项目提交测试,趁着中当间的这个空档期,把springboot的多数据源配置学习一下,总体来说多数据源配置有两种方式,一种是静态的,一种是动态的。
静态的方式
我们以两套配置方式为例,在项目中有两套配置文件,两套mapper,两套SqlSessionFactory,各自处理各自的业务,这个两套mapper都可以进行增删改查的操作,在这两个主MYSQL后也可以各自配置自己的slave,实现数据的备份。如果在增加一个数据源就得从头到尾的增加一遍。先看看两个配置文件:
-
## master 数据源配置 -
master1.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/learn?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 -
master1.datasource.username=root -
master1.datasource.password= -
master1.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver -
## slave 数据源配置 -
master2.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3308/learn?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 -
master2.datasource.username=root -
master2.datasource.password= -
master2.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
这两个数据源的配置不分主从,看网上很多这种配置方式,说是主从配置,个人认为既然什么都是两套就没有必要分出主从,分出读写了,根据业务的需求以及数据库服务器的性能进行划分即可。两个配置类
-
@Configuration -
// 扫描 Mapper 接口并容器管理 -
@MapperScan(basePackages = Master1DataSourceConfig.PACKAGE, sqlSessionFactoryRef = "master1SqlSessionFactory") -
public class Master1DataSourceConfig { -
// 精确到 master 目录,以便跟其他数据源隔离 -
static final String PACKAGE = "com.hui.readwrite.mapper.master1"; -
static final String MAPPER_LOCATION = "classpath:mapper/master1.xml"; -
@Value("${master1.datasource.url}") -
private String url; -
@Value("${master1.datasource.username}") -
private String user; -
@Value("${master1.datasource.password}") -
private String password; -
@Value("${master1.datasource.driverClassName}") -
private String driverClass; -
@Bean(name = "master1DataSource") -
@Primary -
public DataSource masterDataSource() { -
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource(); -
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClass); -
dataSource.setUrl(url); -
dataSource.setUsername(user); -
dataSource.setPassword(password); -
return dataSource; -
} -
@Bean(name = "master1TransactionManager") -
@Primary -
public DataSourceTransactionManager masterTransactionManager() { -
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(masterDataSource()); -
} -
@Bean(name = "master1SqlSessionFactory") -
@Primary -
public SqlSessionFactory masterSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("master1DataSource") DataSource masterDataSource) -
throws Exception { -
final SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); -
sessionFactory.setDataSource(masterDataSource); -
sessionFactory.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() -
.getResources(Master1DataSourceConfig.MAPPER_LOCATION)); -
return sessionFactory.getObject(); -
} -
}
-
@Configuration -
// 扫描 Mapper 接口并容器管理 -
@MapperScan(basePackages = Master2DataSourceConfig.PACKAGE, sqlSessionFactoryRef = "master2SqlSessionFactory") -
public class Master2DataSourceConfig { -
// 精确到 master 目录,以便跟其他数据源隔离 -
static final String PACKAGE = "com.hui.readwrite.mapper.master2"; -
static final String MAPPER_LOCATION = "classpath:mapper/master2.xml"; -
@Value("${master2.datasource.url}") -
private String url; -
@Value("${master2.datasource.username}") -
private String user; -
@Value("${master2.datasource.password}") -
private String password; -
@Value("${master2.datasource.driverClassName}") -
private String driverClass; -
@Bean(name = "master2DataSource") -
public DataSource master2DataSource() { -
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource(); -
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driverClass); -
dataSource.setUrl(url); -
dataSource.setUsername(user); -
dataSource.setPassword(password); -
return dataSource; -
} -
@Bean(name = "master2TransactionManager") -
public DataSourceTransactionManager master2TransactionManager() { -
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(master2DataSource()); -
} -
@Bean(name = "master2SqlSessionFactory") -
public SqlSessionFactory clusterSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("master2DataSource") DataSource master2DataSource) throws Exception { -
final SqlSessionFactoryBean sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); -
