Segmented CTE
from math import *
import random
steering_noise = 0.1
distance_noise = 0.03
measurement_noise = 0.3
class plan:
def __init__(self, grid, init, goal, cost = 1):
self.cost = cost
self.grid = grid
self.init = init
self.goal = goal
self.make_heuristic(grid, goal, self.cost)
self.path = []
self.spath = []
def make_heuristic(self, grid, goal, cost):
self.heuristic = [[0 for row in range(len(grid[0]))]
for col in range(len(grid))]
for i in range(len(self.grid)):
for j in range(len(self.grid[0])):
self.heuristic[i][j] = abs(i - self.goal[0]) + \
abs(j - self.goal[1])
def astar(self):
if self.heuristic == []:
raise ValueError, "Heuristic must be defined to run A*"
delta = [[-1, 0],
[ 0, -1],
[ 1, 0],
[ 0, 1]]
closed = [[0 for row in range(len(self.grid[0]))]
for col in range(len(self.grid))]
action = [[0 for row in range(len(self.grid[0]))]
for col in range(len(self.grid))]
closed[self.init[0]][self.init[1]] = 1
x = self.init[0]
y = self.init[1]
h = self.heuristic[x][y]
g = 0
f = g + h
open = [[f, g, h, x, y]]
found = False
resign = False
count = 0
while not found and not resign:
if len(open) == 0:
resign = True
print '###### Search terminated without success'
else:
open.sort()
open.reverse()
next = open.pop()
x = next[3]
y = next[4]
g = next[1]
if x == goal[0] and y == goal[1]:
found = True
else:
for i in range(len(delta)):
x2 = x + delta[i][0]
y2 = y + delta[i][1]
if x2 >= 0 and x2 < len(self.grid) and y2 >= 0 \
and y2 < len(self.grid[0]):
if closed[x2][y2] == 0 and self.grid[x2][y2] == 0:
g2 = g + self.cost
h2 = self.heuristic[x2][y2]
f2 = g2 + h2
open.append([f2, g2, h2, x2, y2])
closed[x2][y2] = 1
action[x2][y2] = i
count += 1
invpath = []
x = self.goal[0]
y = self.goal[1]
invpath.append([x, y])
while x != self.init[0] or y != self.init[1]:
x2 = x - delta[action[x][y]][0]
y2 = y - delta[action[x][y]][1]
x = x2
y = y2
invpath.append([x, y])
self.path = []
for i in range(len(invpath)):
self.path.append(invpath[len(invpath) - 1 - i])
def smooth(self, weight_data = 0.1, weight_smooth = 0.1,
tolerance = 0.000001):
if self.path == []:
raise ValueError, "Run A* first before smoothing path"
self.spath = [[0 for row in range(len(self.path[0]))] \
for col in range(len(self.path))]
for i in range(len(self.path)):
for j in range(len(self.path[0])):
self.spath[i][j] = self.path[i][j]
change = tolerance
while change >= tolerance:
change = 0.0
for i in range(1, len(self.path)-1):
for j in range(len(self.path[0])):
aux = self.spath[i][j]
self.spath[i][j] += weight_data * \
(self.path[i][j] - self.spath[i][j])
self.spath[i][j] += weight_smooth * \
(self.spath[i-1][j] + self.spath[i+1][j]
- (2.0 * self.spath[i][j]))
if i >= 2:
self.spath[i][j] += 0.5 * weight_smooth * \
(2.0 * self.spath[i-1][j] - self.spath[i-2][j]
- self.spath[i][j])
if i <= len(self.path) - 3:
self.spath[i][j] += 0.5 * weight_smooth * \
(2.0 * self.spath[i+1][j] - self.spath[i+2][j]
- self.spath[i][j])
change += abs(aux - self.spath[i][j])
class robot:
def __init__(self, length = 0.5):
self.x = 0.0
self.y = 0.0
self.orientation = 0.0
self.length = length
self.steering_noise = 0.0
self.distance_noise = 0.0
self.measurement_noise = 0.0
self.num_collisions = 0
self.num_steps = 0
def set(self, new_x, new_y, new_orientation):
self.x = float(new_x)
self.y = float(new_y)
self.orientation = float(new_orientation) % (2.0 * pi)
def set_noise(self, new_s_noise, new_d_noise, new_m_noise):
self.steering_noise = float(new_s_noise)
