在项目开发中,有一些场景需要同时使用多个数据库,并且需要能够根据需求能够动态切换,下面介绍一种基于注解+aop的方式。
动态多数据源实现
Spring boot启动类(Application)
首先要将spring boot自带的DataSourceAutoConfiguration禁掉,因为它会读取application.properties文件的spring.datasource.*属性并自动配置单数据源。在@SpringBootApplication注解中添加exclude属性即可:
/**
* springboot启动类
* 使用exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class}
* 禁用springboot默认加载的application.properties单数据源配置
*/
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(Application.class);
app.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);
app.run(args);
}
}数据库配置文件(dynamic-multi-db.yml)
配置数据源,其中前缀为“spring.datasource”的为默认数据源,前缀为“spring.datasource.provider”的为provider数据源,前缀为“spring.datasource.consumer”的为consumer数据源。
spring:
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/default_db?useUnicode=true&noDatetimeStringSync=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: username
password: password
provider:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/provider_db?useUnicode=true&noDatetimeStringSync=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: username
password: password
consumer:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/consumer_db?useUnicode=true&noDatetimeStringSync=true&characterEncoding=utf8
username: username
password: password数据源配置类(DataSourceConfig)
由于我们禁掉了Spring boot的自动数据源配置,因些需要手动将数据源创建出来,通过读取application.properties(dynamic-multi-db.yml)文件生成三个数据源(dataSourceDefault、dataSourceProvider、dataSourceConsumer),并使用这三个数据源动态构建DataSource。
/**
* Mybatis多数据源配置类
*/
@Configuration
@MapperScan("com.wind.test.dao.mybatis")
public class DataSourceConfig {
/**
* 默认数据源
*
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSourceDefault")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public DataSource dataSourceDefault() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 来源库
*
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSourceProvider")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.provider")
public DataSource dataSourceProvider() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 目标库
*
* @return
*/
@Bean(name = "dataSourceConsumer")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource.consumer")
public DataSource dataSourceConsumer() {
return DataSourceBuilder.create().build();
}
/**
* 动态数据源: 通过AOP在不同数据源之间动态切换
* 将数据库实例写入到targetDataSources属性中,并且使用defaultTargetDataSource属性设置默认数据源。
* @Primary 注解用于标识默认使用的 DataSource Bean,并注入到SqlSessionFactory的dataSource属性中去。
*
* @return
*/
@Primary
@Bean(name = "dynamicDataSource")
public DataSource dynamicDataSource() {
DynamicDataSource dynamicDataSource = new DynamicDataSource();
// 默认数据源
dynamicDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dataSourceDefault());
// 配置多数据源
Map<Object, Object> dsMap = new HashMap();
dsMap.put("dataSourceDefault", dataSourceDefault());
dsMap.put("dataSourceProvider", dataSourceProvider());
dsMap.put("dataSourceConsumer", dataSourceConsumer());
dynamicDataSource.setTargetDataSources(dsMap);
return dynamicDataSource;
}
/**
* 配置@Transactional注解事物
* 使用dynamicDataSource作为transactionManager的入参来构造DataSourceTransactionManager
*
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager() {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dynamicDataSource());
}
}数据源上下文(DataSourceContextHolder)
使用ThreadLocal提供一个线程安全的容器,存储创建出来的DataSource Bean的示例名
/**
* 数据源上下文
*/
public class DataSourceContextHolder {
/**
* 默认数据源
*/
public static final String DEFAULT_DS = "dataSourceDefault";
/**
* 使用ThreadLocal存储数据源
*/
private static final ThreadLocal<String> contextHolder = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* 设置数据源
*
* @param dbType
*/
public static void setDB(String dbType) {
contextHolder.set(dbType);
}
/**
* 获取数据源
*
* @return
*/
public static String getDB() {
return (contextHolder.get());
}
/**
* 清除数据源
*/
public static void clearDB() {
contextHolder.remove();
}
}动态数据源(DynamicDataSource)
DynamicDataSource继承AbstractRoutingDataSource并重写其中的方法determineCurrentLookupKey(),在该方法中使用DatabaseContextHolder获取当前线程指定的数据源。