sessionFactory.setDataSource(master2DataSource); -
sessionFactory.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() -
.getResources(Master2DataSourceConfig.MAPPER_LOCATION)); -
return sessionFactory.getObject(); -
} -
}
@Primary 标志这个 Bean 如果在多个同类 Bean 候选时,该 Bean 优先被考虑。「多数据源配置的时候注意,必须要有一个主数据源,用 @Primary 标志该 Bean」
@MapperScan 扫描 Mapper 接口并容器管理,包路径精确到 master,为了和下面 cluster 数据源做到精确区分
@Value 获取全局配置文件 application.properties 的 kv 配置,并自动装配
sqlSessionFactoryRef 表示定义了 key ,表示一个唯一 SqlSessionFactory 实例
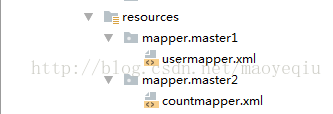
两个mapper接口的路径和xml文件的路径如下:
这样就可以实现同一个项目使用多个数据配置,缺点是不易维护和扩展。
动态方式
这种方式实现了一个写库多个读库,使用的是同一套Mapper接口和XML文件,这样就有很好的拓展性,具体代码如下:
先是生成不同的数据源,其中多个读数据源合并
-
@Configuration -
public class DataBaseConfiguration{ -
@Value("${spring.datasource.type}") -
private Class<? extends DataSource> dataSourceType; -
@Bean(name="writeDataSource", destroyMethod = "close", initMethod="init") -
@Primary -
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.write.datasource") -
public DataSource writeDataSource() { -
return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); -
} -
/** -
* 有多少个从库就要配置多少个 -
* @return -
*/ -
@Bean(name = "readDataSourceOne") -
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.read.one") -
public DataSource readDataSourceOne(){ -
return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); -
} -
@Bean(name = "readDataSourceTwo") -
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.read.two") -
public DataSource readDataSourceTwo() { -
return DataSourceBuilder.create().type(dataSourceType).build(); -
} -
@Bean("readDataSources") -
public List<DataSource> readDataSources(){ -
List<DataSource> dataSources=new ArrayList<DataSource>(); -
dataSources.add(readDataSourceOne()); -
dataSources.add(readDataSourceTwo()); -
return dataSources; -
} -
}
生成一套SqlSessionFactory,进行动态切换
-
@Configuration -
@ConditionalOnClass({EnableTransactionManagement.class}) -
@Import({ DataBaseConfiguration.class}) -
@MapperScan(basePackages={"com.hui.readwrite.mapper.master1"}) -
public class TxxsbatisConfiguration { -
@Value("${spring.datasource.type}") -
private Class<? extends DataSource> dataSourceType; -
@Value("${datasource.readSize}") -
private String dataSourceSize; -
@Resource(name = "writeDataSource") -
private DataSource dataSource; -
@Resource(name = "readDataSources") -
private List<DataSource> readDataSources; -
@Bean -
@ConditionalOnMissingBean -
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory() throws Exception { -
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); -
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(roundRobinDataSouceProxy()); -
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.hui.readwrite.po"); -
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() -
.getResources("classpath:mapper/master1*//*.xml")); -
sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject().getConfiguration().setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(true); -
return sqlSessionFactoryBean.getObject(); -
} -
/** -
* 有多少个数据源就要配置多少个bean -
* @return -
*/ -
@Bean -
public AbstractRoutingDataSource roundRobinDataSouceProxy() { -
int size = Integer.parseInt(dataSourceSize); -
TxxsAbstractRoutingDataSource proxy = new TxxsAbstractRoutingDataSource(size); -
Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources = new HashMap<Object, Object>(); -
targetDataSources.put(DataSourceType.write.getType(),dataSource); -
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) { -
targetDataSources.put(i, readDataSources.get(i)); -
} -
proxy.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dataSource); -
proxy.setTargetDataSources(targetDataSources); -
return proxy; -
} -
}
进行选择,和读库的简单负载。Spring boot提供了AbstractRoutingDataSource根据用户定义的规则选择当前的数据库,这样我们可以在执行查询之前,设置读取从库,在执行完成后,恢复到主库。实现可动态路由的数据源,在每次数据库查询操作前执行
-
public class TxxsAbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource { -
private final int dataSourceNumber; -