self.distance_noise = float(new_d_noise)
self.measurement_noise = float(new_m_noise)
def check_collision(self, grid):
for i in range(len(grid)):
for j in range(len(grid[0])):
if grid[i][j] == 1:
dist = sqrt((self.x - float(i)) ** 2 +
(self.y - float(j)) ** 2)
if dist < 0.5:
self.num_collisions += 1
return False
return True
def check_goal(self, goal, threshold = 1.0):
dist = sqrt((float(goal[0]) - self.x) ** 2 + (float(goal[1]) - self.y) ** 2)
return dist < threshold
def move(self, grid, steering, distance,
tolerance = 0.001, max_steering_angle = pi / 4.0):
if steering > max_steering_angle:
steering = max_steering_angle
if steering < -max_steering_angle:
steering = -max_steering_angle
if distance < 0.0:
distance = 0.0
res = robot()
res.length = self.length
res.steering_noise = self.steering_noise
res.distance_noise = self.distance_noise
res.measurement_noise = self.measurement_noise
res.num_collisions = self.num_collisions
res.num_steps = self.num_steps + 1
steering2 = random.gauss(steering, self.steering_noise)
distance2 = random.gauss(distance, self.distance_noise)
turn = tan(steering2) * distance2 / res.length
if abs(turn) < tolerance:
res.x = self.x + (distance2 * cos(self.orientation))
res.y = self.y + (distance2 * sin(self.orientation))
res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2.0 * pi)
else:
radius = distance2 / turn
cx = self.x - (sin(self.orientation) * radius)
cy = self.y + (cos(self.orientation) * radius)
res.orientation = (self.orientation + turn) % (2.0 * pi)
res.x = cx + (sin(res.orientation) * radius)
res.y = cy - (cos(res.orientation) * radius)
return res
def sense(self):
return [random.gauss(self.x, self.measurement_noise),
random.gauss(self.y, self.measurement_noise)]
def measurement_prob(self, measurement):
error_x = measurement[0] - self.x
error_y = measurement[1] - self.y
error = exp(- (error_x ** 2) / (self.measurement_noise ** 2) / 2.0) \
/ sqrt(2.0 * pi * (self.measurement_noise ** 2))
error *= exp(- (error_y ** 2) / (self.measurement_noise ** 2) / 2.0) \
/ sqrt(2.0 * pi * (self.measurement_noise ** 2))
return error
def __repr__(self):
return '[%.5f, %.5f]' % (self.x, self.y)
class particles:
def __init__(self, x, y, theta,
steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise, N = 100):
self.N = N
self.steering_noise = steering_noise
self.distance_noise = distance_noise
self.measurement_noise = measurement_noise
self.data = []
for i in range(self.N):
r = robot()
r.set(x, y, theta)
r.set_noise(steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise)
self.data.append(r)
def get_position(self):
x = 0.0
y = 0.0
orientation = 0.0
for i in range(self.N):
x += self.data[i].x
y += self.data[i].y
orientation += (((self.data[i].orientation
- self.data[0].orientation + pi) % (2.0 * pi))
+ self.data[0].orientation - pi)
return [x / self.N, y / self.N, orientation / self.N]
def move(self, grid, steer, speed):
newdata = []
for i in range(self.N):
r = self.data[i].move(grid, steer, speed)
newdata.append(r)
self.data = newdata
def sense(self, Z):
w = []
for i in range(self.N):
w.append(self.data[i].measurement_prob(Z))
p3 = []
index = int(random.random() * self.N)
beta = 0.0
mw = max(w)
for i in range(self.N):
beta += random.random() * 2.0 * mw
while beta > w[index]:
beta -= w[index]
index = (index + 1) % self.N
p3.append(self.data[index])
self.data = p3
def run(grid, goal, spath, params, printflag = False, speed = 0.1, timeout = 1000):
myrobot = robot()
myrobot.set(0., 0., 0.)