/**
* 动态数据源
*/
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DataSourceContextHolder.getDB();
}
}数据源切换注解(DS)
定义一个@DS注解类,在运行时动态切换数据源。
/**
* 数据源切换注解
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
public @interface DS {
public static final String dataSourceProvider = "dataSourceProvider";
public static final String dataSourceConsumer = "dataSourceConsumer";
String value() default "dataSourceDefault";
}数据源切换切面(DynamicDataSourceAspect)
使用AOP解析@DS注解的方法,实现动态数据源切换。
/**
* 自定义注解@DS + AOP的方式实现数据源动态切换。
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class DynamicDataSourceAspect {
@Before("@annotation(DS)")
public void beforeSwitchDS(JoinPoint point) {
//获得当前访问的class
Class<?> className = point.getTarget().getClass();
//获得访问的方法名
String methodName = point.getSignature().getName();
//得到方法的参数的类型
Class[] argClass = ((MethodSignature) point.getSignature()).getParameterTypes();
String dataSource = DataSourceContextHolder.DEFAULT_DS;
try {
// 得到访问的方法对象
Method method = className.getMethod(methodName, argClass);
// 判断是否存在@DS注解
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(DS.class)) {
DS annotation = method.getAnnotation(DS.class);
// 取出注解中的数据源名
dataSource = annotation.value();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 切换数据源
DataSourceContextHolder.setDB(dataSource);
}
@After("@annotation(DS)")
public void afterSwitchDS(JoinPoint point) {
DataSourceContextHolder.clearDB();
}
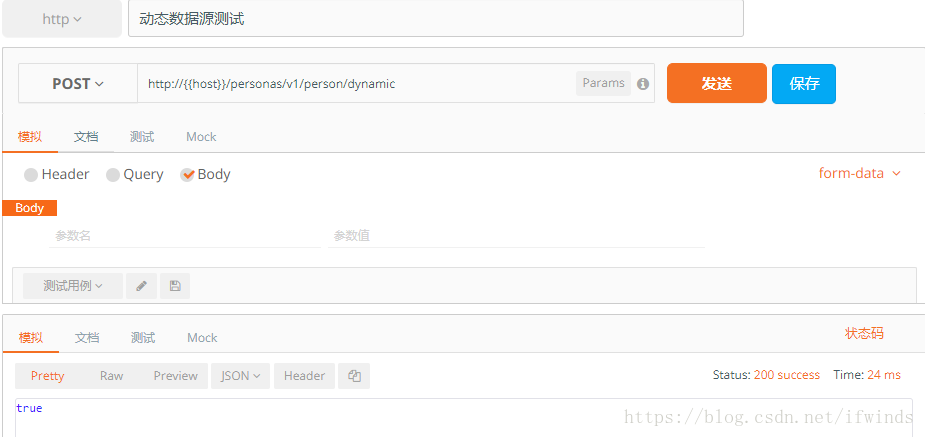
}动态多数据源测试
测试方法:在provider库中查询数据插入到consumer库中,如果插入成功则动态多数据源配置成功。

建表语句
CREATE TABLE `person` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=20 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
-- 下面语句provider库执行,consumer库不执行
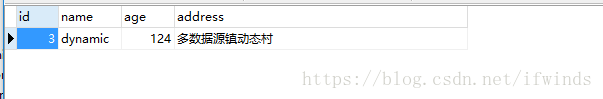
-- insert into person (name,age,address) values ('dynamic',124,'多数据源镇动态村');数据库实体(person)
/**
* 数据库实体-动态多数据源测试
*/
@Setter
@Getter
@TableName("person")
public class PersonEntity extends BaseMybatisEntity<PersonEntity> {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String address;
}数据访问对象(PersonDao)
/**
* DAO - 多数据源测试
*/
public interface PersonDao extends MybatisMapper<PersonEntity> {
}Service层接口(PersonService )
/**
* Service - 动态多数据源测试
*/
public interface PersonService extends BaseMybatisService<PersonEntity> {
/**
* 查询
*
* @param name
* @return
*/
PersonEntity findOne(String name);
/**
* 新增
*
* @param personEntity
* @return
*/
@Override
boolean insert(PersonEntity personEntity);
}Service接口实现(PersonServiceImpl )
/**
* ServiceImpl - 动态多数据源测试
*/
@Service
public class PersonServiceImpl extends BaseMybatisServiceImpl<PersonDao, PersonEntity> implements PersonService {
/**
* 从数据源获取数据
*
* @param name
* @return
*/
@Override
@DS(DS.dataSourceProvider)
public PersonEntity findOne(String name) {
Wrapper<PersonEntity> wrapper = Condition.create().eq("name", name);
PersonEntity personEntity = super.selectOne(wrapper);
return personEntity;
}
/**
* 将数据插入目标数据库
*
* @param personEntity
* @return
*/
@Override
@DS(DS.dataSourceConsumer)
public boolean insert(PersonEntity personEntity) {
return super.insert(personEntity);
}
}Controller(PersonController )
/**
* Controller - 动态多数据源测试
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping()
public class PersonController extends BaseController {
@Autowired
PersonService personService;
/**
* 动态多数据源测试
* 从provider数据库读取数据插入到consumer数据库
*
* @param personDto
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/v1/person/{name}")
public boolean add(@PathVariable String name) {
logger.info("Request-URI: Post/v1/person/{}", name);
PersonEntity personEntity = personService.findOne(name);
return personService.insert(personEntity);
}
}测试结果
请求之后可以看到consumer数据库中已经插入了从provider库中查询出来的数据
参考文献
https://blog.csdn.net/neosmith/article/details/61202084
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaosheng_papa/article/details/80218006
https://www.cnblogs.com/java-zhao/p/5413845.html