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0); -
public TxxsAbstractRoutingDataSource(int dataSourceNumber) { -
this.dataSourceNumber = dataSourceNumber; -
} -
@Override -
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() { -
String typeKey = DataSourceContextHolder.getJdbcType(); -
if (typeKey.equals(DataSourceType.write.getType())) -
return DataSourceType.write.getType(); -
// 读 简单负载均衡 -
int number = count.getAndAdd(1); -
int lookupKey = number % dataSourceNumber; -
return new Integer(lookupKey); -
} -
}
利用AOP的方式实现,方法的控制
-
@Aspect -
@Component -
public class DataSourceAop { -
public static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DataSourceAop.class); -
@Before("execution(* com.hui.readwrite.mapper..*.select*(..)) || execution(* com.hui.readwrite.mapper..*.get*(..))") -
public void setReadDataSourceType() { -
DataSourceContextHolder.read(); -
logger.info("dataSource切换到:Read"); -
} -
@Before("execution(* com.hui.readwrite.mapper..*.insert*(..)) || execution(* com.hui.readwrite.mapper..*.update*(..))") -
public void setWriteDataSourceType() { -
DataSourceContextHolder.write(); -
logger.info("dataSource切换到:write"); -
} -
}
配置文件:
-
#一些总的配置文件 -
spring.aop.auto=true -
spring.datasource.type=com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource -
datasource.readSize=2 -
# 主数据源,默认的 -
spring.write.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver -
spring.write.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/learn?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 -
spring.write.datasource.username=root -
spring.write.datasource.password=root -
# 从数据源 -
spring.read.one.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver -
spring.read.one.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/learn?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 -
spring.read.one.username=root -
spring.read.one.password=root -
spring.read.two.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver -
spring.read.two.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3308/learn?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8 -
spring.read.two.username=root -
spring.read.two.password=root
我们可以看到效果:
关于事务的观点
核心思想,spring提供了一个DataSource的子类,该类支持多个数据源
org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.lookup.AbstractRoutingDataSource
上述静态多个数据库的这种配置是不支持分布式事务的,也就是同一个事务中,不能操作多个数据库。
一些实时性要求很高的select语句,我们也可能需要放到master上执行,这些查询可能也需要放在master上执行,而不能放在slave上去执行,因为slave上可能存在延时。
如果有多台 master 或者有多台 slave。多台master组成一个HA,要实现当其中一台master挂了是,自动切换到另一台master,这个功能可以使用LVS/Keepalived来实现,也可以通过进一步扩展ThreadLocalRountingDataSource来实现,可以另外加一个线程专门来每个一秒来测试mysql是否正常来实现。同样对于多台slave之间要实现负载均衡,同时当一台slave挂了时,要实现将其从负载均衡中去除掉,这个功能既可以使用LVS/Keepalived来实现,同样也可以通过近一步扩展ThreadLocalRountingDataSource来实现。
因为事务是依赖数据源的,你用注解切换数据源的操作 跟 用注解加事务控制的操作应该是注意下先后关系。切换数据源的注解配置是要放在事务注解配置前面的,不然有问题。
解决方案添加分布式的事务,Atomikos和spring结合来处理。
配置多个不同的数据源,使用一个sessionFactory,在业务逻辑使用的时候自动切换到不同的数据源,有一个种是在拦截器里面根据不同的业务现切换到不同的datasource;有的会在业务层根据业务来自动切换。但这种方案在多线程并发的时候会出现一些问题,需要使用threadlocal等技术来实现多线程竞争切换数据源的问题。
由于我使用的注解式事务,和我们的AOP数据源切面有一个顺序的关系。数据源切换必须先执行,数据库事务才能获取到正确的数据源。所以要明确指定 注解式事务和 我们AOP数据源切面的先后顺序。我们数据源切换的AOP是通过注解来实现的,只需要在AOP类上加上一个order(1)注解即可,其中1代表顺序号。
spring的事务管理,是基于数据源的,所以如果要实现动态数据源切换,而且在同一个数据源中保证事务是起作用的话,就需要注意二者的顺序问题,即:在事物起作用之前就要把数据源切换回来。
举一个例子:web开发常见是三层结构:controller、service、dao。一般事务都会在service层添加,如果使用spring的声明式事物管理,在调用service层代码之前,spring会通过aop的方式动态添加事务控制代码,所以如果要想保证事物是有效的,那么就必须在spring添加事务之前把数据源动态切换过来,也就是动态切换数据源的aop要至少在service上添加,而且要在spring声明式事物aop之前添加.根据上面分析:
最简单的方式是把动态切换数据源的aop加到controller层,这样在controller层里面就可以确定下来数据源了。不过,这样有一个缺点就是,每一个controller绑定了一个数据源,不灵活。对于这种:一个请求,需要使用两个以上数据源中的数据完成的业务时,就无法实现了。
针对上面的这种问题,可以考虑把动态切换数据源的aop放到service层,但要注意一定要在事务aop之前来完成。这样,对于一个需要多个数据源数据的请求,我们只需要在controller里面注入多个service实现即可。但这种做法的问题在于,controller层里面会涉及到一些不必要的业务代码,例如:合并两个数据源中的list…
此外,针对上面的问题,还可以再考虑一种方案,就是把事务控制到dao层,然后在service层里面动态切换数据源。
感谢:
http://www.itwendao.com/article/detail/210530.html
http://www.jianshu.com/p/8813ec02926a
http://blog.csdn.net/dream_broken/article/details/72851329