myrobot.set_noise(steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise)
filter = particles(myrobot.x, myrobot.y, myrobot.orientation,
steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise)
cte = 0.0
err = 0.0
N = 0
index = 0
while not myrobot.check_goal(goal) and N < timeout:
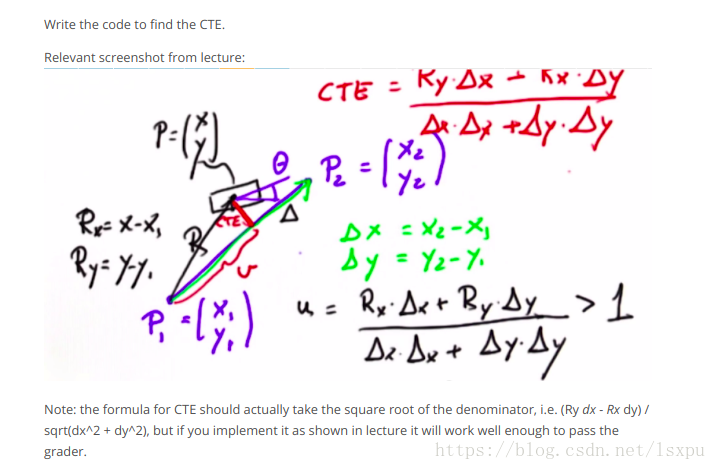
diff_cte = - cte
estimate = filter.get_position()
rx = estimate[0] - spath[index][0]
ry = estimate[1] - spath[index][1]
dx = spath[index+1][0] - spath[index][0]
dy = spath[index+1][1] - spath[index][1]
if float(rx*dx+ry*dy)/float(dx**2+dy**2) > 1:
index = index + 1
dx = spath[index+1][0] - spath[index][0]
dy = spath[index+1][1] - spath[index][1]
cte = float(ry*dx - rx*dy)/float(dx**2 +dy**2)
diff_cte += cte
steer = - params[0] * cte - params[1] * diff_cte
myrobot = myrobot.move(grid, steer, speed)
filter.move(grid, steer, speed)
Z = myrobot.sense()
filter.sense(Z)
if not myrobot.check_collision(grid):
print '##### Collision ####'
err += (cte ** 2)
N += 1
if printflag:
print myrobot, cte, index, u
return [myrobot.check_goal(goal), myrobot.num_collisions, myrobot.num_steps]
def main(grid, init, goal, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise,
weight_data, weight_smooth, p_gain, d_gain):
path = plan(grid, init, goal)
path.astar()
path.smooth(weight_data, weight_smooth)
return run(grid, goal, path.spath, [p_gain, d_gain])
grid = [[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0]]
init = [0, 0]
goal = [len(grid)-1, len(grid[0])-1]
steering_noise = 0.1
distance_noise = 0.03
measurement_noise = 0.3
weight_data = 0.1
weight_smooth = 0.2
p_gain = 2.0
d_gain = 6.0
print main(grid, init, goal, steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise,
weight_data, weight_smooth, p_gain, d_gain)
def twiddle(init_params):
n_params = len(init_params)
dparams = [1.0 for row in range(n_params)]
params = [0.0 for row in range(n_params)]
K = 10
for i in range(n_params):
params[i] = init_params[i]
best_error = 0.0;
for k in range(K):
ret = main(grid, init, goal,
steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise,
params[0], params[1], params[2], params[3])
if ret[0]:
best_error += ret[1] * 100 + ret[2]
else:
best_error += 99999
best_error = float(best_error) / float(k+1)
print best_error
n = 0
while sum(dparams) > 0.0000001:
for i in range(len(params)):
params[i] += dparams[i]
err = 0
for k in range(K):
ret = main(grid, init, goal,
steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise,
params[0], params[1], params[2], params[3], best_error)
if ret[0]:
err += ret[1] * 100 + ret[2]
else:
err += 99999
print float(err) / float(k+1)
if err < best_error:
best_error = float(err) / float(k+1)
dparams[i] *= 1.1
else:
params[i] -= 2.0 * dparams[i]
err = 0
for k in range(K):
ret = main(grid, init, goal,
steering_noise, distance_noise, measurement_noise,
params[0], params[1], params[2], params[3], best_error)
if ret[0]:
err += ret[1] * 100 + ret[2]
else:
err += 99999
print float(err) / float(k+1)
if err < best_error:
best_error = float(err) / float(k+1)
dparams[i] *= 1.1
else:
params[i] += dparams[i]
dparams[i] *= 0.5
n += 1
print 'Twiddle #', n, params, ' -> ', best_error
print ' '
return params
