
size++;
modCount++;
}3)addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) :添加集合
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
checkPositionIndex(index); //判断下标元素是否存在
Object[] a = c.toArray(); //转换为数组
int numNew = a.length;
if (numNew == 0) //判断是否是空数组
return false;
Node<E> pred, succ;
if (index == size) { //判断是否是在尾节点添加数据
succ = null;
pred = last;
} else {
succ = node(index);
pred = succ.prev;
}
for (Object o : a) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") E e = (E) o;
Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); //创建新的节点
if (pred == null) //将next指针指向新节点
first = newNode;
else
pred.next = newNode;
pred = newNode; //将新节点附为前节点
}
if (succ == null) { //判断当前是否是尾节点
last = pred;
} else {
pred.next = succ;
succ.prev = pred;
}
size += numNew;
modCount++;
return true;
}